Intro to Operating Systems - Introductory Lectures - Software Engineering
- 2. What is an Operating System? A program that acts as an intermediary between a user of a computer and the computer hardware Operating system goals: Execute user programs and make solving user problems easier Make the computer system convenient to use Use the computer hardware in an efficient manner
- 3. Computer System Structure Computer system can be divided into four components: Hardware – provides basic computing resources CPU, memory, I/O devices Operating system Controls and coordinates use of hardware among various applications and users Application programs – define the ways in which the system resources are used to solve the computing problems of the users Word processors, compilers, web browsers, database systems, video games Users People, machines, other computers
- 4. Four Components of a Computer System
- 5. Operating System Definition OS is a resource allocator Manages all resources Decides between conflicting requests for efficient and fair resource use OS is a control program Controls execution of programs to prevent errors and improper use of the computer
- 6. Computer System Organization Computer-system operation One or more CPUs, device controllers connect through common bus providing access to shared memory Concurrent execution of CPUs and devices competing for memory cycles
- 7. Review Computer System Components What is an OS? Why do we need to have OS? Agenda Computer System Operations Interrupts Storage Hierarchy Computer Architecture
- 8. Computer-System Operation I/O devices and the CPU can execute concurrently Each device controller is in charge of a particular device type Each device controller has a local buffer CPU moves data from/to main memory to/from local buffers I/O is from the device to local buffer of controller Device controller informs CPU that it has finished its operation by causing an interrupt
- 9. Common Functions of Interrupts Interrupt transfers control to the interrupt service routine generally, through the interrupt vector, which contains the addresses of all the service routines Interrupt architecture must save the address of the interrupted instruction A trap or exception is a software-generated interrupt caused either by an error or a user request An operating system is interrupt driven
- 10. Storage Structure Main memory – only large storage media that the CPU can access directly Random access Typically volatile Secondary storage – extension of main memory that provides large nonvolatile storage capacity Hard disks – rigid metal or glass platters covered with magnetic recording material Disk surface is logically divided into tracks, which are subdivided into sectors The disk controller determines the logical interaction between the device and the computer Solid-state disks – faster than hard disks, nonvolatile Various technologies Becoming more popular
- 11. Storage Hierarchy Storage systems organized in hierarchy Speed Cost Volatility Caching – copying information into faster storage system; main memory can be viewed as a cache for secondary storage Device Driver for each device controller to manage I/O Provides uniform interface between controller and kernel
- 13. Computer-System Architecture Most systems use a single general-purpose processor Most systems have special-purpose processors as well Multiprocessors systems growing in use and importance Also known as parallel systems, tightly-coupled systems Advantages include: 1. Increased throughput 2. Economy of scale 3. Increased reliability – graceful degradation or fault tolerance Two types: 1. Asymmetric Multiprocessing – each processor is assigned a specie task. 2. Symmetric Multiprocessing – each processor performs all tasks
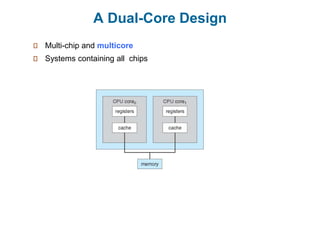
- 15. A Dual-Core Design Multi-chip and multicore Systems containing all chips
- 16. Review Computer System Operations Interrupts Storage Hierarchy Computer Architecture Agenda Protection Computing Environments
- 17. Protection and Security Protection – any mechanism for controlling access of processes or users to resources defined by the OS Security – defense of the system against internal and external attacks Huge range, including denial-of-service, worms, viruses, identity theft, theft of service Systems generally first distinguish among users, to determine who can do what User identities (user IDs, security IDs) include name and associated number, one per user User ID then associated with all files, processes of that user to determine access control Group identifier (group ID) allows set of users to be defined and controls managed, then also associated with each process, file
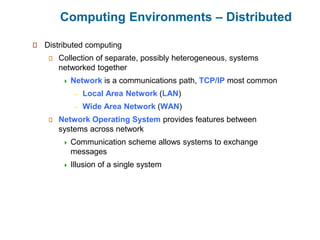
- 18. Computing Environments – Distributed Distributed computing Collection of separate, possibly heterogeneous, systems networked together Network is a communications path, TCP/IP most common – Local Area Network (LAN) – Wide Area Network (WAN) Network Operating System provides features between systems across network Communication scheme allows systems to exchange messages Illusion of a single system
- 19. Computing Environments – Client-Server Client-Server Computing Many systems now servers, responding to requests generated by clients
- 20. Computing Environments - Virtualization
- 21. Computing Environments – Cloud Computing Delivers computing, storage, even apps as a service across a network Logical extension of virtualization because it uses virtualization as the base for it functionality. Many types Public cloud – available via Internet to anyone willing to pay Private cloud – run by a company for the company’s own use Hybrid cloud – includes both public and private cloud components Software as a Service (SaaS) – one or more applications available via the Internet (i.e., word processor) Platform as a Service (PaaS) – software stack ready for application use via the Internet (i.e., a database server) Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) – servers or storage available over Internet (i.e., storage available for backup use)
- 22. Computing Environments – Real-Time Embedded Systems Real-time embedded systems most prevalent form of computers Vary considerable, special purpose, limited purpose OS, real-time OS Use expanding Real-time OS has well-defined fixed time constraints Processing must be done within constraint Correct operation only if constraints met
- 23. Open-Source Operating Systems Operating systems made available in source-code format rather than just binary closed-source Counter to the copy protection and Digital Rights Management (DRM) movement Started by Free Software Foundation (FSF), which has “copyleft” GNU Public License (GPL) Examples include GNU/Linux and BSD UNIX (including core of Mac OS X), and many more Can use VMM like VMware Player (Free on Windows), Virtualbox (open source and free on many platforms - http://www.virtualbox.com) Use to run guest operating systems for exploration