Integrating React.js with PHP projects
- 1. PHP UK Conference February 2017 Integrating React.js with PHP Projects Nacho Martín @nacmartin
- 2. My name is Nacho Martin. Almost every project needs a rich frontend, for one reason or another. We build tailor-made projects. So we have been thinking about this for some time. I write code at Limenius
- 3. Why (as a PHP developer) should I care about the frontend?
- 6. Pour eggs in the pan The fundamental premise How to cook an omelette Buy eggs Break eggs
- 7. Pour eggs in the pan Beat eggs The fundamental premise How to cook an omelette Buy eggs Break eggs
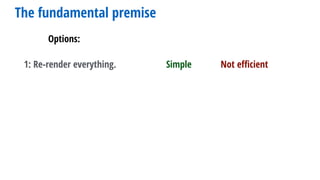
- 9. Options: The fundamental premise 1: Re-render everything.
- 10. Options: The fundamental premise 1: Re-render everything. Simple
- 11. Options: The fundamental premise 1: Re-render everything. Simple Not efficient
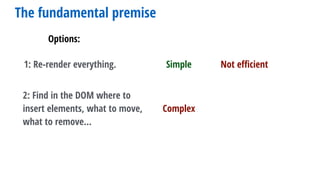
- 12. Options: 2: Find in the DOM where to insert elements, what to move, what to remove… The fundamental premise 1: Re-render everything. Simple Not efficient
- 13. Options: 2: Find in the DOM where to insert elements, what to move, what to remove… The fundamental premise 1: Re-render everything. Simple Complex Not efficient
- 14. Options: 2: Find in the DOM where to insert elements, what to move, what to remove… The fundamental premise 1: Re-render everything. Simple EfficientComplex Not efficient
- 15. Options: 2: Find in the DOM where to insert elements, what to move, what to remove… The fundamental premise 1: Re-render everything. Simple EfficientComplex Not efficient React allows us to do 1, although it does 2 behind the scenes
- 16. Give me a state and a render() method that depends on it and forget about how and when to render.* The fundamental premise
- 17. Give me a state and a render() method that depends on it and forget about how and when to render.* The fundamental premise * Unless you want more control, which is possible.
- 18. Click me! Clicks: 0 Our first component
- 19. Click me! Clicks: 1Click me! Our first component
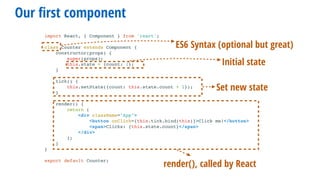
- 20. Our first component import React, { Component } from 'react'; class Counter extends Component { constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = {count: 1}; } tick() { this.setState({count: this.state.count + 1}); } render() { return ( <div className="App"> <button onClick={this.tick.bind(this)}>Click me!</button> <span>Clicks: {this.state.count}</span> </div> ); } } export default Counter;
- 21. Our first component import React, { Component } from 'react'; class Counter extends Component { constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = {count: 1}; } tick() { this.setState({count: this.state.count + 1}); } render() { return ( <div className="App"> <button onClick={this.tick.bind(this)}>Click me!</button> <span>Clicks: {this.state.count}</span> </div> ); } } export default Counter; ES6 Syntax (optional but great)
- 22. Our first component import React, { Component } from 'react'; class Counter extends Component { constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = {count: 1}; } tick() { this.setState({count: this.state.count + 1}); } render() { return ( <div className="App"> <button onClick={this.tick.bind(this)}>Click me!</button> <span>Clicks: {this.state.count}</span> </div> ); } } export default Counter; ES6 Syntax (optional but great) Initial state
- 23. Our first component import React, { Component } from 'react'; class Counter extends Component { constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = {count: 1}; } tick() { this.setState({count: this.state.count + 1}); } render() { return ( <div className="App"> <button onClick={this.tick.bind(this)}>Click me!</button> <span>Clicks: {this.state.count}</span> </div> ); } } export default Counter; ES6 Syntax (optional but great) Set new state Initial state
- 24. Our first component import React, { Component } from 'react'; class Counter extends Component { constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = {count: 1}; } tick() { this.setState({count: this.state.count + 1}); } render() { return ( <div className="App"> <button onClick={this.tick.bind(this)}>Click me!</button> <span>Clicks: {this.state.count}</span> </div> ); } } export default Counter; ES6 Syntax (optional but great) Set new state render(), called by React Initial state
- 26. Working with state constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = {count: 1}; } Initial state
- 27. Working with state constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = {count: 1}; } Initial state this.setState({count: this.state.count + 1}); Assign state
- 28. Working with state constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = {count: 1}; } Initial state this.setState({count: this.state.count + 1}); Assign state this.state.count = this.state.count + 1; Just remember: avoid this
- 29. render() and JSX render() { return ( <div className="App"> <button onClick={this.tick.bind(this)}>Clícame!</button> <span>Clicks: {this.state.count}</span> </div> ); It is not HTML, it is JSX. React transforms it internally to HTML elements. Good practice: make render() as clean as possible, only a return.
- 30. render() and JSX render() { return ( <div className="App"> <button onClick={this.tick.bind(this)}>Clícame!</button> <span>Clicks: {this.state.count}</span> </div> ); It is not HTML, it is JSX. React transforms it internally to HTML elements. Some things change Good practice: make render() as clean as possible, only a return.
- 31. render() and JSX render() { return ( <div className="App"> <button onClick={this.tick.bind(this)}>Clícame!</button> <span>Clicks: {this.state.count}</span> </div> ); It is not HTML, it is JSX. React transforms it internally to HTML elements. Some things change We can insert JS expressions between {} Good practice: make render() as clean as possible, only a return.
- 32. Thinking in React render() { return ( <div className="App"> <button onClick={this.tick.bind(this)}>Click me!</button> <span>Clicks: {this.state.count}</span> </div> ); }
- 33. Thinking in React render() { return ( <div className="App"> <button onClick={this.tick.bind(this)}>Click me!</button> <span>Clicks: {this.state.count}</span> </div> ); } Here we don’t modify state
- 34. Thinking in React render() { return ( <div className="App"> <button onClick={this.tick.bind(this)}>Click me!</button> <span>Clicks: {this.state.count}</span> </div> ); } Here we don’t make Ajax calls
- 35. Thinking in React render() { return ( <div className="App"> <button onClick={this.tick.bind(this)}>Click me!</button> <span>Clicks: {this.state.count}</span> </div> ); } Here we don’t calculate decimals of PI and send an e-mail with the result
- 36. Important: think our hierarchy
- 37. Important: think our hierarchy
- 38. Component hierarchy: props class CounterGroup extends Component { render() { return ( <div> <Counter name="amigo"/> <Counter name="señor"/> </div> ); } }
- 39. render() { return ( <div className="App"> <button onClick={this.tick.bind(this)}> Click me! {this.props.name} </button> <span>Clicks: {this.state.count}</span> </div> ); } and in Counter… Component hierarchy: props class CounterGroup extends Component { render() { return ( <div> <Counter name="amigo"/> <Counter name="señor"/> </div> ); } }
- 40. render() { return ( <div className="App"> <button onClick={this.tick.bind(this)}> Click me! {this.props.name} </button> <span>Clicks: {this.state.count}</span> </div> ); } and in Counter… Component hierarchy: props class CounterGroup extends Component { render() { return ( <div> <Counter name="amigo"/> <Counter name="señor"/> </div> ); } }
- 41. Pro tip: Stateless components const Greeter = (props) => ( <div> <div>Hi {props.name}!</div> </div> )
- 42. Tip: Presentational and Container components const TaskList = (props) => ( <div> {props.tasks.map((task, idx) => { <div key={idx}>{task.name}</div> })} </div> ) class TasksListContainer extends React.Component { constructor(props) { super(props) this.state = {tasks: []} } componentDidMount() { // Load data with Ajax and whatnot } render() { return <TaskList tasks={this.state.tasks}/> } }
- 43. Everything depends on the state, therefore we can:
- 44. Everything depends on the state, therefore we can: •Reproduce states,
- 45. Everything depends on the state, therefore we can: •Reproduce states, •Rewind,
- 46. Everything depends on the state, therefore we can: •Reproduce states, •Rewind, •Log state changes,
- 47. Everything depends on the state, therefore we can: •Reproduce states, •Rewind, •Log state changes, •Make storybooks,
- 48. Everything depends on the state, therefore we can: •Reproduce states, •Rewind, •Log state changes, •Make storybooks, •…
- 50. What if instead of this… render() { return ( <div className="App"> <button onClick={this.tick.bind(this)}>Click me!</button> <span>Clicks: {this.state.count}</span> </div> ); }
- 51. …we have something like this? render () { return ( <View> <ListView dataSource={dataSource} renderRow={(rowData) => <TouchableOpacity > <View> <Text>{rowData.name}</Text> <View> <SwitchIOS onValueChange={(value) => this.setMissing(item, value)} value={item.missing} /> </View> </View> </TouchableOpacity> } /> </View> ); }
- 52. …we have something like this? render () { return ( <View> <ListView dataSource={dataSource} renderRow={(rowData) => <TouchableOpacity > <View> <Text>{rowData.name}</Text> <View> <SwitchIOS onValueChange={(value) => this.setMissing(item, value)} value={item.missing} /> </View> </View> </TouchableOpacity> } /> </View> ); } React Native
- 53. React Targets •Web - react-dom •Mobile - react-native •Gl shaders - gl-react •Canvas - react-canvas •Terminal - react-blessed
- 55. Setup
- 57. Webpack Pros
- 59. Webpack • Manages dependencies • Allows several environments: production, development, …. Pros
- 60. Webpack • Manages dependencies • Allows several environments: production, development, …. • Automatic page reload (even hot reload). Pros
- 61. Webpack • Manages dependencies • Allows several environments: production, development, …. • Automatic page reload (even hot reload). • Can use preprocessors/“transpilers”, like Babel. Pros
- 62. Webpack • Manages dependencies • Allows several environments: production, development, …. • Automatic page reload (even hot reload). • Can use preprocessors/“transpilers”, like Babel. Pros Cons
- 63. Webpack • Manages dependencies • Allows several environments: production, development, …. • Automatic page reload (even hot reload). • Can use preprocessors/“transpilers”, like Babel. Pros Cons • It has a non trivial learning curve.
- 64. Webpack • Manages dependencies • Allows several environments: production, development, …. • Automatic page reload (even hot reload). • Can use preprocessors/“transpilers”, like Babel. Pros Cons • It has a non trivial learning curve. I maintain a sandbox: https://github.com/Limenius/symfony-react-sandbox
- 65. Insertion <div id="react-placeholder"></div> import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'; ReactDOM.render( <Counter name="amigo">, document.getElementById('react-placeholder') ); HTML JavaScript
- 68. ReactRenderer {{ react_component('RecipesApp', {'props': props}) }} import ReactOnRails from 'react-on-rails'; import RecipesApp from './RecipesAppServer'; ReactOnRails.register({ RecipesApp }); Twig: JavaScript:
- 69. ReactRenderer {{ react_component('RecipesApp', {'props': props}) }} import ReactOnRails from 'react-on-rails'; import RecipesApp from './RecipesAppServer'; ReactOnRails.register({ RecipesApp }); Twig: JavaScript:
- 70. ReactRenderer {{ react_component('RecipesApp', {'props': props}) }} import ReactOnRails from 'react-on-rails'; import RecipesApp from './RecipesAppServer'; ReactOnRails.register({ RecipesApp }); Twig: JavaScript: <div class="js-react-on-rails-component" style="display:none" data-component-name=“RecipesApp” data-props=“[my Array in JSON]" data-trace=“false" data-dom-id=“sfreact-57d05640f2f1a”></div> Generated HTML:
- 73. Give me a state and a render() method that depends on it and forget about how and when to render. The fundamental premise
- 74. Give me a state and a render() method that depends on it and forget about how and when to render. The fundamental premise We can render components in the server
- 75. Give me a state and a render() method that depends on it and forget about how and when to render. The fundamental premise We can render components in the server • SEO friendly.
- 76. Give me a state and a render() method that depends on it and forget about how and when to render. The fundamental premise We can render components in the server • SEO friendly. • Faster perceived page loads.
- 77. Give me a state and a render() method that depends on it and forget about how and when to render. The fundamental premise We can render components in the server • SEO friendly. • Faster perceived page loads. • We can cache.
- 78. Client-side + Server-side {{ react_component('RecipesApp', {'props': props, rendering': 'both'}}) }} TWIG
- 79. Client-side + Server-side {{ react_component('RecipesApp', {'props': props, rendering': 'both'}}) }} TWIG HTML returned by the server <div id="sfreact-57d05640f2f1a"><div data-reactroot="" data-reactid="1" data-react- checksum=“2107256409"><ol class="breadcrumb" data-reactid="2"><li class="active" data- reactid=“3”>Recipes</li> … … </div>
- 80. Client-side + Server-side {{ react_component('RecipesApp', {'props': props, rendering': 'both'}}) }} TWIG HTML returned by the server <div id="sfreact-57d05640f2f1a"><div data-reactroot="" data-reactid="1" data-react- checksum=“2107256409"><ol class="breadcrumb" data-reactid="2"><li class="active" data- reactid=“3”>Recipes</li> … … </div> An then React in the browser takes control over the component
- 82. Option 1: Call a node.js subprocess Make a call to node.js using Symfony Process component * Easy (if we have node.js installed). * Slow. Library: https://github.com/nacmartin/phpexecjs
- 83. Option 2: v8js Use PHP extension v8js * Easy (although compiling the extension and v8 is not a breeze). * Currently slow, maybe we could have v8 preloaded using php-pm so it is not destroyed after every request-response cycle. Library: https://github.com/nacmartin/phpexecjs
- 84. Option 3: External node.js server We have “stupid” node.js server used only to render React components. It has <100 LoC, and it doesn’t know anything about our logic. * “Annoying” (we have to keep it running, which is not super annoying either). * Faster. There is an example a dummy server for this purpose at https://github.com/Limenius/symfony-react-sandbox
- 85. Options 1 & 2 $renderer = new PhpExecJsReactRenderer(‘path_to/server-bundle.js’); $ext = new ReactRenderExtension($renderer, 'both'); $twig->addExtension($ext); phpexecjs detects the presence of the extension v8js, if not, calls node.js
- 86. Option 3 $renderer = new ExternalServerReactRenderer(‘../some_path/node.sock’); $ext = new ReactRenderExtension($renderer, 'both'); $twig->addExtension($ext);
- 87. The best of the two worlds In development use node.js or v8js with phpexecjs. In production use an external server. If we can cache server-side responses, even better.
- 88. Server side rendering, is it worth it?
- 89. Server side rendering, is it worth it? Sometimes yes, but it introduces complexity
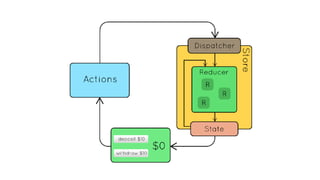
- 90. Redux support (+very brief introduction to Redux)
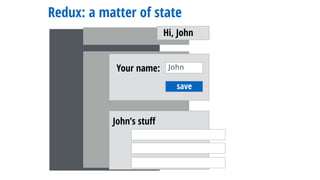
- 91. Redux: a matter of state save Your name: John Hi, John John’s stuff
- 92. Redux: a matter of state save Your name: John Hi, John John’s stuff
- 93. Redux: a matter of state save Your name: John Hi, John John’s stuff state.name callback to change it
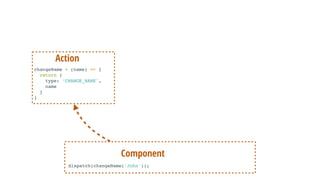
- 95. dispatch(changeName(‘John')); Component changeName = (name) => { return { type: ‘CHANGE_NAME', name } } Action
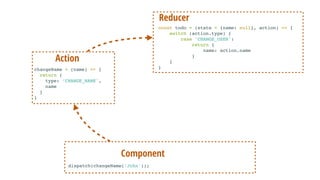
- 96. dispatch(changeName(‘John')); Component changeName = (name) => { return { type: ‘CHANGE_NAME', name } } Action const todo = (state = {name: null}, action) => { switch (action.type) { case 'CHANGE_USER': return { name: action.name } } } Reducer
- 97. dispatch(changeName(‘John')); Component changeName = (name) => { return { type: ‘CHANGE_NAME', name } } Action const todo = (state = {name: null}, action) => { switch (action.type) { case 'CHANGE_USER': return { name: action.name } } } Reducer Store
- 98. this.props.name == ‘John';dispatch(changeName(‘John')); Component changeName = (name) => { return { type: ‘CHANGE_NAME', name } } Action const todo = (state = {name: null}, action) => { switch (action.type) { case 'CHANGE_USER': return { name: action.name } } } Reducer Store
- 101. Redux with ReactRenderer Sample code in https://github.com/Limenius/symfony-react-sandbox import ReactOnRails from 'react-on-rails'; import RecipesApp from './RecipesAppClient'; import recipesStore from '../store/recipesStore'; ReactOnRails.registerStore({recipesStore}) ReactOnRails.register({ RecipesApp }); Twig: JavaScript: {{ redux_store('recipesStore', props) }} {{ react_component('RecipesApp') }}
- 102. Redux with ReactRenderer Sample code in https://github.com/Limenius/symfony-react-sandbox import ReactOnRails from 'react-on-rails'; import RecipesApp from './RecipesAppClient'; import recipesStore from '../store/recipesStore'; ReactOnRails.registerStore({recipesStore}) ReactOnRails.register({ RecipesApp }); Twig: JavaScript: {{ redux_store('recipesStore', props) }} {{ react_component('RecipesApp') }} {{ react_component('AnotherComponent') }}
- 103. Share store between components
- 104. React React React Twig Twig React By sharing store they can share state Twig Share store between components
- 105. Forms, a special case
- 106. Dynamic forms, why? •Inside of React components. •Important forms where UX means better conversions. •Very specific forms. •Very dynamic forms that aren’t boring (see Typeform for instance).
- 108. Typically PHP frameworks have a Form Component
- 109. Typically PHP frameworks have a Form Component $form (e.g. Form Symfony Component)
- 110. Typically PHP frameworks have a Form Component $form (e.g. Form Symfony Component) Initial values
- 111. Typically PHP frameworks have a Form Component $form (e.g. Form Symfony Component) Initial values UI hints (widgets, attributes)
- 112. Typically PHP frameworks have a Form Component $form (e.g. Form Symfony Component) Initial values UI hints (widgets, attributes) Bind incoming data
- 113. Typically PHP frameworks have a Form Component $form (e.g. Form Symfony Component) Initial values UI hints (widgets, attributes) Bind incoming data Deserialize
- 114. Typically PHP frameworks have a Form Component $form (e.g. Form Symfony Component) Initial values UI hints (widgets, attributes) Bind incoming data Deserialize Validate
- 115. Typically PHP frameworks have a Form Component $form (e.g. Form Symfony Component) Initial values UI hints (widgets, attributes) Bind incoming data Deserialize Validate Return errors
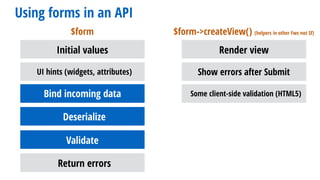
- 116. Typically PHP frameworks have a Form Component $form (e.g. Form Symfony Component) $form->createView() (helpers in other Fws not Sf) Initial values UI hints (widgets, attributes) Bind incoming data Deserialize Validate Return errors
- 117. Typically PHP frameworks have a Form Component $form (e.g. Form Symfony Component) $form->createView() (helpers in other Fws not Sf) Initial values UI hints (widgets, attributes) Bind incoming data Deserialize Validate Return errors Render view
- 118. Typically PHP frameworks have a Form Component $form (e.g. Form Symfony Component) $form->createView() (helpers in other Fws not Sf) Initial values UI hints (widgets, attributes) Bind incoming data Deserialize Validate Return errors Render view Show errors after Submit
- 119. Typically PHP frameworks have a Form Component $form (e.g. Form Symfony Component) $form->createView() (helpers in other Fws not Sf) Initial values UI hints (widgets, attributes) Bind incoming data Deserialize Validate Return errors Render view Some client-side validation (HTML5) Show errors after Submit
- 120. Using forms in an API $form $form->createView() (helpers in other Fws not Sf) Initial values UI hints (widgets, attributes) Bind incoming data Deserialize Validate Return errors Render view Some client-side validation (HTML5) Show errors after Submit
- 121. …and we want more $form $form->createView() (helpers in other Fws not Sf) Initial values UI hints (widgets, attributes) Bind incoming data Deserialize Validate Return errors Render view On Submit validation Some client-side validation (HTML5)
- 122. …and we want more $form $form->createView() (helpers in other Fws not Sf) Initial values UI hints (widgets, attributes) Bind incoming data Deserialize Validate Return errors Render view On blur sync validation On Submit validation Some client-side validation (HTML5)
- 123. …and we want more $form $form->createView() (helpers in other Fws not Sf) Initial values UI hints (widgets, attributes) Bind incoming data Deserialize Validate Return errors Render view On blur sync validation On Submit validation On blur async validation Some client-side validation (HTML5)
- 124. …and we want more $form $form->createView() (helpers in other Fws not Sf) Initial values UI hints (widgets, attributes) Bind incoming data Deserialize Validate Return errors Render view On blur sync validation On Submit validation On blur async validation Some client-side validation (HTML5) All the dynamic goodies
- 125. Suppose this Symfony form public function buildForm(FormBuilderInterface $builder, array $options) { $builder ->add('country', ChoiceType::class, [ 'choices' => [ 'United Kingdom' => 'gb', 'Deutschland' => 'de', 'España' => 'es', ] ]) ->add('addresses', CollectionType::class, ...); };
- 126. Forms rendered to HTML $form->createView(); state.usuario
- 127. Forms rendered to HTML $form->createView(); state.usuario
- 128. Forms rendered to HTML $form->createView(); submit Country: España Deutschland España Addresses: Some St.- +state.usuario
- 129. Forms rendered to HTML $form->createView(); submit Country: España Deutschland España Addresses: Some St.- +state.usuario POST well formed with country:’es’ and not ‘España’, ‘espana', ‘spain', ‘0’…
- 130. Forms rendered to HTML $form->createView(); $form->submit($request); submit Country: España Deutschland España Addresses: Some St.- +state.usuario POST well formed with country:’es’ and not ‘España’, ‘espana', ‘spain', ‘0’…
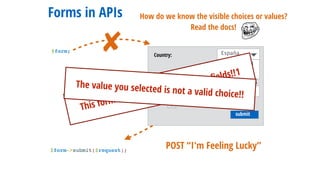
- 132. submit Country: España Deutschland España Addresses: Some St.- +state.usuario Forms in APIs $form; ✘ How do we know the visible choices or values? Read the docs!
- 133. submit Country: España Deutschland España Addresses: Some St.- +state.usuario Forms in APIs $form; $form->submit($request); POST “I'm Feeling Lucky” ✘ How do we know the visible choices or values? Read the docs!
- 134. submit Country: España Deutschland España Addresses: Some St.- +state.usuario This form should not contain extra fields!!1 Forms in APIs $form; $form->submit($request); POST “I'm Feeling Lucky” ✘ How do we know the visible choices or values? Read the docs!
- 135. submit Country: España Deutschland España Addresses: Some St.- +state.usuario This form should not contain extra fields!!1 The value you selected is not a valid choice!! Forms in APIs $form; $form->submit($request); POST “I'm Feeling Lucky” ✘ How do we know the visible choices or values? Read the docs!
- 136. submit Country: España Deutschland España Addresses: Some St.- +state.usuario This form should not contain extra fields!!1 The value you selected is not a valid choice!!One or more of the given values is invalid!! :D Forms in APIs $form; $form->submit($request); POST “I'm Feeling Lucky” ✘ How do we know the visible choices or values? Read the docs!
- 137. submit Country: España Deutschland España Addresses: Some St.- +state.usuario This form should not contain extra fields!!1 The value you selected is not a valid choice!!One or more of the given values is invalid!! :DMUHAHAHAHAHA!!!!! Forms in APIs $form; $form->submit($request); POST “I'm Feeling Lucky” ✘ How do we know the visible choices or values? Read the docs!
- 140. Define, maintain and keep in sync in triplicate Form Server API docs Form Client :_( How many devs does it take to write a form?
- 141. Wizard type form? “While you code this we will be preparing different versions for other use cases”
- 142. Case: Complex Wizard Form
- 143. Case: Complex Wizard Form
- 144. Case: Complex Wizard Form
- 146. What we need $form->createView(); HTML Serialize! Ok, into which format? API $mySerializer->serialize($form);
- 147. JSON Schema
- 148. json-schema.org
- 149. How does it look like { "$schema": "http://json-schema.org/draft-04/schema#", "title": "Product", "description": "A product from Acme's catalog", "type": "object", "properties": { "name": { "description": "Name of the product", "type": "string" }, "price": { "type": "number", "minimum": 0, "exclusiveMinimum": true }, "tags": { "type": "array", "items": { "type": "string" }, "minItems": 1, "uniqueItems": true } }, "required": ["id", "name", "price"] } Definitions Types, Validation rules :_) New resource: my-api/products/form
- 150. Liform & LiformBundle https://github.com/Limenius/Liform use LimeniusLiformResolver; use LimeniusLiformLiform; $resolver = new Resolver(); $resolver->setDefaultTransformers(); $liform = new Liform($resolver); $form = $this->createForm(CarType::class, $car, ['csrf_protection' => false]); $schema = json_encode($liform->transform($form));
- 151. Transform piece by piece {"title":"task", "type":"object", "properties":{ "name":{ "type":"string", "title":"Name", "default":"I'm a placeholder", "propertyOrder":1 }, "description":{ "type":"string", "widget":"textarea", "title":"Description", "description":"An explanation of the task", "propertyOrder":2 }, "dueTo":{ "type":"string", "title":"Due to", "widget":"datetime", "format":"date-time", "propertyOrder":3 } }, “required":[ “name", "description","dueTo"]} public function buildForm(FormBuilderInterface $builder, array $options) { $builder ->add('name',TypeTextType::class, [ 'label' => 'Name', 'required' => true, 'attr' => ['placeholder' => 'I'm a placeholder’]]) ->add('description',TypeTextType::class, [ 'label' => 'Description', 'liform' => [ 'widget' => 'textarea', 'description' => 'An explanation of the task', ]]) ->add('dueTo',TypeDateTimeType::class, [ 'label' => 'Due to', 'widget' => 'single_text'] ) ; }
- 152. Transform piece by piece {"title":"task", "type":"object", "properties":{ "name":{ "type":"string", "title":"Name", "default":"I'm a placeholder", "propertyOrder":1 }, "description":{ "type":"string", "widget":"textarea", "title":"Description", "description":"An explanation of the task", "propertyOrder":2 }, "dueTo":{ "type":"string", "title":"Due to", "widget":"datetime", "format":"date-time", "propertyOrder":3 } }, “required":[ “name", "description","dueTo"]} public function buildForm(FormBuilderInterface $builder, array $options) { $builder ->add('name',TypeTextType::class, [ 'label' => 'Name', 'required' => true, 'attr' => ['placeholder' => 'I'm a placeholder’]]) ->add('description',TypeTextType::class, [ 'label' => 'Description', 'liform' => [ 'widget' => 'textarea', 'description' => 'An explanation of the task', ]]) ->add('dueTo',TypeDateTimeType::class, [ 'label' => 'Due to', 'widget' => 'single_text'] ) ; }
- 153. Transform piece by piece {"title":"task", "type":"object", "properties":{ "name":{ "type":"string", "title":"Name", "default":"I'm a placeholder", "propertyOrder":1 }, "description":{ "type":"string", "widget":"textarea", "title":"Description", "description":"An explanation of the task", "propertyOrder":2 }, "dueTo":{ "type":"string", "title":"Due to", "widget":"datetime", "format":"date-time", "propertyOrder":3 } }, “required":[ “name", "description","dueTo"]} public function buildForm(FormBuilderInterface $builder, array $options) { $builder ->add('name',TypeTextType::class, [ 'label' => 'Name', 'required' => true, 'attr' => ['placeholder' => 'I'm a placeholder’]]) ->add('description',TypeTextType::class, [ 'label' => 'Description', 'liform' => [ 'widget' => 'textarea', 'description' => 'An explanation of the task', ]]) ->add('dueTo',TypeDateTimeType::class, [ 'label' => 'Due to', 'widget' => 'single_text'] ) ; }
- 154. Transform piece by piece {"title":"task", "type":"object", "properties":{ "name":{ "type":"string", "title":"Name", "default":"I'm a placeholder", "propertyOrder":1 }, "description":{ "type":"string", "widget":"textarea", "title":"Description", "description":"An explanation of the task", "propertyOrder":2 }, "dueTo":{ "type":"string", "title":"Due to", "widget":"datetime", "format":"date-time", "propertyOrder":3 } }, “required":[ “name", "description","dueTo"]} public function buildForm(FormBuilderInterface $builder, array $options) { $builder ->add('name',TypeTextType::class, [ 'label' => 'Name', 'required' => true, 'attr' => ['placeholder' => 'I'm a placeholder’]]) ->add('description',TypeTextType::class, [ 'label' => 'Description', 'liform' => [ 'widget' => 'textarea', 'description' => 'An explanation of the task', ]]) ->add('dueTo',TypeDateTimeType::class, [ 'label' => 'Due to', 'widget' => 'single_text'] ) ; }
- 155. Transformers Transformers extract information from each Form Field. We can extract a lot of information: •Default values and placeholders. •Field attributes. •Validation rules.
- 156. Also important •FormView serializer for initial values. •Form serializer that extracts errors. { "code":null, "message":"Validation Failed", "errors":{ "children":{ "name":{ "errors":[ "This value should not be equal to Beetlejuice." ] }, "description":[], "dueTo":[] } } }
- 157. So far we have: $form $form->createView() (helpers in other Fws not Sf) Initial values UI hints (widgets, attributes) Bind incoming data Deserialize Validate Return errors Render view On blur sync validation On Submit validation On blur async validation Some client-side validation (HTML5) All the dynamic goodies
- 158. Form Server API docs Form Client $form Json-schema Liform
- 159. Leverage json-schema: Validators let valid = ajv.validate(schema, data) if (!valid) console.log(ajv.errors) https://github.com/epoberezkin/ajv
- 160. Leverage json-schema: Form generators • mozilla/react-jsonschema-form: React. • limenius/liform-react: React + Redux; integrated with redux-form (we ♥ redux-form). • … • Creating our own generator is not so difficult (you typically only need all the widgets, only a subset)
- 161. liform-react By using redux-form we can: • Have sane and powerful representation of state in Redux. • Integrate on-blur validation, async validation & on Submit validation. • Define our own widgets/themes. • Know from the beginning that it is flexible enough.
- 162. liform-react import React from 'react' import { createStore, combineReducers } from 'redux' import { reducer as formReducer } from 'redux-form' import { Provider } from 'react-redux' import Liform from 'liform-react' const MyForm = () => { const reducer = combineReducers({ form: formReducer }) const store = createStore(reducer) const schema = { //… } } return ( <Provider store={store}> <Liform schema={schema} onSubmit={(v) => {console.log(v)}}/> </Provider> ) }
- 163. liform-react { "properties": { "name": { "title":"Task name", "type":"string", "minLength": 2 }, "description": { "title":"Description", "type":"string", "widget":"textarea" }, "dueTo": { "title":"Due to", "type":"string", "widget":"datetime", "format":"date-time" } }, "required":["name"] }
- 164. Form Server API docs Form Client $form Json-schema React form Liform liform-react
- 165. =:D $form $form->createView() Initial values UI hints (widgets, attributes) Bind incoming data Deserialize Validate Return errors Render view On blur sync validation On Submit validation On blur async validation Some client-side validation (HTML5) All the dynamic goodies
- 166. https://github.com/Limenius/symfony-react-sandbox Example with • Webpack • ReactRenderer/ReactBundle • Liform/LiformBudle & liform-react
- 167. MADRID · NOV 27-28 · 2015 Thanks! @nacmartin [email protected] http://limenius.com Formation, Consulting and Development.







































![Tip: Presentational and Container components
const TaskList = (props) => (
<div>
{props.tasks.map((task, idx) => {
<div key={idx}>{task.name}</div>
})}
</div>
)
class TasksListContainer extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {tasks: []}
}
componentDidMount() {
// Load data with Ajax and whatnot
}
render() {
return <TaskList tasks={this.state.tasks}/>
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-react-170216162921/85/Integrating-React-js-with-PHP-projects-42-320.jpg)



























![ReactRenderer
{{ react_component('RecipesApp', {'props': props}) }}
import ReactOnRails from 'react-on-rails';
import RecipesApp from './RecipesAppServer';
ReactOnRails.register({ RecipesApp });
Twig:
JavaScript:
<div class="js-react-on-rails-component" style="display:none" data-component-name=“RecipesApp”
data-props=“[my Array in JSON]" data-trace=“false" data-dom-id=“sfreact-57d05640f2f1a”></div>
Generated HTML:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-react-170216162921/85/Integrating-React-js-with-PHP-projects-70-320.jpg)
















































![Suppose this Symfony form
public function buildForm(FormBuilderInterface $builder, array $options)
{
$builder
->add('country', ChoiceType::class, [
'choices' => [
'United Kingdom' => 'gb',
'Deutschland' => 'de',
'España' => 'es',
]
])
->add('addresses', CollectionType::class, ...);
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-react-170216162921/85/Integrating-React-js-with-PHP-projects-125-320.jpg)





















![How does it look like
{
"$schema": "http://json-schema.org/draft-04/schema#",
"title": "Product",
"description": "A product from Acme's catalog",
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"name": {
"description": "Name of the product",
"type": "string"
},
"price": {
"type": "number",
"minimum": 0,
"exclusiveMinimum": true
},
"tags": {
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "string"
},
"minItems": 1,
"uniqueItems": true
}
},
"required": ["id", "name", "price"]
}
Definitions
Types,
Validation rules
:_)
New resource: my-api/products/form](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-react-170216162921/85/Integrating-React-js-with-PHP-projects-149-320.jpg)
![Liform & LiformBundle
https://github.com/Limenius/Liform
use LimeniusLiformResolver;
use LimeniusLiformLiform;
$resolver = new Resolver();
$resolver->setDefaultTransformers();
$liform = new Liform($resolver);
$form = $this->createForm(CarType::class, $car, ['csrf_protection' => false]);
$schema = json_encode($liform->transform($form));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-react-170216162921/85/Integrating-React-js-with-PHP-projects-150-320.jpg)
![Transform piece by piece
{"title":"task",
"type":"object",
"properties":{
"name":{
"type":"string",
"title":"Name",
"default":"I'm a placeholder",
"propertyOrder":1
},
"description":{
"type":"string",
"widget":"textarea",
"title":"Description",
"description":"An explanation of the task",
"propertyOrder":2
},
"dueTo":{
"type":"string",
"title":"Due to",
"widget":"datetime",
"format":"date-time",
"propertyOrder":3
}
},
“required":[ “name", "description","dueTo"]}
public function buildForm(FormBuilderInterface $builder, array $options)
{
$builder
->add('name',TypeTextType::class, [
'label' => 'Name',
'required' => true,
'attr' => ['placeholder' => 'I'm a placeholder’]])
->add('description',TypeTextType::class, [
'label' => 'Description',
'liform' => [
'widget' => 'textarea',
'description' => 'An explanation of the task',
]])
->add('dueTo',TypeDateTimeType::class, [
'label' => 'Due to',
'widget' => 'single_text']
)
;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-react-170216162921/85/Integrating-React-js-with-PHP-projects-151-320.jpg)
![Transform piece by piece
{"title":"task",
"type":"object",
"properties":{
"name":{
"type":"string",
"title":"Name",
"default":"I'm a placeholder",
"propertyOrder":1
},
"description":{
"type":"string",
"widget":"textarea",
"title":"Description",
"description":"An explanation of the task",
"propertyOrder":2
},
"dueTo":{
"type":"string",
"title":"Due to",
"widget":"datetime",
"format":"date-time",
"propertyOrder":3
}
},
“required":[ “name", "description","dueTo"]}
public function buildForm(FormBuilderInterface $builder, array $options)
{
$builder
->add('name',TypeTextType::class, [
'label' => 'Name',
'required' => true,
'attr' => ['placeholder' => 'I'm a placeholder’]])
->add('description',TypeTextType::class, [
'label' => 'Description',
'liform' => [
'widget' => 'textarea',
'description' => 'An explanation of the task',
]])
->add('dueTo',TypeDateTimeType::class, [
'label' => 'Due to',
'widget' => 'single_text']
)
;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-react-170216162921/85/Integrating-React-js-with-PHP-projects-152-320.jpg)
![Transform piece by piece
{"title":"task",
"type":"object",
"properties":{
"name":{
"type":"string",
"title":"Name",
"default":"I'm a placeholder",
"propertyOrder":1
},
"description":{
"type":"string",
"widget":"textarea",
"title":"Description",
"description":"An explanation of the task",
"propertyOrder":2
},
"dueTo":{
"type":"string",
"title":"Due to",
"widget":"datetime",
"format":"date-time",
"propertyOrder":3
}
},
“required":[ “name", "description","dueTo"]}
public function buildForm(FormBuilderInterface $builder, array $options)
{
$builder
->add('name',TypeTextType::class, [
'label' => 'Name',
'required' => true,
'attr' => ['placeholder' => 'I'm a placeholder’]])
->add('description',TypeTextType::class, [
'label' => 'Description',
'liform' => [
'widget' => 'textarea',
'description' => 'An explanation of the task',
]])
->add('dueTo',TypeDateTimeType::class, [
'label' => 'Due to',
'widget' => 'single_text']
)
;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-react-170216162921/85/Integrating-React-js-with-PHP-projects-153-320.jpg)
![Transform piece by piece
{"title":"task",
"type":"object",
"properties":{
"name":{
"type":"string",
"title":"Name",
"default":"I'm a placeholder",
"propertyOrder":1
},
"description":{
"type":"string",
"widget":"textarea",
"title":"Description",
"description":"An explanation of the task",
"propertyOrder":2
},
"dueTo":{
"type":"string",
"title":"Due to",
"widget":"datetime",
"format":"date-time",
"propertyOrder":3
}
},
“required":[ “name", "description","dueTo"]}
public function buildForm(FormBuilderInterface $builder, array $options)
{
$builder
->add('name',TypeTextType::class, [
'label' => 'Name',
'required' => true,
'attr' => ['placeholder' => 'I'm a placeholder’]])
->add('description',TypeTextType::class, [
'label' => 'Description',
'liform' => [
'widget' => 'textarea',
'description' => 'An explanation of the task',
]])
->add('dueTo',TypeDateTimeType::class, [
'label' => 'Due to',
'widget' => 'single_text']
)
;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-react-170216162921/85/Integrating-React-js-with-PHP-projects-154-320.jpg)

![Also important
•FormView serializer for initial values.
•Form serializer that extracts errors.
{ "code":null,
"message":"Validation Failed",
"errors":{
"children":{
"name":{
"errors":[
"This value should not be equal to Beetlejuice."
]
},
"description":[],
"dueTo":[]
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-react-170216162921/85/Integrating-React-js-with-PHP-projects-156-320.jpg)






![liform-react
{
"properties": {
"name": {
"title":"Task name",
"type":"string",
"minLength": 2
},
"description": {
"title":"Description",
"type":"string",
"widget":"textarea"
},
"dueTo": {
"title":"Due to",
"type":"string",
"widget":"datetime",
"format":"date-time"
}
},
"required":["name"]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-react-170216162921/85/Integrating-React-js-with-PHP-projects-163-320.jpg)



