Java 8 lambda
- 1. Design and Implementation of Lambda Expressions in Java 8
- 2. Outline 1. What is the lambda calculus? 2. What is functional programming? 3. What are the benefits of functional programming? 4. Functional programming in Java 8 5. Java 8 lambda expressions 6. Implementation of Java 8 lambda expressions 7. Streams
- 3. The Lambda Calculus • The lambda calculus was introduced in the 1930s by Alonzo Church as a mathematical system for defining computable functions. • The lambda calculus is equivalent in definitional power to that of Turing machines. • The lambda calculus serves as the computational model underlying functional programming languages such as Lisp, Haskell, and Ocaml. • Features from the lambda calculus such as lambda expressions have been incorporated into many widely used programming languages like C++ and now very recently Java 8.
- 4. What is the Lambda Calculus? • The central concept in the lambda calculus is an expression generated by the following grammar which can denote a function definition, function application, variable, or parenthesized expression: expr → λ var . expr | expr expr | var | (expr) • We can think of a lambda-calculus expression as a program which when evaluated by beta-reductions returns a result consisting of another lambda- calculus expression.
- 5. Example of a Lambda Expression • The lambda expression λ x . (+ x 1) 2 represents the application of a function λ x . (+ x 1) with a formal parameter x and a body + x 1 to the argument 2. Notice that the function definition λ x . (+ x 1) has no name; it is an anonymous function. • In Java 8, we would represent this function definition by the Java 8 lambda expression x -> x + 1.
- 6. More Examples of Java 8 Lambdas • A Java 8 lambda is basically a method in Java without a declaration usually written as (parameters) -> { body }. Examples, 1. (int x, int y) -> { return x + y; } 2. x -> x * x 3. ( ) -> x • A lambda can have zero or more parameters separated by commas and their type can be explicitly declared or inferred from the context. • Parenthesis are not needed around a single parameter. • ( ) is used to denote zero parameters. • The body can contain zero or more statements. • Braces are not needed around a single-statement body.
- 7. What is Functional Programming? • A style of programming that treats computation as the evaluation of mathematical functions • Eliminates side effects • Treats data as being immutable • Expressions have referential transparency • Functions can take functions as arguments and return functions as results • Prefers recursion over explicit for-loops
- 8. Why do Functional Programming? • Allows us to write easier-to-understand, more declarative, more concise programs than imperative programming • Allows us to focus on the problem rather than the code • Facilitates parallelism
- 9. Java 8 • Java 8 is the biggest change to Java since the inception of the language • Lambdas are the most important new addition • Java is playing catch-up: most major programming languages already have support for lambda expressions • A big challenge was to introduce lambdas without requiring recompilation of existing binaries
- 10. Benefits of Lambdas in Java 8 • Enabling functional programming • Writing leaner more compact code • Facilitating parallel programming • Developing more generic, flexible and reusable APIs • Being able to pass behaviors as well as data to functions
- 11. Java 8 Lambdas • Syntax of Java 8 lambda expressions • Functional interfaces • Variable capture • Method references • Default methods
- 12. Example 1: Print a list of integers with a lambda List<Integer> intSeq = Arrays.asList(1,2,3); intSeq.forEach(x -> System.out.println(x)); • x -> System.out.println(x) is a lambda expression that defines an anonymous function with one parameter named x of type Integer
- 13. Example 2: A multiline lambda List<Integer> intSeq = Arrays.asList(1,2,3); intSeq.forEach(x -> { x += 2; System.out.println(x); }); • Braces are needed to enclose a multiline body in a lambda expression.
- 14. Example 3: A lambda with a defined local variable List<Integer> intSeq = Arrays.asList(1,2,3); intSeq.forEach(x -> { int y = x * 2; System.out.println(y); }); • Just as with ordinary functions, you can define local variables inside the body of a lambda expression
- 15. Example 4: A lambda with a declared parameter type List<Integer> intSeq = Arrays.asList(1,2,3); intSeq.forEach((Integer x -> { x += 2; System.out.println(x); }); • You can, if you wish, specify the parameter type.
- 16. Implementation of Java 8 Lambdas • The Java 8 compiler first converts a lambda expression into a function • It then calls the generated function • For example, x -> System.out.println(x) could be converted into a generated static function public static void genName(Integer x) { System.out.println(x); } • But what type should be generated for this function? How should it be called? What class should it go in?
- 17. Functional Interfaces • Design decision: Java 8 lambdas are assigned to functional interfaces. • A functional interface is a Java interface with exactly one non-default method. E.g., public interface Consumer<T> { void accept(T t); } • The package java.util.function defines many new useful functional interfaces.
- 18. Assigning a Lambda to a Local Variable public interface Consumer<T> { void accept(T t); } void forEach(Consumer<Integer> action { for (Integer i:items) { action.accept(t); } } List<Integer> intSeq = Arrrays.asList(1,2,3); Consumer<Integer> cnsmr = x -> System.out.println(x); intSeq.forEach(cnsmr);
- 19. Properties of the Generated Method • The method generated from a Java 8 lambda expression has the same signature as the method in the functional interface • The type is the same as that of the functional interface to which the lambda expression is assigned • The lambda expression becomes the body of the method in the interface
- 20. Variable Capture • Lambdas can interact with variables defined outside the body of the lambda • Using these variables is called variable capture
- 21. Local Variable Capture Example public class LVCExample { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Integer> intSeq = Arrays.asList(1,2,3); int var = 10; intSeq.forEach(x -> System.out.println(x + var)); } } • Note: local variables used inside the body of a lambda must be final or effectively final
- 22. Static Variable Capture Example public class SVCExample { private static int var = 10; public static void main(String[] args) { List<Integer> intSeq = Arrays.asList(1,2,3); intSeq.forEach(x -> System.out.println(x + var)); } }
- 23. Method References • Method references can be used to pass an existing function in places where a lambda is expected • The signature of the referenced method needs to match the signature of the functional interface method
- 24. Summary of Method References Method Reference Type Syntax Example static ClassName::StaticMethodName String::valueOf constructor ClassName::new ArrayList::new specific object instance objectReference::MethodName x::toString arbitrary object of a given type ClassName::InstanceMethodName Object::toString
- 25. Conciseness with Method References We can rewrite the statement intSeq.forEach(x -> System.out.println(x)); more concisely using a method reference intSeq.forEach(System.out::println);
- 26. Default Methods Java 8 uses lambda expressions and default methods in conjunction with the Java collections framework to achieve backward compatibility with existing published interfaces For a full discussion see Brian Goetz, Lambdas in Java: A peek under the hood. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MLksirK9nnE
- 27. Stream API • The new java.util.stream package provides utilities to support functional-style operations on streams of values. • A common way to obtain a stream is from a collection: Stream<T> stream = collection.stream(); • Streams can be sequential or parallel. • Streams are useful for selecting values and performing actions on the results.
- 28. Stream Operations • An intermediate operation keeps a stream open for further operations. Intermediate operations are lazy. • A terminal operation must be the final operation on a stream. Once a terminal operation is invoked, the stream is consumed and is no longer usable.
- 29. Example Intermediate Operations • filter excludes all elements that don’t match a Predicate. • map performs a one-to-one transformation of elements using a Function.
- 30. A Stream Pipeline A stream pipeline has three components: 1. A source such as a Collection, an array, a generator function, or an IO channel; 2. Zero or more intermediate operations; and 3. A terminal operation
- 31. Stream Example int sum = widgets.stream() .filter(w -> w.getColor() == RED) .mapToInt(w -> w.getWeight()) .sum(); Here, widgets is a Collection<Widget>. We create a stream of Widget objects via Collection.stream(), filter it to produce a stream containing only the red widgets, and then transform it into a stream of int values representing the weight of each red widget. Then this stream is summed to produce a total weight. From Java Docs Interface Stream<T>
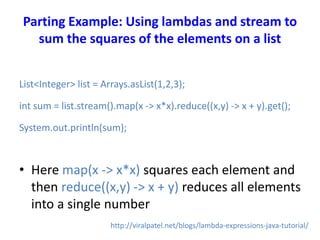
- 32. Parting Example: Using lambdas and stream to sum the squares of the elements on a list List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1,2,3); int sum = list.stream().map(x -> x*x).reduce((x,y) -> x + y).get(); System.out.println(sum); • Here map(x -> x*x) squares each element and then reduce((x,y) -> x + y) reduces all elements into a single number http://viralpatel.net/blogs/lambda-expressions-java-tutorial/
Editor's Notes
- #13: List<Integer> is a parameterized type, parameterized by the type argument <Integer> the Arrays.asList method returns a fixed-size list backed by an array; it can take “vararg” arguments forEach is a method that takes as input a function and calls the function for each value on the list Note the absence of type declarations in the lambda; the Java 8 compiler does type inference Java 8 is still statically typed Braces are not needed for single-line lambdas (but could be used if desired).
- #14: Note: braces are needed to enclose a multiline lambda expression
- #15: Just as with ordinary functions, you can define local variables inside the lambda expression
- #16: You can, if you wish, specify the parameter type The compiler knows the type of intSeq is a list of Integers Since the compiler can do type inference, you don’t need to specify the type of x.
- #17: What type should be generated for this function? How should it be called? What class should the translated lambda expression function be placed it? Should the generated method be a static or an instance method? The Java 8 designers spent a lot of time thinking about how to implement lambdas!
- #18: Functional interfaces are a common idiom in Java code. Examples of existing JDK functional interfaces: Runnable, Comparable<T>, Callable<V>. Design decision: Java 8 lambdas should work with existing Java code without requiring recompilation.
- #19: Here is an interface called Consumer with a single method called accept. The forEach method iterates through the items in the object Consumer and performs the action accept on each item. The lambda expression becomes the body of the function in the interface. The signature of the function is defined by the interface.
- #20: Any interface with only one nondefault method is considered a functional interface by Java 8. So functional interfaces are Java 8’s secret sauce for backward compatibility.
- #22: This lambda “captures” the variable var.




















![Local Variable Capture Example
public class LVCExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> intSeq = Arrays.asList(1,2,3);
int var = 10;
intSeq.forEach(x -> System.out.println(x + var));
}
}
• Note: local variables used inside the body of a lambda
must be final or effectively final](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java8lambda-151226161406/85/Java-8-lambda-21-320.jpg)
![Static Variable Capture Example
public class SVCExample {
private static int var = 10;
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> intSeq = Arrays.asList(1,2,3);
intSeq.forEach(x -> System.out.println(x + var));
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java8lambda-151226161406/85/Java-8-lambda-22-320.jpg)