Internet security protocol
- 1. INTERNET SECURITY PROTOCOL TYIT UNIT V
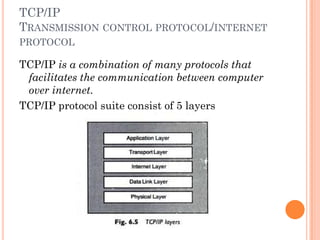
- 2. TCP/IP TRANSMISSION CONTROL PROTOCOL/INTERNET PROTOCOL TCP/IP is a combination of many protocols that facilitates the communication between computer over internet. TCP/IP protocol suite consist of 5 layers
- 3. SECURE SOCKET LAYER(SSL) The SSL protocol is an internet protocol for secure exchange of information between a web browser and a web server. It provides two basic security services: authentication and confidentiality SSL can be conceptually considered as an additional layer in TCP/IP protocol suite. It is located between application and transport layer. The application layer data is passed to the SSL layer, SSL layer performs encryption on the data received and also add its own encryption information header called as SSL Header to encrypted data
- 4. HOW SSL WORKS SSL has 3 sub protocols Handshake protocol Record protocol Alert protocol The Handshake protocol is similar to how two people shake hand with each other before they start conversing. Each handshake message has 3 fields Type(1 byte): one of the 10 possible message type Length (3 byte): length of message in bytes Content (1 or more bytes): parameters associated with this message.
- 5. SSL HANDSHAKE PROTOCOL PHASES The handshake protocol is actually made up of 4 phases. 1. 2. 3. 4. Establish security capabilities Server authentication and key exchange Client authentication and key exchange Finish
- 6. PHASE 1: ESTABLISH SECURITY CAPABILITIES: This first phase is used to initiate a logical connection and establish the security capabilities associated with that connection. It consists of two messages, the “client hello” and the “server hello” Step 1: Client Hello Step 2 Server Hello
- 7. CLIENT HELLO PARAMETERS: Version: highest version of SSL that client supports. Random: this field is useful for later actual communication , it consists of 2 sub fields A 32 bit data-time field that identifies current date and time of clients computer A 28 bit random number generated by the random number generator software. Session Id: if this fields contains non-zero value, it means that there is already a connection. A zero value indicates that client wants to create a new connection. Cipher Suite: list of cryptographic algorithm supported by client Compression method: list of compression algorithm supported by the client
- 8. SERVER HELLO PARAMETERS Version: highest version that server supports from the list. Random: same structure as random field of client. However, the random value generated is depended on clients random value. Session Id: server creates a new session id and puts it in this field. Cipher Suite: Contains a single cipher suite, which server selects from the list sent by the client. Compression method: contains a compression algorithm, which the server selects from the list.
- 9. PHASE 2 SERVER AUTHENTICATION AND KEY EXCHANGE The server initiates this second phase of the SSL This phase contains four steps: Certificate Server key exchange Certificate request Sever hello done
- 10. PHASE 3 CLIENT AUTHENTICATION AND KEY EXCHANGE The client initiates this third phase of the SSL This phase contains three steps: Certificate Client key exchange(premaster secret key) Certificate verify
- 11. PHASE 4 FINISH The client initiates this fourth phase of SSL handshake which the server ends First 2 messages from client 1. Change cipher specs 2. Finished Server responds 1. Change cipher specs, 2. Finished
- 12. MASTER KEY GENERATION Client creates 48 byte pre master secret key and encrypts it with servers public key. And sends pre master secret key to the server. Finally the Symmetric keys to be used by the client and the server are generated
- 13. THE RECORD PROTOCOL The record protocol in SSL comes into picture after a successful handshake is completed. This protocol provides 2 services Confidentiality: achieved using secret key that is defined by handshake protocol Integrity: the handshake protocol also defines shared secret Key (MAC)that is used for assuring the message integrity.
- 14. SSL RECORD PROTOCOL 1. Fragmentations 2. Compression 3. Addition of MAC 4. Encryption 5. Append header 1. Content type 2. Major version 3. Minor version 4. Compressed length
- 15. THE ALERT PROTOCOL When the server detects an error, the detecting party sends an alert message to other party. Both the parties close the SSL connection and destroys the session id, secret keys. Alert message is of 2 bytes 1st byte is error type 2nd byte specifies the reason for actual error.