Java Collections Framework - Interfaces, Classes and Algorithms
- 2. Learning Outcome • To understand the need and definitions, hierarchy of collection framework • Various interfaces – Iterable – Collection – List – Set – Queue – Deque
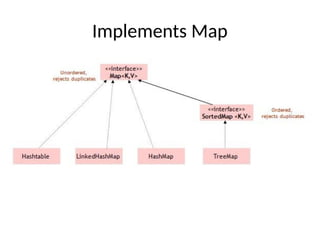
- 3. Collections Framework • The Collection in Java is a framework that provides an architecture to store and manipulate the group of objects. • Java Collections can achieve all the operations that you perform on a data such as searching, sorting, insertion, manipulation, and deletion. • Java Collection means a single unit of objects. Java Collection framework provides many interfaces (Set, List, Queue, Deque) and classes (ArrayList, Vector, LinkedList, PriorityQueue, HashSet, LinkedHashSet, TreeSet).
- 5. Class implements various interfaces
- 7. java.util • classes that generate pseudorandom numbers, manage date and time, observe events, manipulate sets of bits, tokenize strings, and handle formatted data • The java.util package also contains one of Java’s most powerful subsystems: the Collections Framework. • The Collections Framework is a sophisticated hierarchy of interfaces and classes that provide state- of-the-art technology for managing groups of objects
- 10. Collections Framework • The framework should provide high-performance. • The framework allow different types of collections to work in a similar manner and with a high degree of interoperability. • Extending and/or adapting a collection had to be easy. • Entire Collections Framework is built upon a set of standard interfaces • Integration of standard arrays into the Collections Framework. • Algorithms operate on collections and are defined as static methods within the Collections class. • All collections are now generic, and many of the methods that operate on collections take generic type parameters. Ensure Type Safety
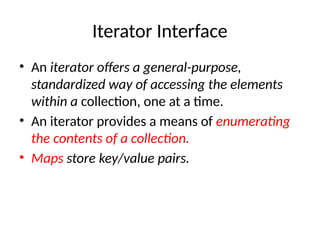
- 11. Iterator Interface • An iterator offers a general-purpose, standardized way of accessing the elements within a collection, one at a time. • An iterator provides a means of enumerating the contents of a collection. • Maps store key/value pairs.
- 12. Lists and Sets A list is a collection that maintains the order of its elements. • Ordered Lists – ArrayList List • Stores a list of items in a dynamically sized array – LinkedList List, Queue • Allows speedy insertion and removal of items from the list Copyright © 2013 by John Wiley & Sons. All rights reserved.
- 13. Lists and Sets A set is an unordered collection of unique elements. • Unordered Sets – HashSet Set • Uses hash tables to speed up finding, adding, and removing elements – TreeSet SortedSet • Uses a binary tree to speed up finding, adding, and removing elements Copyright © 2013 by John Wiley & Sons. All rights reserved.
- 14. Set Vs List import java.util.*; public class MyClass { public static void main(String args[]) { Set<String> s=new HashSet<String>(); s.add("fggg"); s.add("Wewe"); s.add("EREW"); s.add("Wewer"); s.add("rtrer"); System.out.println("Set of elements " + s); List<String> l=new ArrayList<String>(); l.add("fggg"); l.add("Wewe"); l.add("EREW"); l.add("Wewer"); l.add("rtrer"); System.out.println("List of elements " + l); }} Output: Set of elements [rtrer, Wewe, fggg, EREW, Wewer] List of elements [fggg, Wewe, EREW, Wewer, rtrer]
- 15. Stacks and Queues • Another way of gaining efficiency in a collection is to reduce the number of operations available • Two examples are: – Stack • Remembers the order of its elements, but it does not allow you to insert elements in every position • You can only add and remove elements at the top – Queue • Add items to one end (the tail) • Remove them from the other end (the head) • Example: A line of people waiting for a bank teller Copyright © 2013 by John Wiley & Sons. All rights reserved.
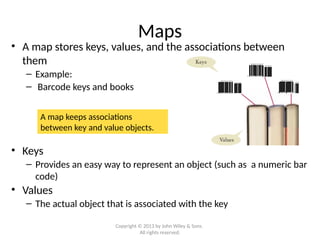
- 16. Maps • A map stores keys, values, and the associations between them – Example: – Barcode keys and books • Keys – Provides an easy way to represent an object (such as a numeric bar code) • Values – The actual object that is associated with the key A map keeps associations between key and value objects. Copyright © 2013 by John Wiley & Sons. All rights reserved.
- 17. Internal working of Set
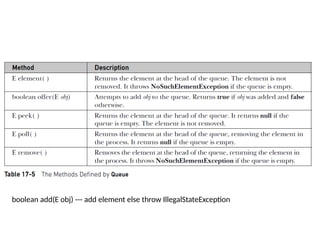
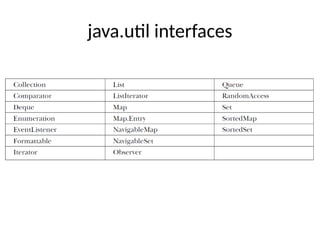
- 18. Collection Interfaces Interface Description Collection Enables you to work with groups of objects; it is at the top of the collections hierarchy. List Extends Collection to handle sequences (lists of objects). Set Extends Collection to handle sets, which must contain unique elements. Queue Extends Collection to handle special types of lists in which elements are removed only from the head. SortedSet Extends Set to handle sorted sets. NavigableSet Extends SortedSet to handle retrieval of elements based on closest- match searches. Deque Extends Queue to handle a double-ended queue.
- 19. Other Interfaces mainly used • Collections also use the Comparator, RandomAccess, Iterator, and ListIterator interfaces. • Comparator defines how two objects are compared; • Iterator and ListIterator enumerate the objects within a collection. • By implementing RandomAccess, a list indicates that it supports efficient, random access to its elements.
- 20. Collection Interface – Extends Iterable interface • public interface Collection<E> extends Iterable<E>
- 22. Exceptions in Collection • Several of these methods can throw an • UnsupportedOperationException - occurs if a collection cannot be modified. • ClassCastException – occurs when one object is incompatible with another, such as when an attempt is made to add an incompatible object to a collection. • NullPointerException - occurs if an attempt is made to store a null object and null elements are not allowed in the collection. • IllegalArgumentException - occurs if an invalid argument is used. • IllegalStateException - occurs if an attempt is made to add an element to a fixed-length collection that is full.
- 23. List Interface • public interface List<E> extends Collection<E> • It stores a sequence of elements • Elements are inserted or accessed based on their position in list • List can contain duplicate elements
- 25. Set Interface • Set interface defines a set • It does not allow duplicate elements • public interface Set<E> extends Collection<E> • add() method returns false if an attempt is made to add duplicate elements to a set • Same methods as Collection interface
- 26. Queue Interface • The Queue interface extends Collection and declares the behavior of a queue, which is often a first-in, first-out list • public interface Queue<E> extends Collection<E>
- 27. boolean add(E obj) --- add element else throw IllegalStateException
- 28. Deque Interface • The Deque interface extends Queue and declares the behavior of a double-ended queue. • Double-ended queues can function as standard, first-in, first-out queues or as last-in, firstout stacks. • public interface Deque<E> extends Queue<E>
- 29. Deque methods • addFirst, addLast, getFirst, getLast, offerFirst, offerLast, peekFirst, peekLast, pollFirst, pollLast, pop, push, removeFirst, removeLast, removeFirstOccurrence, removeLastOccurrence
- 30. References • Herbert Schildt,“Java:The Complete Reference”, 8th Edition,McGrawHill Education, 2011. • https://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/jav a/util/









![Set Vs List
import java.util.*;
public class MyClass {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Set<String> s=new HashSet<String>();
s.add("fggg");
s.add("Wewe");
s.add("EREW");
s.add("Wewer");
s.add("rtrer");
System.out.println("Set of elements " + s);
List<String> l=new ArrayList<String>();
l.add("fggg");
l.add("Wewe");
l.add("EREW");
l.add("Wewer");
l.add("rtrer");
System.out.println("List of elements " + l);
}}
Output:
Set of elements [rtrer, Wewe, fggg, EREW, Wewer]
List of elements [fggg, Wewe, EREW, Wewer, rtrer]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-1-collectionsframework-250313043156-f8ce5233/85/Java-Collections-Framework-Interfaces-Classes-and-Algorithms-14-320.jpg)