Inheritance
- 1. Prepared by : SELVIN JOSY BAI. S
- 3. Itis the capability of one class to inherit properties from another class. The technique of building new classes from the existing classes is called inheritance.
- 4. Base Class / Super Class Derived from Derived Class / Sub Class
- 5. It is the class whose properties are inherited by another class. It is also called Super Class.
- 6. It is the class that inherit properties from base class(es). It is also called Sub Class. It inherits all the properties of the base class and can add additional features to the derived class.
- 7. CODE REUSABILITY EASY TO IMPLEMENT REAL WORLD MODELS TRANSITIVE NATURE
- 8. It is any of the access labels: private, public or protected. It defines the accessibility of the members of the base class within the derived class. If the visibility mode is not specified, it will be taken as private by default.
- 9. Privatemembers can never be inherited. Only the public and protected members can be inherited to the derived class. This is the difference between the private and protected members.
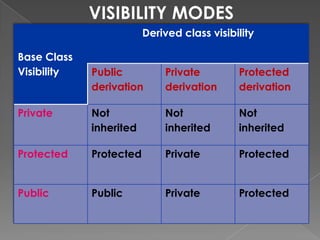
- 10. VISIBILITY MODES Derived class visibility Base Class Visibility Public Private Protected derivation derivation derivation Private Not Not Not inherited inherited inherited Protected Protected Private Protected Public Public Private Protected
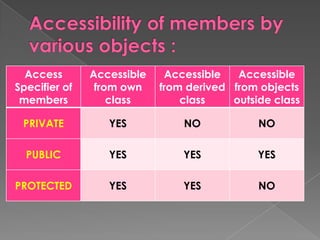
- 11. Access Accessible Accessible Accessible Specifier of from own from derived from objects members class class outside class PRIVATE YES NO NO PUBLIC YES YES YES PROTECTED YES YES NO
- 12. Private members of the base class cannot be inherited with any of the visibility mode. One is by making the visibility mode of private members as public, but they will be exposed to the outside world. Another is to convert the private members into protected so that they will be hidden from the outside world but can be inherited.
- 13. Friendship Derivation Provide access to private and Private members cannot be protected members. derived into another class. A non-member function can It shares the features of base make friendship to a class class and adds some more attributes Two independent classes can The derived classes are created have friendship, where friend with the help of base class. function acts as bridge Derived class is a special between them. instance of base class. Friendship is not Derivation Derivation is a kind of Friendship.
- 14. 1. SINGLE INHERITANCE 2. MULTIPLE INHERITANCE 3. HIERARCHICAL INHERITANCE 4. MULTILEVEL INHERITANCE 5. HYBRID INHERITANCE
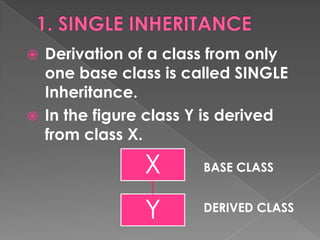
- 15. Derivation of a class from only one base class is called SINGLE Inheritance. In the figure class Y is derived from class X. X BASE CLASS Y DERIVED CLASS
- 16. class DerivedClassName : [visibility mode] BaseClassName { //DataMembers and MemberFunctions; } Example: class Automobile : public Vehicle { //DataMembers and MemberFunctions; }
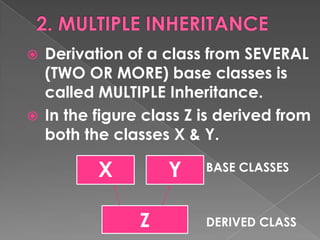
- 17. Derivation of a class from SEVERAL (TWO OR MORE) base classes is called MULTIPLE Inheritance. In the figure class Z is derived from both the classes X & Y. X Y BASE CLASSES Z DERIVED CLASS
- 18. class DerivedClassName : [visibility mode] BaseClassName1, [visibility mode] BaseClassName1 { //DataMembers and MemberFunctions; } Example: class CHILD : public FATHER, public MOTHER { //DataMembers and MemberFunctions; }
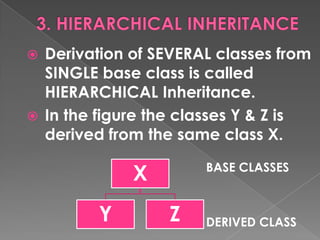
- 19. Derivation of SEVERAL classes from SINGLE base class is called HIERARCHICAL Inheritance. In the figure the classes Y & Z is derived from the same class X. X BASE CLASSES Y Z DERIVED CLASS
- 20. class DerivedClassName1 : [visibility mode] BaseClassName { ----------; } class DerivedClassName2 : [visibility mode] BaseClassName { ----------; } Example: Example: class Y : public X class Z : public X { { ---------; ---------; } }
- 21. When a sub class is derived from a base X class which itself is derived from another class, it is known as MULTILEVEL Inheritance. Y In the figure the class Z is derived from class Y, which is a derived class that is inherited from the Z class X.
- 22. class DerivedClassName1 : [visibility mode] BaseClassName { ----------; } class DerivedClassName2 : [visibility mode] DerivedClassName1 { ----------; } Example: Example: class Y : public X class Z : public Y { { ---------; ---------; } }
- 23. Derivation of a class involving more than W one form of Inheritance is known as HYBRID inheritance. X Y As it is the derivation of a class from other derived classes, which Z are derived from the same base class.
- 24. The derived class need have a constructor as long as the base class has a no-argument constructor. If the base class has constructors with arguments, then it is mandatory for the derived class to have a constructor and pass the arguments to the base class constructor.
- 25. When an object of a derived class is created, the constructor of the base class is executed first and later the constructor of the derived class. Unlike constructors, destructors in the class hierarchy are invoked in the reverse order of the constructor invocation.
- 26. It is one that has no instances and is not designed to create objects. It is only designed to be inherited from. It specifies an interface at a certain level of inheritance and provides a framework or skeleton, upon which other classes can be built.
- 27. When classes are derived in the form of hybrid inheritance, there can be a problem by which multiple copies of the base class members come in the lowest level derived class through the various intermediate subclasses. Here comes the virtual base class for rescue.
- 28. class A { public: int a; }; Class B class B : public A { public: contains int b; a and b }; class C : public A Class C { public: contains int c; a and c }; class D : public B, public C Class D { public: contains a,b, int d; }; a,c, & d
- 29. class A { public: only one copy of A will be inherited int a; }; Class B class B : virtual public A { public: contains int b; a and b }; class C : virtual public A Class C { public: contains int c; a and c }; class D : public B, public C Class D { public: contains a,b, int d; }; c, & d
- 30. In inheritance, if the class D is derived from the class B, it is said that D is a kind of B; the class D has all the properties of B in addition to the features of its own. In OOP, the containership occurs when an object of one class is contained in another class as a data member. In other words, a class can contain objects of other classes as its members.
- 31. class ABC { int a; float b; public: void fab(); }; class PQR { int p; float q; public: ABC ob1; void fab(); };













![class DerivedClassName : [visibility mode]
BaseClassName
{
//DataMembers and MemberFunctions;
}
Example:
class Automobile : public Vehicle
{
//DataMembers and MemberFunctions;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance-121003054533-phpapp01/85/Inheritance-16-320.jpg)
![class DerivedClassName : [visibility mode]
BaseClassName1, [visibility mode] BaseClassName1
{
//DataMembers and MemberFunctions;
}
Example:
class CHILD : public FATHER, public MOTHER
{
//DataMembers and MemberFunctions;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance-121003054533-phpapp01/85/Inheritance-18-320.jpg)
![class DerivedClassName1 : [visibility mode] BaseClassName
{
----------;
}
class DerivedClassName2 : [visibility mode] BaseClassName
{
----------;
}
Example: Example:
class Y : public X class Z : public X
{ {
---------; ---------;
} }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance-121003054533-phpapp01/85/Inheritance-20-320.jpg)

![class DerivedClassName1 : [visibility mode] BaseClassName
{
----------;
}
class DerivedClassName2 : [visibility mode] DerivedClassName1
{
----------;
}
Example: Example:
class Y : public X class Z : public Y
{ {
---------; ---------;
} }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance-121003054533-phpapp01/85/Inheritance-22-320.jpg)








