Intro to Graphs and Neo4j
- 1. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Graph Database Introduction Meetup April 2014 Michael Hunger [email protected] @mesirii @neo4j
- 2. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Agenda 1. Why Graphs,Why Now? 2. What Is A Graph, Anyway? 3. Graphs In The Real World 4. The Graph Landscape i) Popular Graph Models ii) Graph Databases iii)Graph Compute Engines
- 3. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Why Graphs?
- 4. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 The World is a Graph
- 5. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Some Use-Cases
- 6. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Social Network
- 7. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 (Network) Impact Analysis
- 8. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Route Finding
- 9. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Recommenda<ons
- 10. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Logis<cs
- 11. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Access Control
- 12. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Fraud Analysis
- 13. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Securi<es & Debt
- 14. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 What Is A Graph, Anyway?
- 15. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 A Graph Node Relationship
- 16. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Four Graph Model Building Blocks
- 17. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Property Graph Data Model
- 18. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Nodes
- 19. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Rela<onships
- 20. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Rela<onships (con<nued) Nodes can have more than one rela<onship Self rela<onships are allowed Nodes can be connected by more than one rela<onship
- 21. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Labels
- 22. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Four Building Blocks ๏ Nodes • En<<es ๏ Rela<onships • Connect en<<es and structure domain ๏ Proper<es • AJributes and metadata ๏ Labels • Group nodes by role
- 23. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Whiteboard Friendlyness Easy to design and model direct representation of the model
- 24. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014
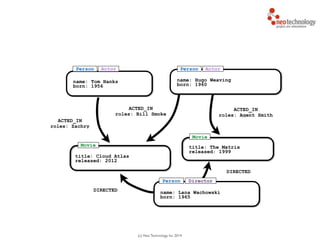
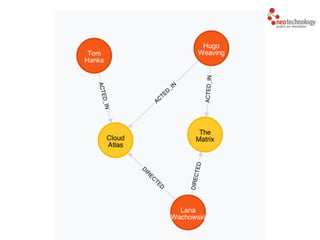
- 25. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Tom Hanks Hugo Weaving Cloud Atlas The Matrix Lana Wachowski ACTED_IN ACTED_IN ACTED_IN DIRECTED DIRECTED
- 26. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 name: Tom Hanks born: 1956 title: Cloud Atlas released: 2012 title: The Matrix released: 1999 name: Lana Wachowski born: 1965 ACTED_IN roles: Zachry ACTED_IN roles: Bill Smoke DIRECTED DIRECTED ACTED_IN roles: Agent Smith name: Hugo Weaving born: 1960 Person Movie Movie Person Director ActorPerson Actor
- 27. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014
- 28. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Aggregate vs. Connected Data-Model
- 29. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 What is NOSQL? It’s not “No to SQL” It’s not “Never SQL” It’s “Not Only SQL” NOSQL no-seek-wool n. Describes ongoing trend where developers increasingly opt for non-relational databases to help solve their problems, in an effort to use the right tool for the right job.
- 30. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 NOSQL Relational Graph Document KeyValue Riak Column oriented Redis Cassandra Mongo Couch Neo4j MySQL Postgres NOSQL Databases
- 31. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 31
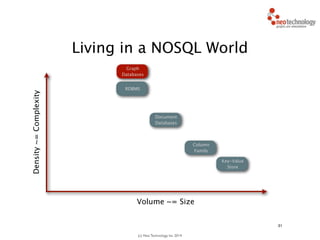
- 32. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 31 Living in a NOSQL World
- 33. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 31 Living in a NOSQL World Volume ~= Size
- 34. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 31 Living in a NOSQL World Density~=Complexity Volume ~= Size
- 35. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 31 Living in a NOSQL World Density~=Complexity Volume ~= Size Key-Value Store
- 36. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 31 Living in a NOSQL World Density~=Complexity Column Family Volume ~= Size Key-Value Store
- 37. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 31 Living in a NOSQL World Density~=Complexity Column Family Volume ~= Size Key-Value Store Document Databases
- 38. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 31 Living in a NOSQL World RDBMS Density~=Complexity Column Family Volume ~= Size Key-Value Store Document Databases
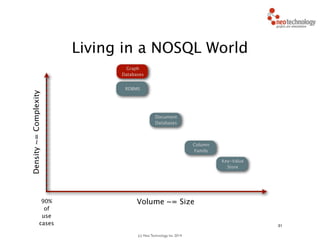
- 39. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 31 Living in a NOSQL World RDBMS Density~=Complexity Column Family Volume ~= Size Key-Value Store Document Databases Graph Databases
- 40. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 31 Living in a NOSQL World RDBMS Density~=Complexity Column Family Volume ~= Size Key-Value Store Document Databases Graph Databases 90% of use cases
- 41. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 31 Living in a NOSQL World RDBMS Density~=Complexity Column Family Volume ~= Size Key-Value Store Document Databases Graph Databases 90% of use cases
- 42. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 31 Living in a NOSQL World Aggregate Oriented RDBMS Density~=Complexity Column Family Volume ~= Size Key-Value Store Document Databases Graph Databases 90% of use cases
- 43. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 “There is a significant downside - the whole approach works really well when data access is aligned with the aggregates, but what if you want to look at the data in a different way? Order entry naturally stores orders as aggregates, but analyzing product sales cuts across the aggregate structure. The advantage of not using an aggregate structure in the database is that it allows you to slice and dice your data different ways for different audiences. ! This is why aggregate-oriented stores talk so much about map- reduce.” Martin Fowler Aggregate Oriented Model
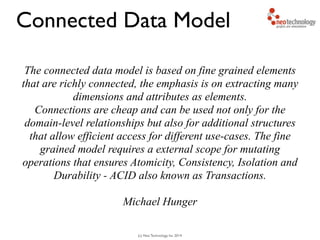
- 44. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 The connected data model is based on fine grained elements that are richly connected, the emphasis is on extracting many dimensions and attributes as elements. Connections are cheap and can be used not only for the domain-level relationships but also for additional structures that allow efficient access for different use-cases. The fine grained model requires a external scope for mutating operations that ensures Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation and Durability - ACID also known as Transactions. ! Michael Hunger Connected Data Model
- 45. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Relational vs. Graph 34
- 46. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Relational vs. Graph You know relational 34
- 47. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Relational vs. Graph You know relational 34
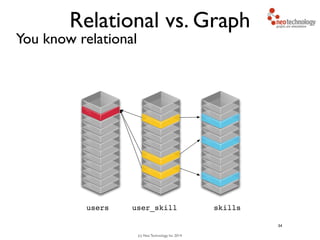
- 48. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Relational vs. Graph You know relational 34 users
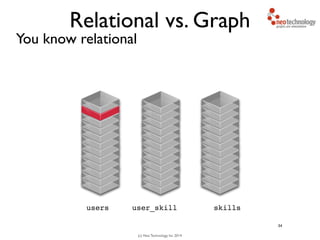
- 49. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Relational vs. Graph You know relational 34 users skills
- 50. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Relational vs. Graph You know relational 34 users skillsuser_skill
- 51. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Relational vs. Graph You know relational 34 users skillsuser_skill
- 52. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Relational vs. Graph You know relational 34 users skillsuser_skill
- 53. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Relational vs. Graph You know relational 34 users skillsuser_skill
- 54. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Relational vs. Graph You know relational 34 now consider relationships...
- 55. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Relational vs. Graph You know relational 34 now consider relationships...
- 56. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Relational vs. Graph You know relational 34 now consider relationships...
- 57. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Relational vs. Graph You know relational 34 now consider relationships...
- 58. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Relational vs. Graph You know relational 34 now consider relationships...
- 59. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Relational vs. Graph You know relational 34 now consider relationships...
- 60. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Relational vs. Graph 34
- 61. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 35
- 62. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Looks different, fine.Who cares? 35
- 63. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Looks different, fine.Who cares? ๏a sample social graph 35
- 64. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Looks different, fine.Who cares? ๏a sample social graph •with ~1,000 persons 35
- 65. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Looks different, fine.Who cares? ๏a sample social graph •with ~1,000 persons ๏average 50 friends per person 35
- 66. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Looks different, fine.Who cares? ๏a sample social graph •with ~1,000 persons ๏average 50 friends per person ๏pathExists(a,b) limited to depth 4 35
- 67. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Looks different, fine.Who cares? ๏a sample social graph •with ~1,000 persons ๏average 50 friends per person ๏pathExists(a,b) limited to depth 4 ๏caches warmed up to eliminate disk I/O 35
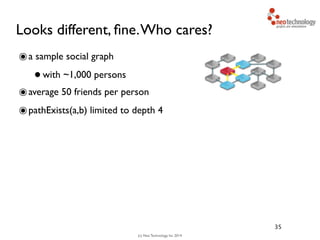
- 68. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Looks different, fine.Who cares? ๏a sample social graph •with ~1,000 persons ๏average 50 friends per person ๏pathExists(a,b) limited to depth 4 ๏caches warmed up to eliminate disk I/O 35 # persons query time Relational database 1.000 2000ms
- 69. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Looks different, fine.Who cares? ๏a sample social graph •with ~1,000 persons ๏average 50 friends per person ๏pathExists(a,b) limited to depth 4 ๏caches warmed up to eliminate disk I/O 35 # persons query time Relational database 1.000 2000ms Neo4j 1.000 2ms
- 70. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Looks different, fine.Who cares? ๏a sample social graph •with ~1,000 persons ๏average 50 friends per person ๏pathExists(a,b) limited to depth 4 ๏caches warmed up to eliminate disk I/O 35 # persons query time Relational database 1.000 2000ms Neo4j 1.000 2ms Neo4j 1.000.000 2ms
- 71. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 35
- 72. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Neo4j is a Graph Database
- 73. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Neo4j is a Graph Database • A Graph Database:
- 74. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Neo4j is a Graph Database • A Graph Database: • a schema-free labeled Property Graph
- 75. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Neo4j is a Graph Database • A Graph Database: • a schema-free labeled Property Graph • perfect for complex, highly connected data
- 76. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Neo4j is a Graph Database • A Graph Database: • a schema-free labeled Property Graph • perfect for complex, highly connected data • A Graph Database:
- 77. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Neo4j is a Graph Database • A Graph Database: • a schema-free labeled Property Graph • perfect for complex, highly connected data • A Graph Database: • reliable with real ACID Transactions
- 78. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Neo4j is a Graph Database • A Graph Database: • a schema-free labeled Property Graph • perfect for complex, highly connected data • A Graph Database: • reliable with real ACID Transactions • scalable: Billions of Nodes and Relationships, Scale out with highly available Neo4j-Cluster
- 79. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Neo4j is a Graph Database • A Graph Database: • a schema-free labeled Property Graph • perfect for complex, highly connected data • A Graph Database: • reliable with real ACID Transactions • scalable: Billions of Nodes and Relationships, Scale out with highly available Neo4j-Cluster • fast with more than 2M traversals / second
- 80. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Neo4j is a Graph Database • A Graph Database: • a schema-free labeled Property Graph • perfect for complex, highly connected data • A Graph Database: • reliable with real ACID Transactions • scalable: Billions of Nodes and Relationships, Scale out with highly available Neo4j-Cluster • fast with more than 2M traversals / second • Server with HTTP API, or Embeddable on the JVM
- 81. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Neo4j is a Graph Database • A Graph Database: • a schema-free labeled Property Graph • perfect for complex, highly connected data • A Graph Database: • reliable with real ACID Transactions • scalable: Billions of Nodes and Relationships, Scale out with highly available Neo4j-Cluster • fast with more than 2M traversals / second • Server with HTTP API, or Embeddable on the JVM • Declarative Query Language
- 82. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Graph Database: Pros & Cons • Strengths • Powerful data model, as general as RDBMS • Whiteboard friendly, agile development • Fast, for connected data • Easy to query • Weaknesses: • Sharding (they can scale up and out reasonably well) • Global Queries / Number Crunching • Binary Data / Blobs • Requires conceptual shift • graph-like thinking becomes addictive
- 83. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Graph Querying
- 84. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 You know how to query a relational database!
- 85. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 40
- 86. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Just use SQL 40
- 87. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Just use SQL 40users skillsuser_skills
- 88. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Just use SQL 40users skillsuser_skills select skills.name from users join user_skills on (...) join skills on (...) where users.name = “Michael“
- 89. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 How to query a graph?
- 90. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 42
- 91. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 You traverse the graph 42
- 92. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 // find starting nodes MATCH (me:Person {name:'Andreas'}) Andreas You traverse the graph 42
- 93. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 // find starting nodes MATCH (me:Person {name:'Andreas'}) // then traverse the relationships MATCH (me:Person {name:'Andreas'})-[:FRIEND]-(friend) -[:FRIEND]-(friend2) RETURN friend2 Andreas You traverse the graph 42
- 94. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Cypher a pattern-matching query language for graphs
- 95. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Cypher attributes #1 Declarative You tell Cypher what you want, not how to get it 44
- 96. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Cypher attributes #2 Expressive Optimize syntax for reading 45 MATCH (a:Actor)-[r:ACTS_IN]->(m:Movie) RETURN a.name, r.role, m.title
- 97. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Cypher attributes #3 Pattern Matching Patterns are easy for your human brain 46
- 98. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Cypher attributes #4 Idempotent State change should be expressed idempotently 47
- 99. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Query Structure
- 100. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 MATCH (n:Label)-[:REL]->(m:Label) WHERE n.prop < 42 WITH n, count(m) as cnt, collect(m.attr) as attrs WHERE cnt > 12 RETURN n.prop, extract(a2 in filter(a1 in attrs WHERE a1 =~ "...-.*") | substr(a2,4,size(a2)-1)] AS ids ORDER BY length(ids) DESC LIMIT 10 Query Structure
- 101. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 MATCH describes the pattern
- 102. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 MATCH (n:Label)-[:REL]->(m:Label) WHERE n.prop < 42 WITH n, count(m) as cnt, collect(m.attr) as attrs WHERE cnt > 12 RETURN n.prop, extract(a2 in filter(a1 in attrs WHERE a1 =~ "...-.*") | substr(a2,4,size(a2)-1)] AS ids ORDER BY length(ids) DESC SKIP 5 LIMIT 10 MATCH - Pattern
- 103. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 WHERE filters the result set
- 104. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 MATCH (n:Label)-[:REL]->(m:Label) WHERE n.prop < 42 WITH n, count(m) as cnt, collect(m.attr) as attrs WHERE cnt > 12 RETURN n.prop, extract(a2 in filter(a1 in attrs WHERE a1 =~ "...-.*") | substr(a2,4,size(a2)-1)] AS ids ORDER BY length(ids) DESC SKIP 5 LIMIT 10 WHERE - filter
- 105. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 RETURN returns the result rows
- 106. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 MATCH (n:Label)-[:REL]->(m:Label) WHERE n.prop < 42 WITH n, count(m) as cnt, collect(m.attr) as attrs WHERE cnt > 12 RETURN n.prop, extract(a2 in filter(a1 in attrs WHERE a1 =~ "...-.*") | substr(a2,4,size(a2)-1)] AS ids ORDER BY length(ids) DESC SKIP 5 LIMIT 10 RETURN - project
- 107. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 ORDER BY LIMIT SKIP sort and paginate
- 108. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 MATCH (n:Label)-[:REL]->(m:Label) WHERE n.prop < 42 WITH n, count(m) as cnt, collect(m.attr) as attrs WHERE cnt > 12 RETURN n.prop, extract(a2 in filter(a1 in attrs WHERE a1 =~ "...-.*") | substr(a2,4,size(a2)-1)] AS ids ORDER BY length(ids) DESC SKIP 5 LIMIT 10 ORDER BY LIMIT - Paginate
- 109. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 WITH combines query parts like a pipe
- 110. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 MATCH (n:Label)-[:REL]->(m:Label) WHERE n.prop < 42 WITH n, count(m) as cnt, collect(m.attr) as attrs WHERE cnt > 12 RETURN n.prop, extract(a2 in filter(a1 in attrs WHERE a1 =~ "...-.*") | substr(a2,4,size(a2)-1)] AS ids ORDER BY length(ids) DESC SKIP 5 LIMIT 10 WITH + WHERE = HAVING
- 111. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Collections powerful datastructure handling
- 112. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 MATCH (n:Label)-[:REL]->(m:Label) WHERE n.prop < 42 WITH n, count(m) as cnt, collect(m.attr) as attrs WHERE cnt > 12 RETURN n.prop, extract(a2 in filter(a1 in attrs WHERE a1 =~ "...-.*") | substr(a2,4,size(a2)-1)] AS ids ORDER BY length(ids) DESC LIMIT 10 Collections
- 113. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 MATCH (:Country {name:"Sweden"}) <-[:REGISTERED_IN]-(c:Company) <-[:WORKS_AT]-(p:Person:Developer) WHERE p.age < 42 WITH c, count(p) as cnt, collect(p.empId) as emp_ids WHERE cnt > 12 RETURN c.name AS company_name, extract(id2 in filter(id1 in emp_ids WHERE id1 =~ "...-.*") | substr(id2,4,size(id2)-1)] AS last_emp_id_digits ORDER BY length(last_emp_id_digits) DESC SKIP 5 LIMIT 10 Concrete Example
- 114. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 CREATE creates nodes, relationships and patterns
- 115. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 CREATE (y:Year {year:2014}) FOREACH (m IN range(1,12) | CREATE (:Month {month:m})-[:IN]->(y) ) CREATE - nodes, rels, structures
- 116. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 MERGE matches or creates
- 117. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 MERGE (y:Year {year:2014}) ON CREATE SET y.created = timestamp() FOREACH (m IN range(1,12) | MERGE (:Month {month:m})-[:IN]->(y) ) MERGE - get or create
- 118. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 SET, REMOVE update attributes and labels
- 119. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 MATCH (year:Year) WHERE year.year % 4 = 0 OR year.year % 100 <> 0 AND year.year % 400 = 0 SET year:Leap WITH year MATCH (year)<-[:IN]-(feb:Month {month:2}) SET feb.days = 29 CREATE (feb)<-[:IN]-(:Day {day:29}) SET, REMOVE, DELETE
- 120. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 INDEX, CONSTRAINTS represent optional schema
- 121. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 CREATE CONSTRAINT ON (y:Year) ASSERT y.year IS UNIQUE ! CREATE INDEX ON :Month(month) INDEX / CONSTRAINT
- 122. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Graph Query Examples
- 123. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Social Recommendation
- 124. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014
- 125. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014
- 126. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 MATCH (person:Person)-[:IS_FRIEND_OF]->(friend), (friend)-[:LIKES]->(restaurant), (restaurant)-[:LOCATED_IN]->(loc:Location), (restaurant)-[:SERVES]->(type:Cuisine) ! WHERE person.name = 'Philip' AND loc.location='New York' AND type.cuisine='Sushi' ! RETURN restaurant.name * Cypher query language examplehttp://maxdemarzi.com/?s=facebook
- 127. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014
- 128. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014
- 129. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Network Management Example
- 130. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Network Management - Create CREATE ! ! (crm {name:"CRM"}),! ! (dbvm {name:"Database VM"}),! ! (www {name:"Public Website"}),! ! (wwwvm {name:"Webserver VM"}),! ! (srv1 {name:"Server 1"}),! ! (san {name:"SAN"}),! ! (srv2 {name:"Server 2"}),! ! ! (crm)-[:DEPENDS_ON]->(dbvm),! ! (dbvm)-[:DEPENDS_ON]->(srv2),! ! (srv2)-[:DEPENDS_ON]->(san),! ! (www)-[:DEPENDS_ON]->(dbvm),! ! (www)-[:DEPENDS_ON]->(wwwvm),! ! (wwwvm)-[:DEPENDS_ON]->(srv1),! ! (srv1)-[:DEPENDS_ON]->(san)! Practical Cypher
- 131. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Network Management - Impact Analysis // Server 1 Outage! MATCH (n)<-[:DEPENDS_ON*]-(upstream)! WHERE n.name = "Server 1"! RETURN upstream! Practical Cypher upstream {name:"Webserver VM"} {name:"Public Website"}
- 132. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Network Management - Dependency Analysis // Public website dependencies! MATCH (n)-[:DEPENDS_ON*]->(downstream)! WHERE n.name = "Public Website"! RETURN downstream! ! Practical Cypher downstream {name:"Database VM"} {name:"Server 2"} {name:"SAN"} {name:"Webserver VM"} {name:"Server 1"}
- 133. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 Network Management - Statistics // Most depended on component! MATCH (n)<-[:DEPENDS_ON*]-(dependent)! RETURN n, ! count(DISTINCT dependent) ! AS dependents! ORDER BY dependents DESC! LIMIT 1 Practical Cypher n dependents {name:"SAN"} 6
- 134. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 ๏ Full day Neo4j Training & Online Training ๏ Free e-Books • Graph Databases, Neo4j 2.0 (DE) ๏ neo4j.org • http://neo4j.org/develop/modeling ๏ docs.neo4j.org • Data Modeling Examples ๏ http://console.neo4j.org ๏ http://gist.neo4j.org ๏ Get Neo4j • http://neo4j.org/download ๏ Participate • http://groups.google.com/group/neo4j How to get started? 81
- 135. (c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014 ThankYou Time for Questions!












































































![(c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014
// find starting nodes
MATCH (me:Person {name:'Andreas'})
// then traverse the relationships
MATCH (me:Person {name:'Andreas'})-[:FRIEND]-(friend)
-[:FRIEND]-(friend2)
RETURN friend2
Andreas
You traverse the graph
42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intrographs-140418040232-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Graphs-and-Neo4j-93-320.jpg)


![(c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014
Cypher attributes
#2 Expressive
Optimize syntax for reading
45
MATCH (a:Actor)-[r:ACTS_IN]->(m:Movie)
RETURN a.name, r.role, m.title](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intrographs-140418040232-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Graphs-and-Neo4j-96-320.jpg)



![(c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014
MATCH (n:Label)-[:REL]->(m:Label)
WHERE n.prop < 42
WITH n, count(m) as cnt,
collect(m.attr) as attrs
WHERE cnt > 12
RETURN n.prop,
extract(a2 in
filter(a1 in attrs
WHERE a1 =~ "...-.*")
| substr(a2,4,size(a2)-1)]
AS ids
ORDER BY length(ids) DESC
LIMIT 10
Query Structure](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intrographs-140418040232-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Graphs-and-Neo4j-100-320.jpg)

![(c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014
MATCH (n:Label)-[:REL]->(m:Label)
WHERE n.prop < 42
WITH n, count(m) as cnt,
collect(m.attr) as attrs
WHERE cnt > 12
RETURN n.prop,
extract(a2 in
filter(a1 in attrs
WHERE a1 =~ "...-.*")
| substr(a2,4,size(a2)-1)]
AS ids
ORDER BY length(ids) DESC
SKIP 5 LIMIT 10
MATCH - Pattern](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intrographs-140418040232-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Graphs-and-Neo4j-102-320.jpg)

![(c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014
MATCH (n:Label)-[:REL]->(m:Label)
WHERE n.prop < 42
WITH n, count(m) as cnt,
collect(m.attr) as attrs
WHERE cnt > 12
RETURN n.prop,
extract(a2 in
filter(a1 in attrs
WHERE a1 =~ "...-.*")
| substr(a2,4,size(a2)-1)]
AS ids
ORDER BY length(ids) DESC
SKIP 5 LIMIT 10
WHERE - filter](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intrographs-140418040232-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Graphs-and-Neo4j-104-320.jpg)

![(c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014
MATCH (n:Label)-[:REL]->(m:Label)
WHERE n.prop < 42
WITH n, count(m) as cnt,
collect(m.attr) as attrs
WHERE cnt > 12
RETURN n.prop,
extract(a2 in
filter(a1 in attrs
WHERE a1 =~ "...-.*")
| substr(a2,4,size(a2)-1)]
AS ids
ORDER BY length(ids) DESC
SKIP 5 LIMIT 10
RETURN - project](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intrographs-140418040232-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Graphs-and-Neo4j-106-320.jpg)

![(c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014
MATCH (n:Label)-[:REL]->(m:Label)
WHERE n.prop < 42
WITH n, count(m) as cnt,
collect(m.attr) as attrs
WHERE cnt > 12
RETURN n.prop,
extract(a2 in
filter(a1 in attrs
WHERE a1 =~ "...-.*")
| substr(a2,4,size(a2)-1)]
AS ids
ORDER BY length(ids) DESC
SKIP 5 LIMIT 10
ORDER BY LIMIT - Paginate](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intrographs-140418040232-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Graphs-and-Neo4j-108-320.jpg)

![(c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014
MATCH (n:Label)-[:REL]->(m:Label)
WHERE n.prop < 42
WITH n, count(m) as cnt,
collect(m.attr) as attrs
WHERE cnt > 12
RETURN n.prop,
extract(a2 in
filter(a1 in attrs
WHERE a1 =~ "...-.*")
| substr(a2,4,size(a2)-1)]
AS ids
ORDER BY length(ids) DESC
SKIP 5 LIMIT 10
WITH + WHERE = HAVING](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intrographs-140418040232-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Graphs-and-Neo4j-110-320.jpg)

![(c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014
MATCH (n:Label)-[:REL]->(m:Label)
WHERE n.prop < 42
WITH n, count(m) as cnt,
collect(m.attr) as attrs
WHERE cnt > 12
RETURN n.prop,
extract(a2 in
filter(a1 in attrs
WHERE a1 =~ "...-.*")
| substr(a2,4,size(a2)-1)]
AS ids
ORDER BY length(ids) DESC
LIMIT 10
Collections](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intrographs-140418040232-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Graphs-and-Neo4j-112-320.jpg)
![(c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014
MATCH (:Country {name:"Sweden"})
<-[:REGISTERED_IN]-(c:Company)
<-[:WORKS_AT]-(p:Person:Developer)
WHERE p.age < 42
WITH c, count(p) as cnt,
collect(p.empId) as emp_ids
WHERE cnt > 12
RETURN c.name AS company_name,
extract(id2 in
filter(id1 in emp_ids
WHERE id1 =~ "...-.*")
| substr(id2,4,size(id2)-1)]
AS last_emp_id_digits
ORDER BY length(last_emp_id_digits) DESC
SKIP 5 LIMIT 10
Concrete Example](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intrographs-140418040232-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Graphs-and-Neo4j-113-320.jpg)

![(c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014
CREATE (y:Year {year:2014})
FOREACH (m IN range(1,12) |
CREATE
(:Month {month:m})-[:IN]->(y)
)
CREATE - nodes, rels, structures](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intrographs-140418040232-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Graphs-and-Neo4j-115-320.jpg)

![(c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014
MERGE (y:Year {year:2014})
ON CREATE
SET y.created = timestamp()
FOREACH (m IN range(1,12) |
MERGE
(:Month {month:m})-[:IN]->(y)
)
MERGE - get or create](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intrographs-140418040232-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Graphs-and-Neo4j-117-320.jpg)

![(c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014
MATCH (year:Year)
WHERE year.year % 4 = 0 OR
year.year % 100 <> 0 AND
year.year % 400 = 0
SET year:Leap
WITH year
MATCH (year)<-[:IN]-(feb:Month {month:2})
SET feb.days = 29
CREATE (feb)<-[:IN]-(:Day {day:29})
SET, REMOVE, DELETE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intrographs-140418040232-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Graphs-and-Neo4j-119-320.jpg)






![(c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014
MATCH (person:Person)-[:IS_FRIEND_OF]->(friend),
(friend)-[:LIKES]->(restaurant),
(restaurant)-[:LOCATED_IN]->(loc:Location),
(restaurant)-[:SERVES]->(type:Cuisine)
!
WHERE person.name = 'Philip' AND loc.location='New York' AND
type.cuisine='Sushi'
!
RETURN restaurant.name
* Cypher query language examplehttp://maxdemarzi.com/?s=facebook](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intrographs-140418040232-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Graphs-and-Neo4j-126-320.jpg)



![(c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014
Network Management - Create
CREATE !
! (crm {name:"CRM"}),!
! (dbvm {name:"Database VM"}),!
! (www {name:"Public Website"}),!
! (wwwvm {name:"Webserver VM"}),!
! (srv1 {name:"Server 1"}),!
! (san {name:"SAN"}),!
! (srv2 {name:"Server 2"}),!
!
! (crm)-[:DEPENDS_ON]->(dbvm),!
! (dbvm)-[:DEPENDS_ON]->(srv2),!
! (srv2)-[:DEPENDS_ON]->(san),!
! (www)-[:DEPENDS_ON]->(dbvm),!
! (www)-[:DEPENDS_ON]->(wwwvm),!
! (wwwvm)-[:DEPENDS_ON]->(srv1),!
! (srv1)-[:DEPENDS_ON]->(san)!
Practical Cypher](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intrographs-140418040232-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Graphs-and-Neo4j-130-320.jpg)
![(c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014
Network Management - Impact Analysis
// Server 1 Outage!
MATCH (n)<-[:DEPENDS_ON*]-(upstream)!
WHERE n.name = "Server 1"!
RETURN upstream!
Practical Cypher
upstream
{name:"Webserver VM"}
{name:"Public Website"}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intrographs-140418040232-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Graphs-and-Neo4j-131-320.jpg)
![(c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014
Network Management - Dependency Analysis
// Public website dependencies!
MATCH (n)-[:DEPENDS_ON*]->(downstream)!
WHERE n.name = "Public Website"!
RETURN downstream!
!
Practical Cypher
downstream
{name:"Database VM"}
{name:"Server 2"}
{name:"SAN"}
{name:"Webserver VM"}
{name:"Server 1"}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intrographs-140418040232-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Graphs-and-Neo4j-132-320.jpg)
![(c) Neo Technology, Inc 2014
Network Management - Statistics
// Most depended on component!
MATCH (n)<-[:DEPENDS_ON*]-(dependent)!
RETURN n, !
count(DISTINCT dependent) !
AS dependents!
ORDER BY dependents DESC!
LIMIT 1
Practical Cypher
n dependents
{name:"SAN"} 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intrographs-140418040232-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Graphs-and-Neo4j-133-320.jpg)

