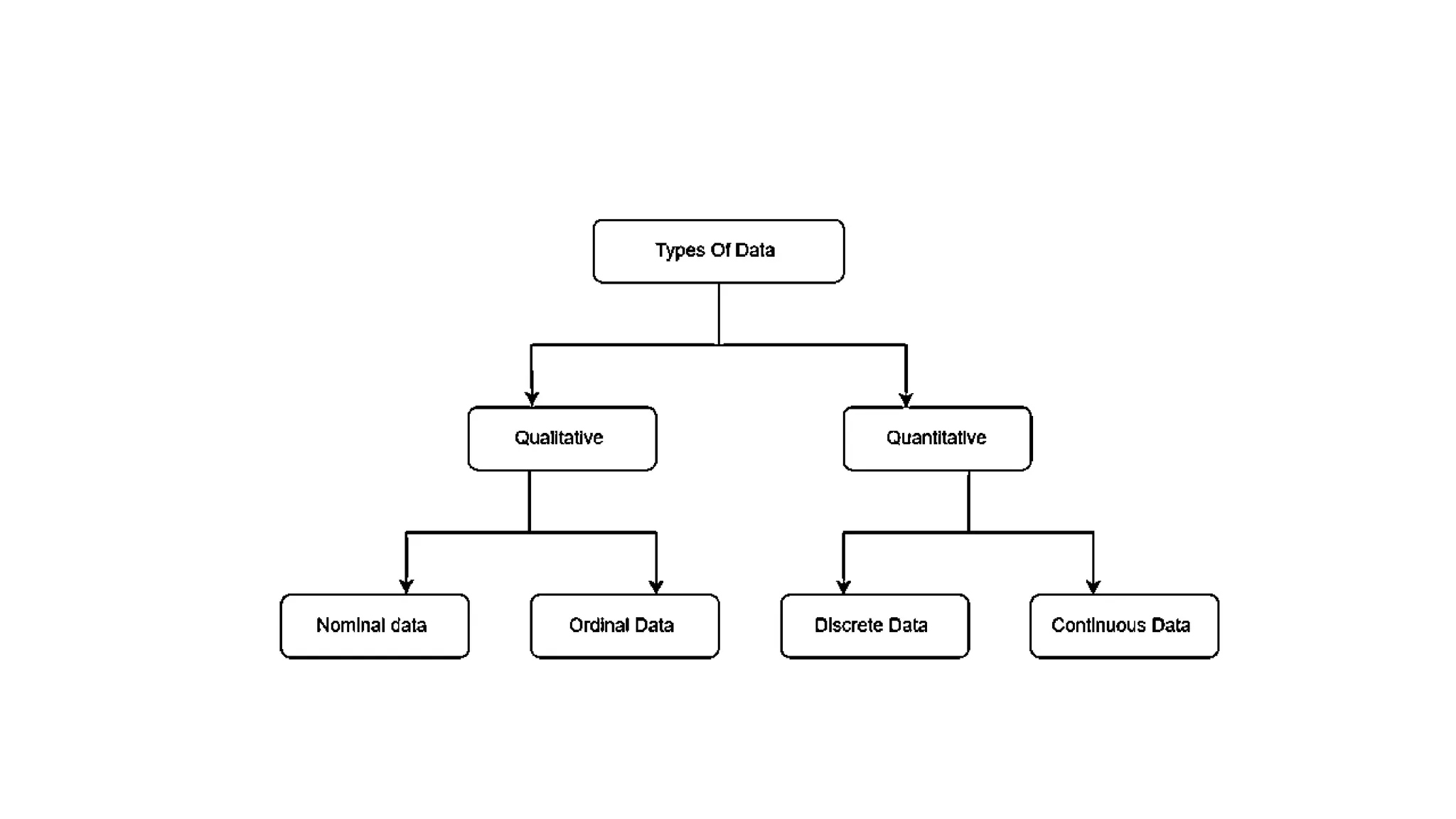
The document outlines the principles and tools of business analytics, emphasizing the transformation of data into insights for improved decision-making through methods like data management, visualization, and predictive modeling. It categorizes data types and illustrates the importance of data visualization in making information accessible and understandable for diverse audiences. Additionally, it lists various data visualization tools and types, highlighting their role in exploring data relationships and driving informed decisions.