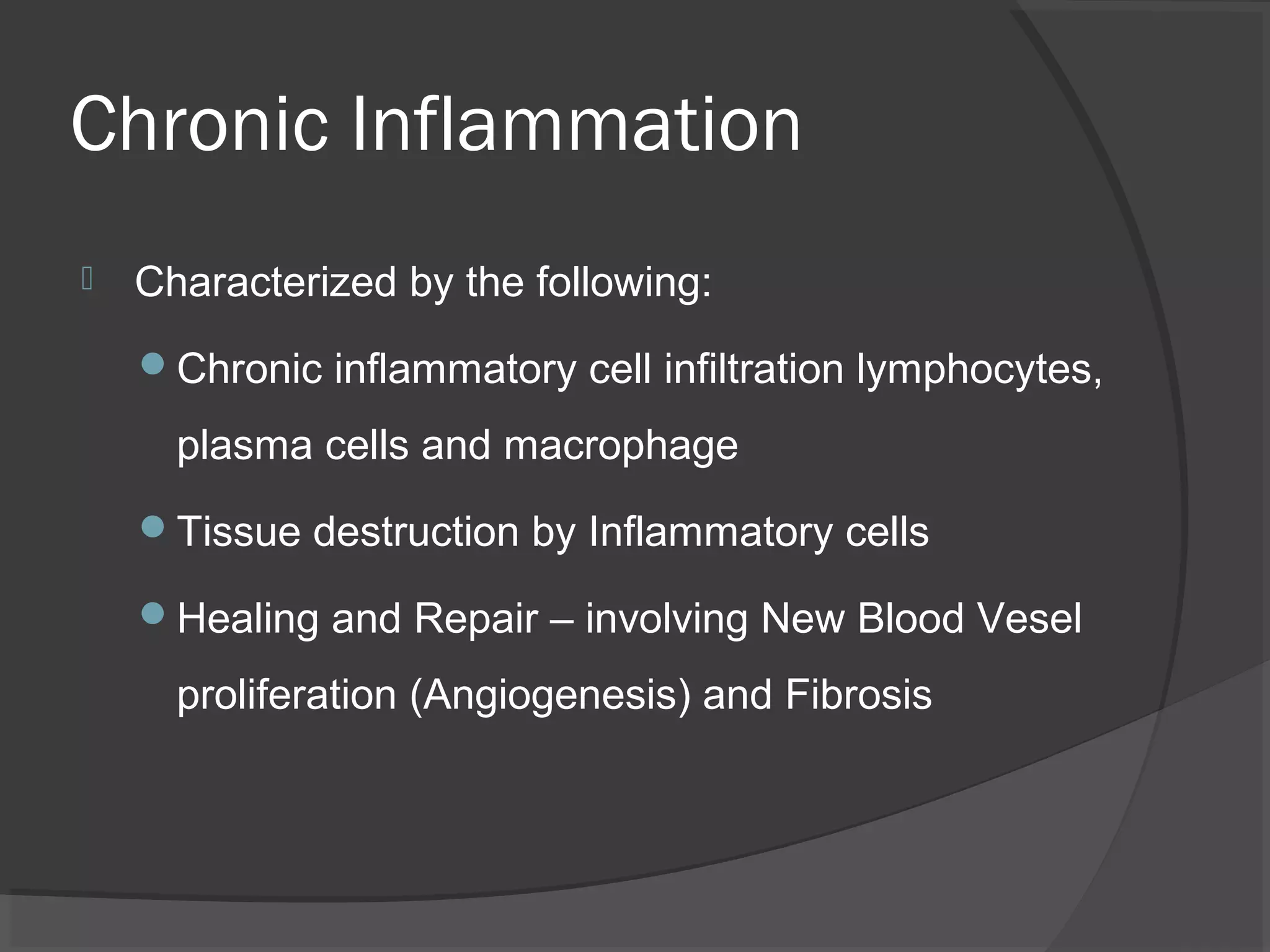
This document provides an overview of inflammation, including its definition, history, types (acute and chronic), classical signs, vascular and cellular events, chemical mediators, and outcomes. Inflammation is defined as a protective response to injury or infection that involves increased blood flow, blood vessel permeability, and the migration of white blood cells. The classical signs of inflammation are heat, redness, swelling, pain, and loss of function. Key events in acute inflammation include increased vascular permeability, chemotaxis of white blood cells, phagocytosis of pathogens, and the release of chemical mediators like histamine and cytokines. Chronic inflammation is long-lasting inflammation that involves ongoing tissue damage and repair. Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS)