Introduction to HBase - NoSqlNow2015
- 1. 1© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Apache HBase: Overview, Hands-‐On, and Use Cases Apekshit Sharma Dima Spivak
- 2. 2© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Apekshit Sharma • Distributed Software Engineer, Cloudera • Software Engineer, Google • Apache HBase contributor • Performance improvements and configuration framework Dima Spivak (@dimaspivak) • Distributed Software Engineer, Cloudera • Research Assistant (Physics), University of Minnesota • Apache HBase contributor • Test frameworks and automation Who we are
- 3. 3© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Contents • Motivation • Introduction to Apache HBase • Data model • Hands-‐On: Installation, HBase shell • Break • A slightly more in-‐depth introduction to Apache HBase • Apache Hadoop • System internals • APIs • Break
- 4. 4© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Contents • Industry use cases & patterns • Augmenting HBase • OpenTSDB • Apache Phoenix
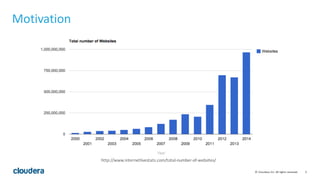
- 5. 5© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Motivation http://www.internetlivestats.com/total-‐number-‐of-‐websites/
- 6. 6© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Motivation “We've known it for a long time: the web is big.” – Jesse Alpert & Nissan Hajaj, Google http://googleblog.blogspot.com/2008/07/we-‐knew-‐web-‐was-‐big.html
- 7. 7© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Motivation • Indexing the internet has challenges: • Scale • Volume • Rate • Diversity of content • URLs • High-‐resolution images • Video • Access
- 8. 8© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Motivation
- 9. 9© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. • What if you’re not trying to index the internet? Motivation
- 10. 10© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. • Data for analytical processing • User-‐facing real-‐time platforms Motivation
- 11. 11© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Introduction to Apache HBase •“Apache HBase™ is the Hadoop database, a distributed, scalable, big data store.” http://hbase.apache.org/
- 12. 12© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Introduction to Apache HBase •Apache HBase is an open source, horizontally scalable, consistent, random access, low latency data store built on top of Apache Hadoop.
- 13. 13© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Apache HBase is open source • Apache 2.0 License • A community project with committers and contributors from diverse organizations • Cloudera, Facebook, Salesforce.com, Huawei, TrendMicro, eBay, HortonWorks, Intel, Twitter, … • Code license means anyone can modify and use the code.
- 14. 14© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. • Adding more servers linearly increases performance and capacity • Storage capacity • Input/output operations • Store and access data on commodity servers • Largest cluster: > 3000 nodes, > 100 PB • Average cluster: 10-‐40 nodes, 100-‐400TB Apache HBase is horizontally scalable 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 Performance (IOPs/Storage/Throughput) # of servers
- 15. 15© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. • Commodity servers (crica 2015) • 12-‐24 2-‐4TB hard disks • 2 octa-‐core CPUs, 2-‐3 GHz • 64 -‐ 512 GBs of RAM • 10 Gbps ethernet • $5,000 -‐ $10,000 / machine Apache HBase is horizontally scalable
- 16. 16© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. •Brewer’s theorem •Consistency •Availability •Partition tolerance Apache HBase is consistent HBase
- 17. 17© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Data model • Data is stored… in a big table • Sorted map datastore • Tables consist of sorted rows, each of which has a primary row key • Each row has a set of columns • A column is specified as a column family and column qualifier pair • A given cell (row, column family:column qualifier) can have different time-‐ stamped values
- 18. 18© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Data model Row key info:height info:state roles:hadoop roles:hbase cutting ‘9ft’ ‘CA’ ‘Founder’ todd ‘5ft7’ ‘CA’ ‘PMC’ (ts=2011) ‘Committer’ (ts=2010) ‘Committer’
- 19. 19© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Hands On Apache HBase installation The HBase shell http://pastebin.com/nMkZeq5S
- 20. 20© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Whats up for the next 1 hour? Understanding basic architecture of HDFS (Apache Hadoop) And, more Hands-‐On with Apache HBase.
- 21. 21© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Break
- 22. 22© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Understanding basic architecture of Hadoop (HDFS)
- 23. 23© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Apache Hadoop open source commodity servers horizontally scalable highly fault-‐tolerant massive processing power
- 24. 24© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Apache Hadoop MapReduce + YARN 2 Core Components HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System)
- 25. 25© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. History 2003
- 26. 26© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. • distributed file system • commodity servers • horizontally scalable • highly fault-‐tolerant • proprietary GFS
- 27. 27© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. • distributed file system • commodity servers • horizontally scalable • highly fault-‐tolerant • open source HDFS
- 28. 28© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. HDFS API • File • Open, Close, Read, Write, Move, etc • Directories • Create, Delete, etc • Permissions • Owners, Groups, rwx permissions
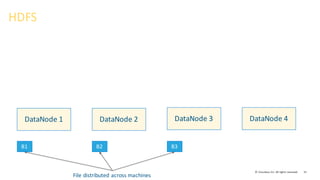
- 29. 29© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Basic Architecture of HDFS
- 30. 30© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. File B1 B2 B3 File system will split the file into blocks DiskB1 B2 B3 Local file system
- 31. 31© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. DataNode 1 DataNode 2 DataNode 3 DataNode 4 HDFS File distributed across machines B1 B2 B3
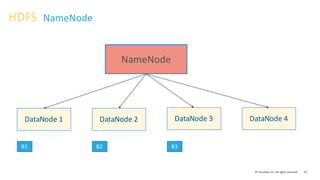
- 32. 32© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. B1 DataNode 1 B2 DataNode 2 B3 DataNode 3 DataNode 4 HDFS DataNode
- 33. 33© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. DataNode 1 DataNode 2 DataNode 3 DataNode 4 HDFS NameNode NameNode B1 B2 B3
- 34. 34© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. DataNode 1 DataNode 2 DataNode 3 DataNode 4 HDFS Reading a file NameNode B1 B2 B3 Client 1. File ‘foo’ 2. Verify client has permissions to read the file 3. List of foo’s bocks and datanodes
- 35. 35© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. DataNode 1 DataNode 2 DataNode 3 DataNode 4 HDFS Fault tolerance NameNode B1 B2 B3
- 36. 36© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. DataNode 1 DataNode 2 DataNode 3 DataNode 4 HDFS Redundancy NameNode B1 B2 B3B1 B1B2 B2 B3B3
- 37. 37© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. DataNode 1 DataNode 2 DataNode 3 DataNode 4 HDFS Horizontal Scalability NameNode B1 B2 B3B1 B1B2 B2 B3B3 DataNode 5
- 38. 38© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Let’s look at some existing HDFS systems...
- 39. 39© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. • Yahoo! HDFS Clusters 40k+ servers, 100k+ CPUs, 450PB data • Facebook HDFS Cluster 15TB new data per day 1200+ machines, 30PB in one cluster • Lots of 5-‐40 node clusters at companies without petabytes of data (web, retail, finance, telecom, research, government)
- 40. 40© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. But…. there are restrictions! It’s not a magic wand!
- 41. 41© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Files are append only • Access Model : Write-‐once-‐read-‐many • Can not change existing contents
- 42. 42© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Not designed for small files • Block sizes are in MB (default 128MB) • Designed for typical GBs / TBs of file sizes • Normal files system have 4kb block size!
- 43. 43© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Summary HDFS is a great distributed file system! • Store massive data • Scalable • High throughput • Fault tolerance
- 44. 44© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. MapReduce • Distributed processing framework • Commodity machines • Fault tolerance
- 45. 45© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. MapReduce Input Data Input 4 Input 3 Input 2 Input 1 Map1 Map2 Map3 Map4 Reduce1 Reduce2 Reduce3 Output 1 Output 2 Output 2 Output Data
- 46. 46© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 47. 47© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. HBase Architecture Name Weight UPC Price Prego Tomato Sauce 67 Oz xxxxxxxx $4.97 Trumoo Lowfat Chocolate Milk 128 Oz xxxxxxxx $2.99 Gatorade Lemon-‐Lime 64 Oz xxxxxxxx $3.98 info:weight info:upc info:price Prego Tomato Sauce 67 Oz xxxxxxxx $4.97 Trumoo Lowfat Chocolate Milk 128 Oz xxxxxxxx $2.99 Gatorade Lemon-‐Lime 64 Oz xxxxxxxx $3.98
- 48. 48© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. HBase Architecture info:weight info:upc info:price Prego Tomato Sauce 67 Oz xxxxxxxx $4.97 Trumoo Lowfat Chocolate Milk 128 Oz xxxxxxxx $2.99 Gatorade Lemon-‐Lime 64 Oz xxxxxxxx $3.98
- 49. 49© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. HBase Architecture info:weight info:upc info:price Prego Tomato Sauce 67 Oz xxxxxxxx $4.97 Trumoo Lowfat Chocolate Milk 128 Oz xxxxxxxx $2.99 Gatorade Lemon-‐Lime 64 Oz xxxxxxxx $3.98 A New Product 4 Oz xxxxxxxx $9.99
- 50. 50© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. HBase Architecture info:weight info:upc info:price Prego Tomato Sauce 67 Oz xxxxxxxx $4.97 Trumoo Lowfat Chocolate Milk 128 Oz xxxxxxxx $2.99 Gatorade Lemon-‐Lime 64 Oz xxxxxxxx $3.98 A New Product 4 Oz xxxxxxxx $9.99 Yet Another New Product 8 Oz xxxxxxxx $19.99
- 51. 51© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. HBase Architecture info:weight info:upc info:price Prego Tomato Sauce 67 Oz xxxxxxxx $4.97 Trumoo Lowfat Chocolate Milk 128 Oz xxxxxxxx $2.99 Gatorade Lemon-‐Lime 64 Oz xxxxxxxx $3.98 A New Product 4 Oz xxxxxxxx $9.99 Yet Another New Product 8 Oz xxxxxxxx $19.99 Four More Products (1) 16 Oz xxxxxxxx $9.99 Four More Products (2) 16 Oz xxxxxxxx $9.99 Four More Products (3) 16 Oz xxxxxxxx $9.99 Four More Products (4) 16 Oz xxxxxxxx $9.99
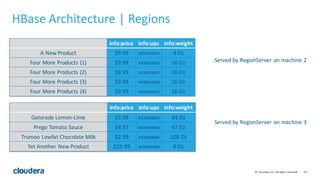
- 52. 52© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. HBase Architecture | Regions • Tables are chopped up into regions (split). • A region is only served by a single “region server” at a time. • RegionServer can serve multiple regions.
- 53. 53© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. HBase Architecture | Regions info:weight info:upc info:price Prego Tomato Sauce 67 Oz xxxxxxxx $4.97 Trumoo Lowfat Chocolate Milk 128 Oz xxxxxxxx $2.99 Gatorade Lemon-‐Lime 64 Oz xxxxxxxx $3.98 Yet Another New Product 8 Oz xxxxxxxx $19.99 info:weight info:upc info:price A New Product 4 Oz xxxxxxxx $9.99 Four More Products (1) 16 Oz xxxxxxxx $9.99 Four More Products (2) 16 Oz xxxxxxxx $9.99 Four More Products (3) 16 Oz xxxxxxxx $9.99 Four More Products (4) 16 Oz xxxxxxxx $9.99 Served by RegionServer on machine 2 Served by RegionServer on machine 3
- 54. 54© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. HBase Architecture | Regions info:price info:upc info:weight Gatorade Lemon-‐Lime $3.98 xxxxxxxx 64 Oz Prego Tomato Sauce $4.97 xxxxxxxx 67 Oz Trumoo Lowfat Chocolate Milk $2.99 xxxxxxxx 128 Oz Yet Another New Product $19.99 xxxxxxxx 8 Oz info:price info:upc info:weight A New Product $9.99 xxxxxxxx 4 Oz Four More Products (1) $9.99 xxxxxxxx 16 Oz Four More Products (2) $9.99 xxxxxxxx 16 Oz Four More Products (3) $9.99 xxxxxxxx 16 Oz Four More Products (4) $9.99 xxxxxxxx 16 Oz Served by RegionServer on machine 2 Served by RegionServer on machine 3
- 55. 55© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. HBase Architecture info:price info:upc info:weight available:store1 available:store2 available:store3 Gatorade Lemon-‐Lime $3.98 xxxxxxxx 64 Oz Yes Yes Yes Prego Tomato Sauce $4.97 xxxxxxxx 67 Oz Yes No Yes Trumoo Lowfat Chocolate Milk $2.99 xxxxxxxx 128 Oz No No Yes Yet Another New Product $19.99 xxxxxxxx 8 Oz Yes Yes Yes info:price info:upc info:weight available:store1 available:store2 available:store3 A New Product $9.99 xxxxxxxx 4 Oz Yes Yes Yes Four More Products (1) $9.99 xxxxxxxx 16 Oz Yes Yes Yes Four More Products (2) $9.99 xxxxxxxx 16 Oz Yes Yes No Four More Products (3) $9.99 xxxxxxxx 16 Oz Yes Yes No Four More Products (4) $9.99 xxxxxxxx 16 Oz No No No
- 56. 56© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. HBase Architecture info:price info:upc info:weight available:store1 available:store2 available:store3 Gatorade Lemon-‐Lime $3.98 xxxxxxxx 64 Oz Yes Yes Yes Prego Tomato Sauce $4.97 xxxxxxxx 67 Oz Yes No Yes Trumoo Lowfat Chocolate Milk $2.99 xxxxxxxx 128 Oz No No Yes Yet Another New Product $19.99 xxxxxxxx 8 Oz Yes Yes Yes info:price info:upc info:weight available:store1 available:store2 available:store3 A New Product $9.99 xxxxxxxx 4 Oz Yes Yes Yes Four More Products (1) $9.99 xxxxxxxx 16 Oz Yes Yes Yes Four More Products (2) $9.99 xxxxxxxx 16 Oz Yes Yes No Four More Products (3) $9.99 xxxxxxxx 16 Oz Yes Yes No Four More Products (4) $9.99 xxxxxxxx 16 Oz No No No
- 57. 57© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. HBase Architecture | Column family • A column family is a set of related columns. • Group sets of columns that have similar access patterns. • Tune read performance. • Compression • Version retention policies • Cache priority
- 58. 58© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. HBase Architecture info: price info: upc info: weight Gatorade Lemon-‐Lime $3.98 xxxxxxx x 64 Oz Prego Tomato Sauce $4.97 xxxxxxx x 67 Oz Trumoo Lowfat Chocolate Milk $2.99 xxxxxxx x 128 Oz available: store1 available: store2 available: store3 Gatorade Lemon-‐Lime Yes Yes Yes Prego Tomato Sauce Yes No Yes Trumoo Lowfat Chocolate Milk No No Yes Region Store Store
- 59. 59© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. HBase Architecture | Write Path 1. Client creates a row to put. 2. Client checks with meta* for which RegionServer hosts this row. 3. Row is written into write-‐ahead log (WAL). 4. Row is written to MemStore.
- 60. 60© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. HBase Architecture | Write Path Put Client: Which RegionServer should host this row? meta: RegionServer 2
- 61. 61© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. HBase Architecture | Write Path Region RegionServer 2 Put MemStore WAL Store MemStore Store
- 62. 62© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. HBase Architecture | Write Path • When MemStore gets full or a flush is triggered, contents of MemStore are flushed to disk. • HFiles are created.
- 63. 63© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. HBase Architecture | Write Path Region RegionServer 2 MemStore WAL Store MemStore Store HFiles HFiles
- 64. 64© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. HBase Architecture | Write Path • Each subsequent write repeats this process. • Write to WAL. • Write to MemStore. • Flush when MemStore fills or a flush is triggered. • Create HFiles. • Lots of HFiles in a Region mean lots of disk seeks on read. • Might be better to combine (compact) HFiles.
- 65. 65© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. HBase Architecture Region RegionServer 2 MemStore Store MemStore Store HFiles HFiles
- 66. 66© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. HBase Architecture | Compactions • Minor compactions • Merge some HFiles (in a given Store). • Major compactions • Merge all HFiles (in a given Store). • Take care of other HBase housekeeping tasks.
- 67. 67© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. HBase Architecture | Compaction Region RegionServer 2 MemStore Store MemStore Store HFiles HFiles
- 68. 68© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. HBase Architecture | Minor compaction Region RegionServer 2 MemStore Store MemStore Store HFiles HFiles
- 69. 69© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. HBase Architecture | Major compaction Region RegionServer 2 MemStore Store MemStore Store HFiles HFiles
- 70. 70© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. HBase Architecture | Compactions • Minor compactions • Controlled by policy (pluggable). • Major compactions • Automatic (by time) or manually triggered. • Tend to be run during off-‐peak times.
- 71. 71© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. HBase Architecture | Splits • Eventually, Regions become imbalanced. • Some grow to be huge, others remain small. • Leads to disparate load across RegionServers. • In these cases, HBase can split a Region into two. • Each Region is then available to be moved to a different RegionServer, if necessary.
- 72. 72© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. HBase Architecture | Splits Region RegionServer 2
- 73. 73© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. HBase Architecture | Splits Region RegionServer 2 Region RegionServer 3: Yeah! Pick me! Master: RegionServer 2 is really busy… Maybe another RegionServer can handle one of its Regions?
- 74. 74© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. HBase Architecture | APIs • Conventional write path can be accessed through multiple APIs: • Java API • Most full-‐featured. • REST API • Easily accessible. • Thrift API • Support for many languages (e.g. C, C++, Perl, Ruby, Python).
- 75. 75© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. HBase Architecture | APIs • This write path is durable, but if you’re importing a lot of data, it can be problematic… • Every put goes into WAL, which means disk seeks. Lots of puts mean lots of disk seeks. • Lots of data into MemStores means lots of flushing to disk. • Lots of flushing to disk might mean lots of compactions.
- 76. 76© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. HBase Architecture | Bulk Loading • Bypass conventional write path. • Extract data from source. • Transform data into HFiles (done with MapReduce job) directly. • Tell RegionServers to serve these HFiles.
- 77. 77© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Enough of Architecture
- 78. 78© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. What’s up next, Doc? • Break • What have we learned from the users • How can you benefit from that information
- 79. 79© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Break
- 80. 80© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Apache HBase “Nascar” Slide
- 81. 81© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Apache HBase “Nascar” Slide
- 82. 82© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Apache HBase “Nascar” Slide
- 83. 83© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Apache HBase “Nascar” Slide
- 84. 84© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Apache HBase “Nascar” Slide
- 85. 85© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Apache HBase “Nascar” Slide
- 86. 86© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Apache HBase “Nascar” Slide
- 87. 87© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. What have we learned from all these users?
- 88. 88© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. There are some patterns which repeat often. Just like a lego block, maybe you can fit one directly in your system!
- 89. 89© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. ● Entity Data ● Time-‐centric Event Data ● Operational ● Analytical ● Real-‐time vs Batch ● Random vs Sequential Data Use of data How it goes in and out Know your ...
- 90. 90© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Know your data ... There are primarily two kinds of big data workloads. They have different storage requirements. • Entity centric data • Time centric event data
- 91. 91© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. • Scales up with # of entities • Billions of distinct entities Entity centric data Users Accounts Location Clicks and Metrics Sensor Data
- 92. 92© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. • Time-‐series data points over a period • Scales up due to finer grained intervals, retention policies, and the passage of time Time centric event data Periodic Sensor DataStock Ticker Data Monitoring applications
- 93. 93© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Time Entities Now e1 e2 e3 e5 e4
- 94. 94© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Time Now Entities data Entities data Millions of entities = Big Data e1 e2 e3 e5 e4 Entities
- 95. 95© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Time Now Time-‐centric events data Time centric events data Millions of events = Big Data
- 96. 96© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Time Now Time-‐centric events about Entities e1 e2 e3 e5 e4 Entities |Entities| * |Events| = Really Big Data
- 97. 97© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. What questions do you ask? • Do you focus in on entity first? OR • Do you focus in on time ranges first? • Your answer will help you determine where and how to store your data.
- 98. 98© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Time Now Entity first questions… For a give user, show all the messages. Entities user1 user2 user3 user4 user5
- 99. 99© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Entity first questions… For a given user, show the last message. Time Now Entities user1 user2 user3 user4 user5
- 100. 100© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Entity first questions… For a give user, show last N messages. Time Now Entities user1 user2 user3 user4 user5
- 101. 101© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Entity first questions… T1 T2 For a give user, show all messages received between time [t1, t2]. Entities Time Now Entities user1 user2 user3 user4 user5
- 102. 102© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Time centric event first questions… T1 T2 Find all messages between time [t1, t2]. Time Now Entities user1 user2 user3 user4 user5
- 103. 103© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Time centric event first questions… T1 T2 Find all messages between time [t1, t2] for all users. Time Time Now Entities user1 user2 user3 user4 user5
- 104. 104© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. How does the data get in and out of HBase?
- 105. 105© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Getting data in... Apache HBase Put, Incr, Append Bulk Import
- 106. 106© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Getting data out... Apache HBase Get, Short Scans Full scan
- 107. 107© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. So, what’s the best way?
- 108. 108© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Depends on your use case Bottom-‐line: Disk I/O takes times. - Limited disk read-‐write heads in a cluster - Use the I/O bandwidth of your cluster efficiently
- 109. 109© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Apache HBase Put, Incr, Append Bulk Import Get, Short Scans Full scan Real-‐time Batch
- 110. 110© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Let’s dive into use case ...
- 111. 111© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Simple Entities • Purely entity data, no relation between entities • Often from many different sources • Could be a well-‐done de-‐normalized RDBMS port Time Now e1 e2 e3 e5 e4 Entities
- 112. 112© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Simple Entities : Schema • Row per entity • Row key => entity ID, or hash of entity ID • Column => Property / field, possibly timestamp
- 113. 113© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Simple Entities : Example OCLC : Online Computer Library Center Workloads: • Lookup books à Real time read • Add new book one at a time, update information about existing books, issue books à Real-‐time write • New library joins the group, import its data à Batch write
- 114. 114© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Simple Entities : Access Pattern • Access Patterns • Writes : Batch / Real-‐time • Reads: Real-‐time Apache HBase Put, Incr, Append Bulk Import Get, Short ScansReal-‐time Batch
- 115. 115© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Linked Entities (Graph Data) • Entity are linked to form a graph Time Now e1 e2 e3 e5 e4 Entities
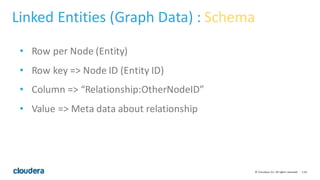
- 116. 116© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Linked Entities (Graph Data) : Schema • Row per Node (Entity) • Row key => Node ID (Entity ID) • Column => “Relationship:OtherNodeID” • Value => Meta data about relationship
- 117. 117© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Linked Entities (Graph Data) : Example Social Network (Facebook) Workloads: • Get any info about a user à Real time read • Update any info about a user à Real time write • Limited graph analysis (based on immediate friends) à Batch read
- 118. 118© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Linked Entities (Graph Data) : Access Pattern • Access Patterns • Reads: Real-‐time or Batch • Writes: Real-‐time Apache HBase Put, Incr, Append Get, Short Scans Full scan Real-‐time Batch
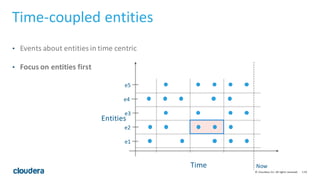
- 119. 119© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Time-‐coupled entities • Events about entities in time centric • Focus on entities first Time Now e1 e2 e3 e5 e4 Entities
- 120. 120© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Time-‐coupled entities : Schema • Row = Entity’s events in a time slice • Row key = Entity ID + (time / k) • Column Qualifier = timestamp
- 121. 121© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Time-‐coupled entities: Example Messaging service Primary Workload • Sending a message, update metadata (read, star, move, delete) à Real-‐time write • Reading a message, get last N messages à Real-‐time read
- 122. 122© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Time-‐coupled entities : Access Pattern • Access Pattern • Writes: Real-‐time • Reads: Real-‐time Apache HBase Put, Incr, Append Get, Short ScansReal-‐time Batch
- 123. 123© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. HBase is great! But not for everything ...
- 124. 124© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Current HBase weak spots • HBase architecture can handle a lot • Engineering tradeoffs optimize for some use cases • HBase can still do things it is not optimal for • Other systems are fundamentally more efficient for some workloads • Just because it is not good today, doesn’t mean it can’t be better tomorrow!
- 125. 125© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. A not so good use case: Large Blob Store • Saving large objects >50 MB per cell • Examples • Raw video storage in HBase • Problems: • Write amplification when re-‐optimizing data for read (compactions on large unchanging data) • New: Medium Object (MOB) supported (lots of 100KB-‐10MB cells)
- 126. 126© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Another not good use case: Analytic archive • Store data chronologically, time as primary index • Row key = timestamp • Real time writes • Column-‐centric aggregations over all rows • Schema • Row key: timestamp • Column qualifiers: properties with data or counters • Example • Machine logs organized by timestamp (causes write hot-‐spotting)
- 127. 127© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Summary • HBase is used widely across industry • Few patterns learnt from these users • Understanding • Data : Entity and time-‐centric events • Questions you ask from your data • How does data gets in and out • When not to use HBase
- 128. 128© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Scalable time series database
- 129. 129© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Time-‐Series Data points for entities over time
- 130. 130© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. • Store trillions of data points • Millisecond precision • Keep raw data forever • Scales to millions of writes per sec • Generate graphs from GUI OpenTSDB
- 131. 131© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. • Store trillions of data points • Millisecond precision • Keep raw data forever • Scales to millions of writes per sec • Generate graphs from GUI OpenTSDB
- 132. 132© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. OpenTSDB : Use Cases • System Monitoring • Servers • Network • Sensor Data • Stock market data
- 133. 133© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. OpenTSDB : Example OVH • Large cloud/hosting provider • Monitor everything: networking, temperature, voltage, application performance, resource utilization, customer-‐facing metrics, etc. • 35 servers, 100k writes/s, 25TB raw data Yahoo! • Monitoring application performance and statistics • 15 servers, 280k writes/s Source: http://www.slideshare.net/HBaseCon/ecosystem-‐session-‐6
- 134. 134© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. OpenTSDB : Datapoints • In OpenTSDB, there are • Metric • Timestamp • Value • Tags (key-‐value pairs) : to identify the entity
- 135. 135© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. OpenTSDB : Datapoints example • E.g. 10 servers handling requests web requets • Metric: num_requests_per_second • Tags: “host=web-‐server-‐1”, “host=web-‐server-‐2”, and so on • Example data points • num_requests_per_second 1439828251 50 host=web-‐server-‐1 • num_requests_per_second 1439828251 72 host=web-‐server-‐2 • num_requests_per_second 1439828252 30 host=web-‐server-‐3 • …so on
- 136. 136© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. OpenTSDB : How it works Image source: http://opentsdb.net/overview.html Sensor1 Sensor2 SensorN………….. TSD TSD HBase OpenTSDB
- 137. 137© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. OpenTSDB : Writing data • Telnet • put <metric> <timestamp> <value> <tagk1=tagv1[ tagk2=tagv2 ...tagkN=tagvN]> • Example: put num_requests_per_second 1439828251 50 host=web-‐server-‐1 • HTTP API • <host>:<port>/api/put • JSON objects containing data points • Bulk Import • Using ‘import’ CLI utility
- 138. 138© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. OpenTSDB : Reading data • OpenTSDB GUI • Select metrics and tags to generate graphs • HTTP API • <host>:<port>/api/query
- 139. 139© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. OpenTSDB : Storing data – row key • Row key is a concatenation of metric, timestamp and tags • num_requests_per_second1439827200host=web-‐server-‐1 • Since data is stored in sorted order, chunking happens in this order 1. Metric • Enables fast scan of all time series for a metric 2. Time • Normalized on 1 hour boundaries • All data points for an hour are stored in a single row 3. Tags
- 140. 140© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. OpenTSDB : Storing data – column • Offset from timestamp in row key • Example • num_requests_per_second1439828251 50 host=web-‐server-‐1 • num_requests_per_second1439828251 72 host=web-‐server-‐2 • num_requests_per_second1439828252 30 host=web-‐server-‐3 Row key Data:1051 Data:1052 num_requests_per_second1439827200host=web-‐server-‐1 50 num_requests_per_second1439827200host=web-‐server-‐2 72 num_requests_per_second1439827200host=web-‐server-‐3 30
- 141. 141© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. OpenTSDB : GUI
- 142. 142© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. • High performance relational database layer over HBase for low-‐ latency applications • JDBC API
- 143. 143© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Phoenix : Use Case Scalability of HBase + SQL interface access
- 144. 144© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Phoenix • Provides typed access to data • Provides secondary indexes • Compiles SQL queries to native HBase scans • Executes scans parallely • Directly uses HBase API, server-‐side hooks and custom filters • Brings computation to the data • Pushes where clause to server-‐side filter • Executes aggregate queries using server-‐side hooks
- 145. 145© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. That’s it folks!
- 146. 146© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved.10/17/14 Strata+Hadoop world 2014. George and Hsieh Try Hadoop Now cloudera.com/live
- 147. 147© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved.10/17/14 Strata+Hadoop world 2014. George and Hsieh Join the Discussion Get community help or provide feedback cloudera.com/community
- 148. 148© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Sources • A Survey of HBase Application Archetypes • Lars George, Jon Hsieh • http://www.slideshare.net/HBaseCon/case-‐studies-‐session-‐7 • OpenTSDB 2.0 • Benoit Sigoure, Chris Larsen • http://www.slideshare.net/HBaseCon/ecosystem-‐session-‐6 • Hadoop and HBase: Motivations, Use cases and Trade-‐offs • Jon Hsieh • Phoenix • https://phoenix.apache.org
- 149. 149© Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved. Questions ?

































































































![101©
Cloudera,
Inc.
All
rights
reserved.
Entity
first
questions…
T1 T2
For
a
give
user,
show
all
messages
received
between
time
[t1,
t2].
Entities
Time
Now
Entities
user1
user2
user3
user4
user5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nosqlnowdeck-151029235427-lva1-app6891/85/Introduction-to-HBase-NoSqlNow2015-101-320.jpg)
![102©
Cloudera,
Inc.
All
rights
reserved.
Time
centric
event
first
questions…
T1 T2
Find
all
messages
between
time
[t1,
t2].
Time
Now
Entities
user1
user2
user3
user4
user5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nosqlnowdeck-151029235427-lva1-app6891/85/Introduction-to-HBase-NoSqlNow2015-102-320.jpg)
![103©
Cloudera,
Inc.
All
rights
reserved.
Time
centric
event
first
questions…
T1 T2
Find
all
messages
between
time
[t1,
t2]
for
all
users.
Time
Time
Now
Entities
user1
user2
user3
user4
user5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nosqlnowdeck-151029235427-lva1-app6891/85/Introduction-to-HBase-NoSqlNow2015-103-320.jpg)































![137©
Cloudera,
Inc.
All
rights
reserved.
OpenTSDB :
Writing
data
• Telnet
• put
<metric>
<timestamp>
<value>
<tagk1=tagv1[
tagk2=tagv2
...tagkN=tagvN]>
• Example:
put
num_requests_per_second 1439828251
50
host=web-‐server-‐1
• HTTP
API
• <host>:<port>/api/put
• JSON
objects
containing
data
points
• Bulk
Import
• Using
‘import’
CLI
utility](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nosqlnowdeck-151029235427-lva1-app6891/85/Introduction-to-HBase-NoSqlNow2015-137-320.jpg)











