Inheritance in C++
- 2. Inheritance • The mechanism by which one class can inherit the properties of another. • It allows a hierarchy of classes to be built, moving from the most general to the most specific.
- 3. Inheritance is the process by which new classes called derived classes are created from existing classes called base classes. The derived classes have all the features of the base class and the programmer can choose to add new features specific to the newly created derived class. C++ Inheritance
- 4. Features or Advantages of Inheritance: Reusability: Inheritance helps the code to be reused in many situations. The base class is defined and once it is compiled, it need not be reworked. Using the concept of inheritance, the programmer can create as many derived classes from the base class as needed while adding specific features to each derived class as needed. C++ Inheritance
- 5. Features or Advantages of Inheritance: Saves Time and Effort: The above concept of reusability achieved by inheritance saves the programmer time and effort. The main code written can be reused in various situations as needed. Increases Program Structure which results in greater reliability. C++ Inheritance
- 6. General Format for implementing the concept of Inheritance: class derived_classname: access specifier baseclassname For example, if the base class is MyClass and the derived class is sample it is specified as: class sample: public MyClass The above makes sample have access to both public and protected variables of base class MyClass C++ Inheritance
- 7. Reminder about public, private and protected access specifiers: 1 If a member or variables defined in a class is private, then they are accessible by members of the same class only and cannot be accessed from outside the class. 2 Public members and variables are accessible from outside the class. 3 Protected access specifier is a stage between private and public. If a member functions or variables defined in a class are protected, then they cannot be accessed from outside the class but can be accessed from the derived class. C++ Inheritance
- 8. When deriving a class from a base class, the base class may be inherited through public, protected or private inheritance. The type of inheritance is specified by the access- specifier. We hardly use protected or private inheritance, but public inheritance is commonly used. While using different type of inheritance, following rules are applied: Type of Inheritance
- 9. Public Inheritance: When deriving a class from a public base class, public members of the base class become public members of the derived class and protected members of the base class become protected members of the derived class. A base class's private members are never accessible directly from a derived class, but can be accessed through calls to the public and protected members of the base class. Type of Inheritance
- 10. Protected Inheritance: When deriving from a protected base class, public and protected members of the base class become protected members of the derived class. Private Inheritance: When deriving from a private base class, public and protected members of the base class become private members of the derived class Type of Inheritance
- 11. 1. Single class Inheritance: Single inheritance is the one where you have a single base class and a single derived class. Types of Inheritance Class Employee Class Manager It is a Base class (super) it is a sub class (derived)
- 12. 2. Multilevel Inheritance: In Multi level inheritance, a class inherits its properties from another derived class. Types of Inheritance Class A Class B it is a Base class (super) of B it is a sub class (derived) of A and base class of class C Class C derived class(sub) of class B
- 13. 3. Multiple Inheritances: In Multiple inheritances, a derived class inherits from multiple base classes. It has properties of both the base classes. Types of Inheritance Class A Class B Base class Class C Derived class
- 14. 4. Hierarchical Inheritance: In hierarchical Inheritance, it's like an inverted tree. So multiple classes inherit from a single base class. It's quite analogous to the File system in a unix based system. Types of Inheritance Class A Class B Class C Class D
- 15. 5. Hybrid Inheritance: In this type of inheritance, we can have mixture of number of inheritances but this can generate an error of using same name function from no of classes, which will bother the compiler to how to use the functions. Therefore, it will generate errors in the program. This has known as ambiguity or duplicity. Ambiguity problem can be solved by using virtual base classes Types of Inheritance
- 16. Types of Inheritance Class A Class B Class D Class C 5. Hybrid Inheritance:
- 17. Base Class, Derived Class • Base Class – Defines all qualities common to any derived classes. • Derived Class – Inherits those general properties and adds new properties that are specific to that class.
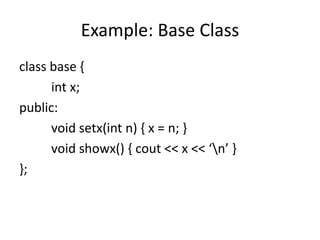
- 18. Example: Base Class class base { int x; public: void setx(int n) { x = n; } void showx() { cout << x << ‘n’ } };
- 19. Example: Derived Class // Inherit as public class derived : public base { int y; public: void sety(int n) { y = n; } void showy() { cout << y << ‘n’;} };
- 20. Access Specifier: public • The keyword public tells the compiler that base will be inherited such that: –all public members of the base class will also be public members of derived. • However, all private elements of base will remain private to it and are not directly accessible by derived.
- 21. Example: main() int main() { derived ob; ob.setx(10); ob.sety(20); ob.showx(); ob.showy(); }
- 22. An incorrect example class derived : public base { int y; public: void sety(int n) { y = n; } /* Error ! Cannot access x, which is private member of base. */ void show_sum() {cout << x+y; } };
- 23. Access Specifier: private • If the access specifier is private: –public members of base become private members of derived. –these members are still accessible by member functions of derived.
- 24. Example: Derived Class // Inherit as private class derived : private base { int y; public: void sety(int n) { y = n; } void showy() { cout << y << ‘n’;} };
- 25. Example: main() int main() { derived ob; ob.setx(10); // Error! setx() is private. ob.sety(20); // OK! ob.showx(); // Error! showx() is private. ob.showy(); // OK! }
- 26. Example: Derived Class class derived : private base { int y; public: // setx is accessible from within derived void setxy(int n, int m) { setx(n); y = m; } // showx is also accessible void showxy() { showx(); cout<<y<< ‘n’;} };
- 27. Protected Members • Sometimes you want to do the following: –keep a member of a base class private –allow a derived class access to it • Use protected members! • If no derived class, protected members is the same as private members.
- 28. Protected Members The full general form of a class declaration: class class-name { // private members protected: // protected members public: // public members };
- 29. 3 Types of Access Specifiers • Type 1: inherit as private Base Derived private members inaccessible protected members private members public members private members
- 30. 3 Types of Access Specifiers • Type 2: inherit as protected Base Derived private members inaccessible protected members protected members public members protected members
- 31. 3 Types of Access Specifiers • Type 3: inherit as public Base Derived private members inaccessible protected members protected members public members public members
- 32. Constructor and Destructor • It is possible for both the base class and the derived class to have constructor and/or destructor functions. • The constructor functions are executed in order of derivation. – i.e.the base class constructor is executed first. • The destructor functions are executed in reverse order.
- 33. Passing arguments • What if the constructor functions of both the base class and derived class take arguments? 1. Pass all necessary arguments to the derived class’s constructor. 2. Then pass the appropriate arguments along to the base class.
- 34. Example: Constructor of base class base { int i; public: base(int n) { cout << “constructing base n”; i = n; } ~base() { cout << “destructing base n”; } };
- 35. Example: Constructor of derived class derived : public base { int j; public: derived (int n, int m) : base (m) { cout << “constructing derivedn”; j = n; } ~derived() { cout << “destructing derivedn”;} };
- 36. Example: main() int main() { derived o(10,20); return 0; } constructing base constructing derived destructing derived destructing base
- 37. Multilevel Inheritance • Type 1: base 1 derived 1 derived 2
- 38. Multiple Inheritance • Type 2: base 1 base 2 derived
- 39. Example: Type 2 // Create first base class class B1 { int a; public: B1(int x) { a = x; } int geta() { return a; } };
- 40. Example: Type 2 // Create second base class class B2 { int b; public: B2(int x) { b = x; } int getb() { return b; } };
- 41. Example: Type 2 // Directly inherit two base classes. class D : public B1, public B2 { int c; public: D(int x, int y, int z) : B1(z), B2(y) { c = x; } void show() { cout << geta() << getb() << c;} } ;
- 42. Potential Problem • Base is inherited twice by Derived 3! Base Base Derived 1 Derived 2 Derived 3
- 43. Virtual Base Class • To resolve this problem, virtual base class can be used. class base { public: int i; };
- 44. Virtual Base Class // Inherit base as virtual class D1 : virtual public base { public: int j; }; class D2 : virtual public base { public: int k; };
- 45. Virtual Base Class /* Here, D3 inherits both D1 and D2. However, only one copy of base is present */ class D3 : public D1, public D2 { public: int product () { return i * j * k; } };
- 46. Pointers to Derived Classes • A pointer declared as a pointer to base class can also be used to point to any class derived from that base. • However, only those members of the derived object that were inherited from the base can be accessed.
- 47. Example base *p; // base class pointer base B_obj; derived D_obj; p = &B_obj; // p can point to base object p = &D_obj; // p can also point to derived // object
- 48. Virtual Function • A virtual function is a member function – declared within a base class – redefined by a derived class (i.e. overriding) • It can be used to support run-time polymorphism.
- 49. Example class base { public: int i; base (int x) { i = x; } virtual void func() {cout << i; } };
- 50. Example class derived : public base { public: derived (int x) : base (x) {} // The keyword virtual is not needed. void func() {cout << i * i; } };
- 51. Example int main() { base ob(10), *p; derived d_ob(10); p = &ob; p->func(); // use base’s func() p = &d_ob; p->func(); // use derived’s func() }
- 52. Pure Virtual Functions • A pure virtual function has no definition relative to the base class. • Only the function’s prototype is included. • General form: virtual type func-name(paremeter-list) = 0
- 53. Example: area class area { public: double dim1, dim2; area(double x, double y) {dim1 = x; dim2 = y;} // pure virtual function virtual double getarea() = 0; };
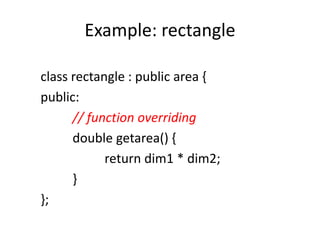
- 54. Example: rectangle class rectangle : public area { public: // function overriding double getarea() { return dim1 * dim2; } };
- 55. Example: triangle class triangle : public area { public: // function overriding double getarea() { return 0.5 * dim1 * dim2; } };