Introduction to System, Simulation and Model
- 2. Introduction To System, Simulation and Model Presentation Title
- 3. Group Member Md. Mahbubur Rahman| SID: 182-15-11742 Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Email: [email protected] Daffodil International University, Dhaka, Bangladesh. Aysha Siddika | SID: 182-15-11639 Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Email: [email protected] Daffodil International University, Dhaka, Bangladesh. Md. Hasan Imam Bijoy | SID: 182-15-11743 Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Email: [email protected] Daffodil International University, Dhaka, Bangladesh.
- 4. Presentation Outline 1 What is System? 2 Component of System 4 Concept of Simulation 1 Concept of Model 5 Types of Simulation 6 Workflow of Simulation 7 Advantages 9 Application of Simulation 8 Disadvantages
- 5. System A system is a simplified representation of reality. System defined as a group of objects that are joined together in some regular interaction or interdependence toward the accomplishment of some purpose Whereas in the real world, a "system" may seem at times an endless series of connected elements. We refer here to a system as A series of selected, chosen elements (this is a first simplification, and thus an implicit assumption) Specified boundaries (a second simplification and implicit assumption) Pre-determined time characteristics (with a third simplification and implicit assumption).
- 6. Component of System Entity : an object of interest in the system. Attribute : a property of an entity. Activity : a time period of specified length. State : the collection of variables necessary to describe the system at any time, relative to the objectives of the study. Event : an instantaneous occurrence that may change the state of the system. Endogenous : to describe activities and events occurring within a system. Exogenous : to describe activities and events in an environment that affect the system.
- 7. Components of Banking System State Variable - Number of Busy tellers - Number of Customer Waiting Attributes - Checking Account Balance Entity - Customer or Client Activates - Making Deposits Event: Arrival and Departure Banking System
- 8. Type of System Continuous Continuous Simulation refers to a computer model of a physical system that continuously tracks system response according to a set of equations typically involving differential equations. Discrete Discrete event simulation (DES) is a method used to model real world systems that can be decomposed into a set of logically separate processes that autonomously progress through time. Time Heat of Water Time Banking Queue
- 9. Model in Simulation A representation of a system for the purpose of studying the system Sufficiently detailed to permit valid conclusions to be drawn about the real system A simplification of the system Model in Simulation
- 10. Types of Model Model Static or Dynamic • Static simulation model (called Monte Carlo simulation) represents a system at a particular point in time. • Dynamic simulation model represents systems as they change over time Determinic or Stochastic • Deterministic simulation models contain no random variables and have a known set of inputs which will result in a unique set of outputs • Stochastic simulation model has one or more random variables as inputs. Random inputs lead to random outputs. The model of interest in this class is discrete, dynamic, and stochastic.
- 11. Simulation A simulation is the imitation of the operation of a real-world process or system over time. whereas the simulation represents the evolution of the model over time. Simulations require the use of models; the model represents the key characteristics or behaviors of the selected system or process Simulation
- 12. Types of Simulation Simulation System Dynamics Simulation This is a very abstract form of simulation modeling. Unlike agent-based modeling and discrete event modeling, system dynamics does not include specific details about the system. Agent-Based Modeling & Simulation An agent-based simulation is a model that examines the impact of an ‘agent’ on the ‘system’ or ‘environment.’ In simple terms, just think of the impact a new laser-cutter or some other factory equipment has on your overall manufacturing line. Monte Carlo Monte Carlo simulation is a method of risk analysis. Businesses use it prior to implementing a major project or change in a process, such as a manufacturing assembly line. Discrete Event Simulation A discrete event simulation model enables our to observe the specific events that result in our business processes. We would use a discrete event simulation model to examine that technical support process
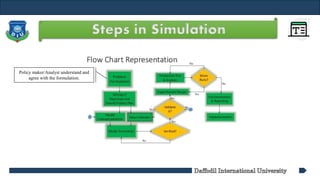
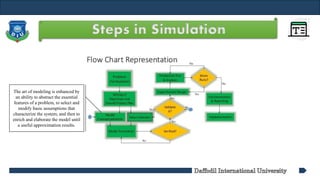
- 13. Steps in Simulation Policy maker/Analyst understand and agree with the formulation.
- 14. Steps in Simulation Setting of objectives and overall project plan
- 15. Steps in Simulation The art of modeling is enhanced by an ability to abstract the essential features of a problem, to select and modify basic assumptions that characterize the system, and then to enrich and elaborate the model until a useful approximation results.
- 16. Steps in Simulation As the complexity of the model changes, the required data elements may also change
- 17. Steps in Simulation GPSS/HTM or special-purpose simulation software
- 18. Steps in Simulation Is the computer program performing properly? Debugging for correct input parameters and logical structure
- 19. Steps in Simulation The determination that a model is an accurate representation of the real system. Validation is achieved through the calibration of the model
- 20. Steps in Simulation The decision on the length of the initialization period, the length of simulation runs, and the number of replications to be made of each run.
- 21. Steps in Simulation To estimate measures of performances
- 22. Steps in Simulation Decision to more Runs
- 23. Steps in Simulation Program documentation : for the relationships between input parameters and output measures of performance, and for a modification Progress documentation : the history of a simulation, a chronology of work done and decision made.
- 24. Steps in Simulation Implementation of Programs
- 25. Advantages New polices, operating procedures, decision rules, information flows, organizational procedures, and so on can be explored without disrupting ongoing operations of the real system. New hardware designs, physical layouts, transportation systems, and so on, can be tested without committing resources for their acquisition. Hypotheses about how or why certain phenomena occur can be tested for feasibility. Insight can be obtained about the interaction of variables. Insight can be obtained about the importance of variables to the performance of the system. Bottleneck analysis can be performed indicating where work-in-process, information, materials, and so on are being excessively delayed. A simulation study can help in understanding how the system operates rather than how individuals think the system operates. “What-if” questions can be answered. This is particularly useful in the design of new system.
- 26. Disadvantages Model building requires special training. It is an art that is learned over time and through experience. Furthermore, if two models are constructed by two competent individuals, they may have similarities, but it is highly unlikely that they will be the same. Simulation results may be difficult to interpret. Since most simulation outputs are essentially random variables (they are usually based on random inputs), it may be hard to determine whether an observation is a result of system interrelationships or randomness. Simulation modeling and analysis can be time consuming and expensive. Skimping on resources for modeling and analysis may result in a simulation model or analysis that is not sufficient for the task. Simulation is used in some cases when an analytical solution is possible, or even preferable. This might be particularly true in the simulation of some waiting lines where closed-form queueing models are available.
- 27. Area of Application Manufacturing Applications Analysis of electronics assembly operations Design and evaluation of a selective assembly station for high-precision scroll compressor shells Comparison of dispatching rules for semiconductor manufacturing using large-facility models Evaluation of cluster tool throughput for thin-film head production Determining optimal lot size for a semiconductor back-end factory Optimization of cycle time and utilization in semiconductor test manufacturing Analysis of storage and retrieval strategies in a warehouse Investigation of dynamics in a service-oriented supply chain Model for an Army chemical munitions disposal facility Semiconductor Manufacturing Comparison of dispatching rules using large-facility models The corrupting influence of variability A new lot-release rule for wafer fabs
- 28. Area of Application Logistics, Transportation, and Distribution Applications Evaluating the potential benefits of a rail-traffic planning algorithm Evaluating strategies to improve railroad performance Parametric modeling in rail-capacity planning Analysis of passenger flows in an airport terminal Proactive flight-schedule evaluation Logistics issues in autonomous food production systems for extended-duration space exploration Sizing industrial rail-car fleets Product distribution in the newspaper industry Design of a toll plaza Choosing between rental-car locations Quick-response replenishment
- 29. Area of Application Construction Engineering Construction of a dam embankment Trenchless renewal of underground urban infrastructures Activity scheduling in a dynamic, multiproject setting Investigation of the structural steel erection process Special-purpose template for utility tunnel construction Military Application Modeling leadership effects and recruit type in an Army recruiting station Design and test of an intelligent controller for autonomous underwater vehicles Modeling military requirements for nonwarfighting operations Multitrajectory performance for varying scenario sizes Using adaptive agent in U.S Air Force pilot retention
- 30. Area of Application Business Process Simulation Impact of connection bank redesign on airport gate assignment Product development program planning Reconciliation of business and systems modeling Personnel forecasting and strategic workforce planning Human Systems Modeling human performance in complex systems Studying the human element in air traffic control