IT109 Microsoft Windows 7 Operating Systems Unit 01
- 1. Welcome to IT109 Where does this course fit in your program? IT109 is all new, and switched from using Windows XP to Windows 7. In addition, Operating Systems concepts are covered first 2 weeks in a nice little book – the IT103 class has been eliminated.
- 2. IT109 and your program How does this course relate to the program? Take a look! Microsoft Desktop Operating System is a course required to achieve an Associates Degree in the Information Technology (IT) program. IT is a diverse area of study encompassing several computer-based system and application areas. The advancement of computers and communication technology continues to have profound impact on our lives. A need exists for technically competent individuals to provide appropriate computing solutions for users. The objective of the IT program is to provide a broad-based foundation in the area of IT and a concentration in one of four IT options.
- 4. Chapter 1 Introduction ( Page 3-47) Chapter 1 is a well written introduction to the various areas of Operating Systems. Read this chapter as your “homework” for this week. Topics on the quiz will be covered in these Powerpoints, but there is much more you can learn by reading this chapter...
- 5. Open Source Today is a great time to study operating systems: many Open Source systems are available. For open source operating systems (such as Linux), source code is freely available. This is what we mean by “Open Source”. Page 7 “The Study of Operating Systems” discusses this in detail.
- 6. What is an Operating System? A program that manager computer hardware and interfaces between user and the hardware. Mainframe OS: Designed to maximize utilization of hardware. OS for personal computers: Support for games, business aps, etc. (what else?) OS for handheld devices: Designed to provide an easy interface for the user to execute programs, access the web, etc. (cell phones? Ipad? What else?)
- 7. Components of an OS An operating system can be thought of as four main components: Hardware The Operating System The Application Programs The users See next slide from page 4
- 8. fg1_01
- 9. OS as a Resource Allocator Many resources to allocate to users and programs Memory: Basic unit is a bit, group of 8 bits is a byte, today GB of memory must be managed. Disk Storage: Magnetic disk is most common Optical and Flash disks also very popular A file system allows users to create and access files CPU cycles What else? A modern computer system may look like next slide
- 10. fg1_02
- 11. Interrupts An important part of computer architecture An interrupt must transfer control to the proper service routine When CPU is interrupted, it stops what it’s doing and immediately transfewrs control to a fixed location that contains the interupt routine (see next slide)
- 12. fg1_03
- 13. Storage Device Hierarchy The wide variety of storage systems can be organized in a hierarchy by speed and cost – see next slide.
- 14. fg1_04
- 15. Components Next slide shows interplay of components of a computer system
- 16. fg1_05
- 17. Computer System Architecture Single Processor System Multiprocessor system Symmetric multiprocessing is most common All processors are peers No master/slave Share the resources (see next slide)
- 18. fg1_06
- 19. Computer System Architecture Multi-core processors are common today More efficient than multiple chips
- 20. fg1_07
- 21. Clustered System Computer systems that work together form a cluster In effect, acts like a high speed computer!
- 22. fg1_08
- 23. Chapter 2 Operating System Structures ( Page 49-76)
- 24. Desktop A Graphical User Interface (or GUI) can be thought of as a “Desktop Metaphor” Instead of entering commands directly, a mouse-based windows-and-menu system is used.
- 25. fg2_03
- 26. Operating System Structure Many comerical operating systems do not have a well-defined structure Some started simple and grew beyond original scope: MS-DOS is a good example (next slide) Some OS systems (Unix/Linux/NT kernel) have a specified structure (Unix on a following slide)
- 27. fg2_12
- 28. fg2_13
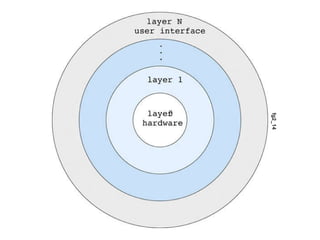
- 29. Layers of an OS An OS can be made modular by following a layered approach Next slide shows this
- 30. fg2_14
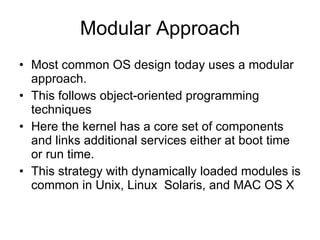
- 31. Modular Approach Most common OS design today uses a modular approach. This follows object-oriented programming techniques Here the kernel has a core set of components and links additional services either at boot time or run time. This strategy with dynamically loaded modules is common in Unix, Linux Solaris, and MAC OS X
- 32. fg2_15
- 33. Mac/OS Strucuture Figure 2.16 in textbook shows the Mac/OS structure Lowest layer is the Mach (micro-kernel) Then SD layer provides CLI, network support, file system support, and the POSIX API. Top layer is applications and services
- 34. fg2_16
- 35. Some final facts… Operating Systems are designed as an interface between hardware, programs, and the user. The interface used by programs is called the API. Client-Server systems (p35-36) are used to connect to a specialized distributed system of data. (Quiz question) Two important considerations for cache memory are speed and replacement policy (on quiz) Replacement policy has to do with keeping the data that’s needed most often in cache memory, and what policies are used to determine what gets swapped out. Interesting stuff, beyond the scope of this class – why is it on the quiz? (IDK) Now get to work on lab…