java package in java.. in java packages.
- 1. PRESENTATION ON JAVA PACKAGES R.HANNAH ROSELINE ASSISTANT PROFESSOR SRI RAMAKRISHNA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE
- 2. CONTENTS Introduction Types Of Packages Pre-Defined Packages or Built in Packages Pre-Defined Packages & Their Classes User Defined Packages. Creating User Defined Packages Steps For Creating Package Accessing a Package o Advantages Of Packages
- 3. INTRODUCTION In java, programmers can create several classes & Interface. After creating these classes and interface, it is better if they are divided into some groups depending on their relationship. Thus, the classes and interface which handle similar or same task are put into the same directory or folder, which is also known as package. Packages act as “containers” for classes. A package represents a directory that contain related group of classes & interface.
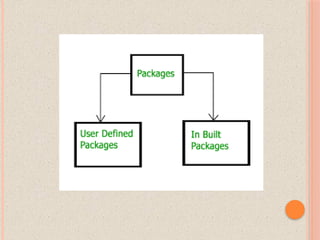
- 4. TYPES OF PACKAGES There are basically only 2 types of java packages. They are as follow : System Packages or Java API User Defined Packages.
- 6. Pre-Defined Packages or Built in Packages As there are built in methods , java also provides inbuilt packages which contain lots of classes & interfaces. These classes inside the packages are already defined & we can use them by importing relevant package in our program. Java has an extensive library of packages, a programmer need not think about logic for doing any task. For everything, there are the methods available in java and that method can be used by the programmer without developing the logic on his own. This makes the programming easy.
- 7. JAVA SYSTEM PACKAGES & THEIR CLASSES java.lang Language Support classes. These are classes that java compiler itself uses & therefore they are automatically imported. They include classes for primitive types, strings, maths function, threads &exception. java .util Language Utility classes such as vector, hash tables ,random numbers, date etc. java.io Input /Output support classes. They provide facilities for the input & output of data java.awt Set of classes for implementing graphical user interface. They include classes for windows, buttons, list, menus & so on. java.net Classes for networking. They include classes for communicating with local computers as well as with internet servers. java.applet Classes for creating & implementing applets.
- 8. 2. USER DEFINED PACKAGES : The users of the Java language can also create their own packages. They are called user-defined packages. User defined packages can also be imported into other classes & used exactly in the same way as the Built in packages. i) Creating User Defined Packages Syntax : package packageName; public class className { - - - - - - - - - - - - - // Body of className - - - - - - - - - - - - } We must first declare the name of the package using the package keyword followed by the package name. This must be the first statement in a Java source file. Then define a classes as normally as define a class.
- 9. Example : package myPackage; public class class1 { - - - - - - - - - - - - - // Body of class1 } In the above example, myPackage is the name of the package. The class class1 is now considered as a part of this package. This listing would be saved as a file called class1.java & located in a directory named mypackage. When the source file is compiled, java will create a .class file & store it in the same directory. The .class files must be located in a directory that has the same name as the package & this directory should be a subdirectory of the directory where classes that will import the package are located.
- 10. STEPS FOR CREATING PACKAGE : To create a user defined package the following steps should be involved :- 1: Declare the package at the beginning of a file using the syntax :- package packageName; 2: Define the class that is to be put in the package & declare it public. 3: Create a subdirectory under the directory where the main source files are stored. 4: Store the listing as the classname.java file in the subdirectory created. 5: Compile the file. This create .class file in the subdirectory.
- 11. Java also supports the concept of package hierarchy. This is done by specifying multiple names in a package statement, seprated by dots (.). Ex :- package firstPackage.secondPackage; This approach allows us to group related classes into a package and their group related package into a larger package. Store this package in a subdirectory named firstpackage/secondPackage. A java package file can have more than one class definition. In such cases, only one of the classes may be declared public & that class name with .java extension is the source file name. When a source file with more than one class definition is compiled, java creates independent .class files for those classes.
- 12. ACCESSING A PACKAGE Java package can be accessed either using a fully qualified class name or using a shortcut approach through the import statement. Syntax : import package1[.package2][.package3].classname; Here, package1 is the name of the top level package, package2 is the name of the package that is inside the package & so on. We can have any number of packages in a package hierarchy. Finally the explicit classname is specified. The import statement must end with a semicolon (;). The import startment should appear before any class definitions in a source file. Multiple import statements are allowed. Ex : import firstpackage.secondPackage.Myclass; or import firstpackage;
- 13. ADVANTAGES OF PACKAGES There are several advantages of package some of them are as follow :- 1: Packages are useful to arrange related classes and interface into a group. This makes all the classes & interface performing the same task to put together in the same package. 2: Packages hide the classes & interfaces in a seprate subdirectory, so that accidental deletion of classes & interfaces will not take place. 3: The classes & interfaces of a packages are isolated form the classes & interfaces of another packages. This means that we can use same names for classes of two different classes. 4: A group of packages is called a library. The classes & interface of a package are like books in a library & can be reused several times. This reusability nature of packages makes programming easy.
- 14. Importing a Package If we want to use a package in Java program it is necessary to import that package at the top of the program by using the import keyword before the package name. Syntax: import packageName;
- 15. SIMPLE EXAMPLE OF JAVA PACKAGE The package keyword is used to create a package in java. /save as Simple.java package mypack; public class Simple{ public static void main(String args[]){ System.out.println("Welcome to package"); } }
- 16. EXAMPLE OF PACKAGE BY IMPORT PACKAGE.CLASSNAME //save by A.java package pack; public class A{ public void msg() { System.out.println("Hello");} } //save by B.java package mypack; import pack.A; class B{ public static void main(String args[]){ A obj = new A(); obj.msg(); } } Output: Hello
- 17. Thank You…










![ACCESSING A PACKAGE
Java package can be accessed either using a fully qualified class
name or using a shortcut approach through the import statement.
Syntax :
import package1[.package2][.package3].classname;
Here, package1 is the name of the top level package, package2 is
the name of the package that is inside the package & so on. We
can have any number of packages in a package hierarchy. Finally
the explicit classname is specified. The import statement must
end with a semicolon (;). The import startment should appear
before any class definitions in a source file. Multiple import
statements are allowed.
Ex :
import firstpackage.secondPackage.Myclass; or
import firstpackage;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javapackage-241105150517-640fef33/85/java-package-in-java-in-java-packages-12-320.jpg)


![SIMPLE EXAMPLE OF JAVA
PACKAGE
The package keyword is used to create a
package in java.
/save as Simple.java
package mypack;
public class Simple{
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println("Welcome to package");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javapackage-241105150517-640fef33/85/java-package-in-java-in-java-packages-15-320.jpg)
![EXAMPLE OF PACKAGE BY IMPORT
PACKAGE.CLASSNAME
//save by A.java
package pack;
public class A{
public void msg()
{
System.out.println("Hello");}
}
//save by B.java
package mypack;
import pack.A;
class B{
public static void main(String args[]){
A obj = new A();
obj.msg();
}
}
Output: Hello](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javapackage-241105150517-640fef33/85/java-package-in-java-in-java-packages-16-320.jpg)
