Information Processing System Computing made easy.ppt
- 1. PRESENTATION OF INFORMATION PROCESSING SYSTEM Presented By: Mrs.Nisha Suhag
- 2. Information Processing System DATA is a collection of independent and unorganized facts. INFORMATION is the processed and organized data presented in a meaningful form. DATA PROCESSING is the course of doing things in a sequence of steps.
- 3. Information Processing System COMPUTER is an electronic machine that follows a set of instructions in order that it may be able to accept and gather data and transform these into information.
- 5. Functions of an Information Processing System 1. It accepts and gather data. (INPUT) 2. It processes data to become information. (PROCESSING) 3. It stores data and information. (STORE) 4. It presents information. (OUTPUT)
- 6. Three Major Components of an Information Processing System HARDWARE is the tangible part of a computer system. SOFTWARE is the non-tangible part that tells the computer how to do its job. PEOPLEWARE refer to people who use and operate the computer system, write computer programs, and analyze and design the information system.
- 7. Basic Units of Measurement BIT is a unit of information equivalent to the result of a choice between only 2 possible alternatives in the binary number system. BYTE is a sequence of 8 bits (enough to represent one character of alphanumeric data) processed as a single unit for information.
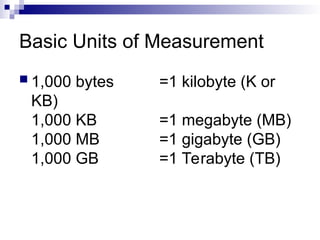
- 9. Basic Units of Measurement 1,000 bytes =1 kilobyte (K or KB) 1,000 KB =1 megabyte (MB) 1,000 MB =1 gigabyte (GB) 1,000 GB =1 Terabyte (TB)
- 10. HARDWARE Hardware refers to the physical parts of a computer and related device. Hardware devices include motherboard,hard drive and RAM. Hardware is the ‘soul’ of the computer.
- 11. Basic hardware of a PC system Central Processing Unit (CPU) Memory Unit Input Devices Output Devices Secondary Storage Devices
- 12. 1. Central Processing Unit Brain of the computer. It directs and controls the entire computer system and performs all arithmetic and logical operations.
- 13. 2. Memory Unit Where the programs and data are stored . READ ONLY MEMORY (ROM) contains the pre- programmed computer instructions such as the Basic Input Output System (BIOS). RANDOM ACCESS MEMORY (RAM) is used to store the programs and data that you will run. Exists only when there is power.
- 14. 3. Input Devices Allows data and programs to be sent to the CPU. Keyboard Mouse Joystick Microphone Webcam Scanner Monitor
- 15. 4. Output Devices Media used by the computer in displaying its responses to our requests and instructions. Monitor Audio Speakers Printer
- 16. 5. Secondary Storage Devices Attached to the computer system to allow you to store programs and data permanently for the purpose of retrieving them for future use. Floppy disk, Hard disk, CD Rom
- 17. Software A set of instructions and its documentations that tells a computer what to do or how to perform a task. Software and programs are interchangeable. Two major types: System and Applications
- 18. Kinds of Software 1. System software is software designed to provide a platform for other software. Examples of system software include operating systems like macOS, Linux OS and Microsoft windows. 2. Application software is a program or group of programs designed for end users. Examples of an application include a word processor, a spreadsheet, an accounting application, a web browser, an email client.