Java EE 7 for Real Enterprise Systems
- 1. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A Java EE 7 for Real Enterprise Systems 実システムのためのJava EE 7 May 24, 2016 Hirofumi Iwasaki Financial Service Department, DU, Rakuten, Inc.
- 2. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A 2 Speaker Biography Hirofumi Iwasaki – Group Manager, Technology Manager – Financial Service Department, Development Unit, Rakuten, Inc. Carrier – 17 Years of experience in planning, designing and implementation of Japanese financial, manufacturing and public enterprise system with emphasis in Java EE and .NET enterprise middleware. Opus, Lectures, etc. – Conferences: JavaOne 2015, 2014, Oracle OpenWorld 2014, Java Day Tokyo 2015, 2014, JJUG CCC Spring & Fall (2014), WebLogic roundtable (2012- 2013), Rakuten Tech Conference 2015 – 2013, etc. – Book: デベロッパーのキャリアと働き方を語ろうVol.1 (2016) – Magazine: 日経コンピュータ 2015年8月号 @IT (2005-2010), CIO Magazine (2009), IT Architect (2005-2009), Web+DB Press (2005), Java World (2001- 2004), etc.
- 3. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A 3 On JavaOne 2015 Key Note Speech Session "Real world batch processing using Java EE"
- 4. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A Consider EE 8 for future-prove
- 6. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A 6 Beyond of the Java EE 7 CDI 2.0 JSON-B 1.0 JMS 2.1 Servlet4.0 JAX-RS2.1 MVC 1.0 JSF 2.3 Java EE Management API 1.0 JSON-P 1.1 Java EE Security API 1.0
- 8. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A 8 Standardization History of Java EE J2EE 1.2 J2EE 1.3 J2EE 1.4 Java EE 5 Java EE 6 Java EE 7 Java EE 8 JDBC EJB/JTA/XA/IIOP Servlet/JSP JMS RMI SOAP JPA JSF/Facelet REST CDI JavaBatch Project JPE or earlier WebSocket MVC …
- 9. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A 9 Terminated Technologies of Java EE J2EE 1.2 J2EE 1.3 J2EE 1.4 Java EE 5 Java EE 6 Java EE 7 Java EE 8 JDBC EJB JSP JMS RMI SOAP JPA JSF/Facelet REST CDI JavaBatch Project JPE or earlier WebSocket EJBEntityBean JSP MVC … Today's Big Topic 2 EJB to CDI Today's Big Topic 1 JSF 2.1 2.2
- 10. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A Java EE 7, For Your Real Systems
- 11. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A 11 Basic Strategy for Applying Java EE 7 Continuous upgrading recommended. – J2EE 1.2 1.3 1.4 Java EE 5 6 7 (on every two – four years) – Wait migrations until the application server matured. Big jump: huge risk – Some APIs were already terminated completely. EJB Entity Bean (1.1, 2.x) Older deployment descriptor (XML files) DTD or XML schema. – Some Application servers were already terminated or stopped development. Silverstream Macromedia JRun Oracle Application Server (Orion, iAS, OC4J) Netscape (iPlanet) Application Server JOnAS Apache Geronimo
- 12. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A 1999 2001 2003 2006 2009 2013 Java EE 7 Servers J2EE 1.2 Servers Pre-J2EE Serv J2EE 1.3 Servers J2EE 1.4 Servers Java EE 5 Servers Java EE 6 Servers 2017?
- 13. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A 13 Update Your Systems Based on Java EE 6 to EE 7 Typical Java EE 6 system configuration (2009 - ) – Oracle WebLogic 12.1, IBM WebSphere 8.x, JBoss 6, 7, other minor products. – JDK 7 JDK 8 (super small jump). – No need to migrate, super easy, just try it. Web front-end – JSF 2.1 or Struts 2.x based JSF 2.2 (jump!) From Struts 2, complete rewrite required from action to page. From JSF 2.1, apply HTML friendly markups, change backing bean to CDI (see next chapter for more details) Back-end – EJB 3 session bean CDI 1.1 (jump!) If you use RMI-IIOP (with XA) for remote connection, consider apply EJB 3.2 instead of CDI. Almost all codes are usable, but need rewritten using JPA for data persistence. Change EJB annotations to CDI annotations. (See more details on next chapter) – JPA 2.0 JPA 2.1 (super small change) Almost no changed.
- 14. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A 14 Update Your Systems Based on Java EE 5 to EE 7 Typical Java EE 5 system configuration (2006 - ) – Oracle WebLogic 10.x, 11, IBM WebSphere 7, JBoss 5.1, other minor products. – JDK 6 JDK 8 (super small jump). – Complete EOL, start migration today! Web front-end – JSF 1.2 or Struts 2.x based JSF 2.2 (jump!) From Struts 2, complete rewrite required from action to page. From JSF 1.2, apply Facelet instead of JSP, change backing bean to CDI (see next chapter for more details) Back-end – EJB 3 session bean CDI 1.1 (jump!) If you use RMI-IIOP (with XA) for remote connection, consider apply EJB 3.2 instead of CDI. Almost all codes are usable, but need rewritten using JPA for data persistence. Change EJB annotations to CDI annotations. (See more details on next chapter) – JPA 1.0 JPA 2.1 (small jump!) Consider apply "PESSIMISTIC_READ" for "FOR UPDATE" SQL locking.
- 15. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A 15 Update Your Systems Based on J2EE 1.4 to EE 7 Typical J2EE 1.4 system configuration (2003 - ) – BEA WebLogic 8.1, 9, IBM WebSphere 5.1, 6.x, JBoss 4.3, other minor products. – JDK 1.4 JDK 8 (big jump!) , apply annotations. – Complete EOL, start migration today! Web front-end – Struts 1.x based JSF 2.2 (big jump!) Complete rewrite required. Back-end – EJB 2.1 session bean or Spring framework 1.x CDI 1.1 (big jump!) If you use RMI-IIOP (with XA) for remote connection, consider apply EJB 3.2 instead of CDI. Almost all codes are usable, but need rewritten using JPA for data persistence. ejb-jar.xml or applicationContext.xml CDI annotations, remove home interface, etc. – EJB 2.1 entity bean (CMP) or Hibernate 2.x, 3.x JPA 2.1 (big jump from EJB!) Regenerate from RDB as "Entity" completely. From EJB, ejb-jar.xml persistence.xml, EJB home interface entity manager, etc. From Hibernate, small changes.
- 16. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A 16 Update Your Systems Based on J2EE 1.3 to EE 7 Typical J2EE 1.3 system configuration (2001 - ) – BEA WebLogic 7.0, IBM WebSphere 5.0, other minor products. – JDK 1.3, 1.4 JDK 8 (big jump!) , apply annotations. – Complete EOL, start migration today! Web front-end – Struts 1.x based JSF 2.2 (big jump!) Complete rewrite required. Back-end – EJB 2.0 session bean CDI 1.1 (big jump!) If you use RMI-IIOP (with XA) for remote connection, consider apply EJB 3.2 instead of CDI. Almost all codes are usable, but need rewritten using JPA for data persistence. ejb-jar.xml CDI annotations, remove home & remote interface, etc. – EJB 2.0 entity bean (CMP) JPA 2.1 (big jump!) Regenerate from RDB as "Entity" completely. ejb-jar.xml persistence.xml, change home interface to DAO. EJB home interface entity manager, etc.
- 17. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A 17 Update Your Systems Based on J2EE 1.2 to EE 7 Typical J2EE 1.2 system configuration (1999 - ) – BEA WebLogic 5.1, 6.0, 6.1, IBM WebSphere 4.0, other minor products. – JDK 1.1, 1.2, 1.3 JDK 8 (big jump!) , apply collection framework, annotations. – Complete EOL, start migration today! Web front-end – Struts 1.x based JSF 2.2 (big jump!) Complete rewrite required. Back-end – EJB 1.1 session bean CDI 1.1 (big jump!) If you use RMI-IIOP (with XA) for remote connection, consider apply EJB 3.2 instead of CDI. Almost all codes are usable, but need rewritten using JPA for data persistence. ejb-jar.xml CDI annotations, remove home & remote interface, etc. – EJB 1.1 entity bean (CMP) JPA 2.1 (big jump!) Regenerate from RDB as "Entity" completely. ejb-jar.xml persistence.xml, change home interface to DAO. EJB home interface entity manager, etc.
- 18. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A 18 Update Your Systems Based on pre-J2EE Era to EE 7 Typical pre-J2EE 1.2 system configuration (1997 - ) – WebLogic Tengah 3.0, 4.51, Netscape Application Server (Kiva), IBM WebSphere 3.5, Apache HTTPD + Apache JServ, other minor products. – JDK 1.1 JDK 8 (super big jump!), apply collection framework, annotations. – Perfect EOL, start migration today! Web front-end – WebLogic JHTML, Netscape Application Builder (NAB)-based, JavaSoft Servlet 2.0, etc. JSF 2.2 (ultra big jump!) Complete rewrite required. Back-end – WebLogic EJB, EJB 1.0 session bean CDI 1.1 (big jump!) If you use T3 (with XA) for remote connection, consider apply EJB 3.2 instead of CDI. Almost all codes are usable, but need rewritten using JPA for data persistence. Deployment descriptor (prop) CDI annotations, etc. – WebLogic EJB, EJB 1.0 entity bean JPA 2.1 (ultra big jump!) Regenerate from RDB completely. Deployment descriptor (prop) persistence.xml EJB home interface EntityManager, etc. WebLogic EJB DD
- 19. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A Web Front-End: JSF 2.1 2.2 for EE 7
- 20. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A 20 Rich Clients Web Presentation Business Logic (no presentations) Typical usage of Java EE 7 JPA EJBJSF DBs Java FX JTA Automatic Transaction JMS MQ Connection RMI-IIOP Other Servers EMail MTAJavaMail JAX Call Call Call Call Call Call Data Access Messaging
- 21. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A 21 <Facelet> View 1 Backing1 - fields + load() + action() <Facelet> View 2 Backing2 - fields + load() + action() <Facelet> View 3 Backing3 - fields + load() + action() Front View & Backing Bean Almost no changed in big architecture view in EE 6 (JSF 2.1) to EE 7 (JSF 2.2).
- 22. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A 22 <Facelet> View 1 Backing1 - fields + load() + action() Front View & Backing Bean Two big changes: 1. HTML friendly markup in Facelet 2. JSF backing bean to CDI 1. HTML friendly markup <h:xxxxxx> JSF special element to normal HTML elements. 2. JSF original backing bean to normal CDI.
- 23. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A 23 HTML Friendly Markups <input type="text” jsf:value="#{bean.property}" /> Java EE 7 (JSF 2.2) Java EE 6 (JSF 2.1) Simplified <input type="text" jsfc="h:inputText" name="id" value="#{bean.property}" /> Nice Relationship with HTML Design Tools
- 24. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A 24 HTML Friendly Markups HTML JSF 2.2 HTML Friendly Tags Older JSF Tags <a> <a jsf:action=“#{cdi.prop}”>~~~</a> <h:commandLink> <input type=“button”> <input type=“submit”> <input type=“button” jsf:value=“#{cdi.prop}”/> <input type=“submit” jsf:value=“#{cdi.prop}”/> <h:commandButton> <input type=“file”> <input type=“file” jsf:value=“#{cdi.prop}”/> <h:inputFile> <input type=“hidden”> <input type=“hidden” jsf:value=“#{cdi.prop}”/> <h:inputHidden> <input type=“password”> <input type=“password” jsf:value=“#{cdi.prop}”/> <h:inputSecret> <textarea> <textarea jsf:value=“#{cdi.prop}”/> <h:inputTextArea> <input type=“checkbox”> <input type=“checkbox” jsf:value=“#{cdi.prop}”/> <h:selectBooleanCheck box>・・・ etc.
- 25. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A 25 Java EE 6: Cannot Access from Outside to JSF Managed Bean Filter Faces Servlet Phase Listeners Facelet Facelet Facelet @View Scoped @View Scoped @View Scoped Managed Bean @Session Scoped Java EE 6 (JSF 2.1) JSF Managed Bean World Cannot Access!
- 26. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A 26 Java EE 6: Cannot Use ViewScoped CDIs, or Use JSF Backing Bean Filter Faces Servlet Phase Listeners Facelet Facelet Facelet CDI don't have @View Scoped CDI don't have @View Scoped CDI don't have @View ScopedManaged Bean @Session Scoped Java EE 6 (JSF 2.1) CDI World OK! Cannot Use "View Scoped"
- 27. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A 27 Java EE 7: All Integrated CDI with JSF Filter Faces Servlet Phase Listeners Facelet Facelet Facelet New CDI @View Scoped New CDI @View Scoped New CDI @View Scoped CDI @Session Scoped Java EE 7 (JSF 2.2) CDI WorldOK! OK! Perfect!
- 28. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A 28 Consideration Points for Applying CDI in JSF Backing Bean Now CDI can be accessible on Filter. – Consider applying @ApplicationScoped, @SessionScoped for some hacking techs. Migration from raw static objects to @ApplicationScoped CDI bean – For easy management especially for controlling initialization timing. Migration from raw HttpSession to @SessionScoped CDI bean – Don't use both HttpSession and @SessionScoped for avoiding confusing on production. – Apply @SessionScoped only for managing session data. Migration from JSF management bean @ViewScoped to CDI @ViewScoped – Same name but in different package (javax.faces.view.ViewScoped) – Just change the package import from javax.faces.bean.ViewScoped. 28
- 29. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A 29 Summary: Recommendation for the Java EE 7 Front-End Use For your web front-end, Apply HTML-Friendly Markups. Implement with Facelet,
- 30. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A Back-End: EJB to CDI for future prove
- 31. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A 31 Rich Clients Web Presentation Business Logic (no presentations) Typical usage of Java EE 7 JPA EJBJSF DBs Java FX JTA Automatic Transaction JMS MQ Connection RMI-IIOP Other Servers EMail MTAJavaMail JAX Call Call Call Call Call Call Data Access Messaging
- 32. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A 32 Java EE 6: What’s EJB? Why EJB? – The Core of Java EE EJBClient 1. Remote Invocation EJB 2. Automatic Transaction Management Database (BEGIN) (COMMIT) EJB EJB EJB EJB Instance Pool Activate 3. Instance Pooling for Faster Operation RMI-IIOP SOAP REST Web Socket EJB Client 4. Security Management
- 33. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A 33 Embedded Container Java EE 6: EJB 3 and beyond – Improved dramatically EJB 1. Introduced Annotations, POJO @Stateless EJB 2. Introduced Injections @Inject @EJB Other Instance ejb-jar.xml 4. No Deployment Descriptor (optional) EJB EJB 5. Embedded EJB Container for Testing & etc. JPA Database 3. Entity Bean JPA
- 34. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A 34 On Java EE 8 and Beyond: EJB to CDI Why EJB should go out? 1. Super old implementation in each Java EE compliant application server. 2. Old-style pre-compile required, need much time to deploy. 3. Ultra tight related with EJB container, difficult to test easily (although using EJB embedded server). 4. Decreasing RMI-IIOP (T3) protocol users, less compliant with CORBA specs. 5. Duplicated specification with latest CDI with directly supported automatic transaction with JTA specifications. Good-bye guys…
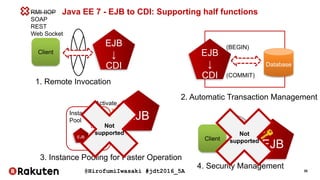
- 35. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A 35 Java EE 7 - EJB to CDI: Supporting half functions EJB ↓ CDI Client 1. Remote Invocation EJB ↓ CDI 2. Automatic Transaction Management Database (BEGIN) (COMMIT) EJB EJB EJB EJB Instance Pool Activate 3. Instance Pooling for Faster Operation RMI-IIOP SOAP REST Web Socket EJB Client 4. Security Management Not supported Not supported
- 36. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A 36 Supported protocols of Java EE 7 in CDI Protocol Supported From Annotation Client Stub Value Marshaling Global Transaction RMI-IIOP J2EE 1.2 @Remote in remote interface Remote interface with auto generate Auto XA Supported SOAP Java EE 5 @WebService Auto generate in development Auto N/A REST Java EE 6 @GET, @POST, etc. (Nothing special) Work with JSON or something (string base) N/A Web Socket Java EE 7 @ServerEndpoint @ClientEndpoint with auto generate Work with JSON or something (string base) N/A
- 37. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A 37 NOT SUPPORTED: Global Transaction Management with XA Protocol Java EE 7 - Limitation of CDI: RMI-IIOP with XA is not supported CDI Client REST, Web Socket Other System’s EJB Database Other Enterprise Information Systems IIOP AUTO BEGIN AUTO COMMIT Not supported Not supported
- 38. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A 38 EE7 - Limitation of CDI: For light-weight usage, or simplified architecture Local Transaction Management CDI Client REST, Web Socket Database AUTO BEGIN AUTO COMMIT Enough for almost small architecture. Other System REST * No XA
- 39. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A How to convert EJB to CDI For From (EJB) To (CDI) Declaration @Stateless @Dependent @Transactional Injection @EJB @Inject Transaction control @TransactionAttibute (TransactionAttibuteType .REQUIRES_NEW) @Transactional (Transactional.TxType .REQUIRES_NEW) Self transaction management @TransactionManagement( TransactionManagementType.BEAN) (delete) Transaction rollback @ApplicationException( rollback = true) @Transactional( rollbackOn = Exception.class) Remote protocol @WebServices, @GET or @POST, @ServerEndpoint, or @Remote in remote interface, @WebServices, @GET, @POST or @ServerEndpoint
- 40. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A EJB to CDI Code – Super Simple Case 40 From (EJB CMT Session Bean) To (CDI) And delete ejb-jar.xml (and weblogic-ejb-jar.xml etc.),
- 41. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A 41 Consideration Points for Applying CDI Merging JSF backing bean (CDI) view with business logics (CDI) – Logically acceptable, but some difficulty for managing. Difficult to visualize transaction boundary with @Transactional. Super tight relationship between view and logics - Less code reusability. – Not recommended for enterprise production, just apply for quick prototyping only. Incompatible points – RMI-IIOP (or T3) with XA (global transaction) Keep using EJB remote interface on communication point only. Plan to change other lightweight protocol like REST+JSON. – EJB Timer Change other products like job scheduler like IBM Tiboli, HITACHI JP1, etc. – Asynchronous operations (@Asynchronous, or EJB Message-Driven bean with JMS) Wait next CDI spec (on EE 8), or keep using EJB. 41
- 42. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A 42 Summary: EJB to CDI Apply simplified architecture, use CDI with JTA automatic transaction management. Migrate EJB to CDI as applying easy replacement rules. Recognize incompatible points, check EE 8 spec candidate, design your next app.
- 43. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A 43 Summary is the world open specification De-Facto standard. “Standard” has many pros & cons, but it can keep your assets and knowledge.
- 44. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A Java EE has many world-wide people and company support. your application will have long-life guaranteed.
- 45. @HirofumiIwasaki #jdt2016_5A Apply Java EE 7 today and be ready for EE 8.
Editor's Notes
- #3: This is Hirofumi Iwasaki speaking. I'm a financial system group manager of Rakuten. And a professional of enterprise financial system management, planning and development.
- #21: Then let's see the typical usage of Java EE 6 specs. Almost all enterprise systems requires data source, and each source type requires suitable framework, JPA, JMS, RMI-IIOP and JAX, and Java Mail. And these data connectivity framework operated transactionaly by EJB. Finally front-end frameworks like JSF & JavaFX call EJB. These are the basic Java EE structure.
- #32: Then let's see the typical usage of Java EE 6 specs. Almost all enterprise systems requires data source, and each source type requires suitable framework, JPA, JMS, RMI-IIOP and JAX, and Java Mail. And these data connectivity framework operated transactionaly by EJB. Finally front-end frameworks like JSF & JavaFX call EJB. These are the basic Java EE structure.