iOS Session-2
- 1. Session - 2 Presented By: A.T.M. Hassan Uzzaman
- 2. Agendas OOP Concepts in Objective-c Delegates and callbacks in Cocoa touch Table View, Customizing Cells PList (Read, write)
- 3. Obj-C vs C# Obj-C C# [[object method] method]; obj.method().method(); Memory Pools Garbage Collection +/- static/instance nil null (void)methodWithArg:(int)value {} void method(int value) {} YES NO true false @protocol interface
- 4. Classes from Apple (and some history) NSString is a string of text that is immutable. NSMutableString is a string of text that is mutable. NSArray is an array of objects that is immutable. NSMutableArray is an array of objects that is mutable. NSNumber holds a numeric value.
- 5. Objective-C Characteristics and Symbols Written differently from other languages Object communicate with messages—does not “call” a method. @ indicates a compiler directive. Objective-C has own preprocessor that processes @ directives. # indicates a preprocessor directive. Processes any # before it compiles.
- 6. Declare in Header file (.h) Each method will start with either a – or a + symbol. - indicates an instance method (the receiver is an instance) +indicates a class method (the receiver is a class name) Example of a instance method -(IBAction)buttonPressed:(id)sender; Or with one argument -(void)setFillColor:(NSColor*) newFillColor;
- 7. Parts of a Method in a Class Implement the method in the .m file Example: -(IBAction)buttonPressed:(id)sender{ do code here…. } Example 2: -(void) setOutlineColor:(NSColor*) outlineColor{ do code here…. }
- 8. Class Declaration (Interface) Node.h #import <Cocoa/Cocoa.h> @interface Node : NSObject { Node *link; int contents; Class is Node who’s parent is } NSObject +(id)new; { class variables } -(void)setContent:(int)number; -(void)setLink:(Node*)next; -(int)getContent; +/- private/public methods of Class -(Node*)getLink; @end Class variables are private
- 9. Class Definition (Implementation) #import “Node.h” @implementation Node Node.m +(id)new { return [Node alloc];} -(void)setContent:(int)number {contents = number;} -(void)setLink:(Node*)next { [link autorelease]; link = [next retain]; Like your C++ .cpp } file -(int)getContent {return contents;} -(Node*)getLink >>just give the {return link;} methods here @end
- 10. Creating class instances Creating an Object ClassName *object = [[ClassName alloc] init]; ClassName *object = [[ClassName alloc] initWith* ]; NSString* myString = [[NSString alloc] init]; Nested method call. The first is the alloc method called on NSString itself. This is a relatively low-level call which reserves memory and instantiates an object. The second is a call to init on the new object. The init implementation usually does basic setup, such as creating instance variables. The details of that are unknown to you as a client of the class. In some cases, you may use a different version of init which takes input: ClassName *object = [ClassName method_to_create]; NSString* myString = [NSString string]; Some classes may define a special method that will in essence call alloc followed by some kind of init
- 11. Reference [[Person alloc] init];action Person *person = counting in Retain count begins at 1 with +alloc [person retain]; Retain count increases to 2 with -retain [person release]; Retain count decreases to 1 with -release [person release]; Retain count decreases to 0, -dealloc automatically called
- 12. Autorelease Example: returning a newly created object -(NSString *)fullName { NSString *result; result = [[NSString alloc] initWithFormat:@“%@ %@”, firstName, lastName]; [result autorelease] return result; }
- 13. Method Names & Autorelease Methods whose names includes alloc, copy, or new return a retained object that the caller needs to release NSMutableString *string = [[NSMutableString alloc] init]; // We are responsible for calling -release or -autorelease [string autorelease]; All other methods return autoreleased objects NSMutableString *string = [NSMutableString string]; // The method name doesn’t indicate that we need to release it, so don’t This is a convention- follow it in methods you define!
- 14. Polymorphism Just as the fields of a C structure are in a protected namespace, so are an object’s instance variables. Method names are also protected. Unlike the names of C functions, method names aren’t global symbols. The name of a method in one class can’t conflict with method names in other classes; two very different classes can implement identically named methods. Objective-C implements polymorphism of method names, but not parameter or operator overloading.
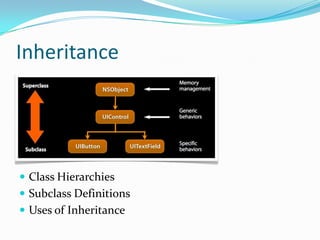
- 15. Inheritance Class Hierarchies Subclass Definitions Uses of Inheritance
- 16. protocol
- 18. Categories
- 21. NSDictionary Immutable hash table. Look up objects using a key to get a value. + (id)dictionaryWithObjects:(NSArray *)values forKeys:(NSArray *)keys; + (id)dictionaryWithObjectsAndKeys:(id)firstObject, ...; Creation example: NSDictionary *base = [NSDictionary dictionaryWithObjectsAndKeys: [NSNumber numberWithInt:2], @“binary”, [NSNumber numberWithInt:16], @“hexadecimal”, nil]; Methods - (int)count; - (id)objectForKey:(id)key; - (NSArray *)allKeys; - (NSArray *)allValues; see documentation (apple.com) for more details
- 22. NSMutableDictionary Changeable + (id)dictionaryWithObjects:(NSArray *)values forKeys:(NSArray *)keys; + (id)dictionaryWithObjectsAndKeys:(id)firstObject, ...; Creation : + (id)dictionary; //creates empty dictionary Methods - (void)setObject:(id)anObject forKey:(id)key; - (void)removeObjectForKey:(id)key; - (void)removeAllObjects; - (void)addEntriesFromDictionary:(NSDictionary *)otherDictionary; see documentation (apple.com) for more details
- 23. We will see this in Property list (plist) practice later A collection of collections Specifically, it is any graph of objects containing only the following classes: NSArray, NSDictionary, NSNumber, NSString, NSDate, NSData Example1 : NSArray is a Property List if all its members are too NSArray of NSString is a Property List NSArray of NSArray as long as those NSArray’s members are Property Lists. Example 2: NSDictionary is one only if all keys and values are too Why define this term? Because the SDK has a number of methods which operate on Property Lists. Usually to read them from somewhere or write them out to somewhere. [plist writeToFile:(NSString *)path atomically:(BOOL)]; // plist is NSArray or NSDictionary
- 24. NSUserDefaults Lightweight storage of Property Lists. an NSDictionary that persists between launches of your application. Not a full-on database, so only store small things like user preferences.
- 25. Use NSError for Most Errors No network connectivity The remote web service may be inaccessible The remote web service may not be able to serve the information you request The data you receive may not match what you were expecting
- 26. Some Methods Pass Errors by Reference
- 27. Exceptions Are Used for Programmer Errors
- 28. Delegates and callbacks in Cocoa touch
- 29. SimpleTable App
- 31. SimpleTable App With Image
- 32. Simple Table App With Diff Image
- 34. Questions ?
- 35. Thank you.



![Obj-C vs C#
Obj-C C#
[[object method] method]; obj.method().method();
Memory Pools Garbage Collection
+/- static/instance
nil null
(void)methodWithArg:(int)value {} void method(int value) {}
YES NO true false
@protocol interface](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ios-session-2-130210214529-phpapp01/85/iOS-Session-2-3-320.jpg)





![Class Definition (Implementation)
#import “Node.h”
@implementation Node Node.m
+(id)new
{ return [Node alloc];}
-(void)setContent:(int)number
{contents = number;}
-(void)setLink:(Node*)next {
[link autorelease];
link = [next retain]; Like your C++ .cpp
} file
-(int)getContent
{return contents;}
-(Node*)getLink >>just give the
{return link;} methods here
@end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ios-session-2-130210214529-phpapp01/85/iOS-Session-2-9-320.jpg)
![Creating class instances
Creating an Object
ClassName *object = [[ClassName alloc] init];
ClassName *object = [[ClassName alloc] initWith* ];
NSString* myString = [[NSString alloc] init];
Nested method call. The first is the alloc method called on NSString itself.
This is a relatively low-level call which reserves memory and instantiates an
object. The second is a call to init on the new object. The init implementation
usually does basic setup, such as creating instance variables. The details of
that are unknown to you as a client of the class. In some cases, you may use a
different version of init which takes input:
ClassName *object = [ClassName method_to_create];
NSString* myString = [NSString string];
Some classes may define a special method that will in essence call alloc followed by some
kind of init](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ios-session-2-130210214529-phpapp01/85/iOS-Session-2-10-320.jpg)
![Reference [[Person alloc] init];action
Person *person =
counting in
Retain count begins at 1 with +alloc
[person retain];
Retain count increases to 2 with -retain
[person release];
Retain count decreases to 1 with -release
[person release];
Retain count decreases to 0, -dealloc automatically
called](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ios-session-2-130210214529-phpapp01/85/iOS-Session-2-11-320.jpg)
![Autorelease
Example: returning a newly created object
-(NSString *)fullName
{
NSString *result;
result = [[NSString alloc] initWithFormat:@“%@
%@”, firstName, lastName];
[result autorelease]
return result;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ios-session-2-130210214529-phpapp01/85/iOS-Session-2-12-320.jpg)
![Method Names & Autorelease
Methods whose names includes alloc, copy, or new return a retained
object that the caller needs to release
NSMutableString *string = [[NSMutableString alloc] init];
// We are responsible for calling -release or -autorelease
[string autorelease];
All other methods return autoreleased objects
NSMutableString *string = [NSMutableString string];
// The method name doesn’t indicate that we need to release
it, so don’t
This is a convention- follow it in methods you define!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ios-session-2-130210214529-phpapp01/85/iOS-Session-2-13-320.jpg)






![NSDictionary
Immutable hash table. Look up objects using a key to get a
value.
+ (id)dictionaryWithObjects:(NSArray *)values forKeys:(NSArray *)keys;
+ (id)dictionaryWithObjectsAndKeys:(id)firstObject, ...;
Creation example:
NSDictionary *base = [NSDictionary dictionaryWithObjectsAndKeys:
[NSNumber numberWithInt:2], @“binary”,
[NSNumber numberWithInt:16], @“hexadecimal”, nil];
Methods
- (int)count;
- (id)objectForKey:(id)key;
- (NSArray *)allKeys;
- (NSArray *)allValues;
see documentation (apple.com) for more details](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ios-session-2-130210214529-phpapp01/85/iOS-Session-2-21-320.jpg)

![We will see this in
Property list (plist) practice later
A collection of collections
Specifically, it is any graph of objects containing only the following classes:
NSArray, NSDictionary, NSNumber, NSString, NSDate, NSData
Example1 : NSArray is a Property List if all its members are too
NSArray of NSString is a Property List
NSArray of NSArray as long as those NSArray’s members are Property Lists.
Example 2: NSDictionary is one only if all keys and values are too
Why define this term?
Because the SDK has a number of methods which operate on Property Lists.
Usually to read them from somewhere or write them out to somewhere.
[plist writeToFile:(NSString *)path atomically:(BOOL)]; // plist is NSArray or
NSDictionary](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ios-session-2-130210214529-phpapp01/85/iOS-Session-2-23-320.jpg)











