Java threads
- 1. THREADS Mr.V.M.Prabhakaran, Department of CSE, KIT- Coimbatore
- 2. INTRODUCTION • A thread is an independent path of execution within a program. • Many threads can run concurrently within a program. • Every thread in Java is created and controlled by the java.lang.Thread class. • A Java program can have many threads, and these threads can run concurrently, either asynchronously or synchronously.
- 3. • Thread is a lightweight sub process • It is a separate path of execution. • Threads are independent, if there occurs exception in one thread, it doesn't affect other threads. It shares a common memory area. • Thread is executed inside the process. There is context- switching between the threads. There can be multiple processes inside the OS and one process can have multiple threads.
- 4. Multitasking and Multithreading • Multitasking: – refers to a computer's ability to perform multiple jobs concurrently – more than one program are running concurrently, e.g., UNIX • Multithreading: – A thread is a single sequence of execution within a program – refers to multiple threads of control within a single program – each program can run multiple threads of control within it, e.g., Web Browser 4
- 5. Concurrency vs. Parallelism 5 CPU CPU1 CPU2
- 6. What are Threads Good For? • To maintain responsiveness of an application during a long running task • To enable cancellation of separable tasks • Some problems are intrinsically parallel • To monitor status of some resource (e.g., DB) • Some APIs and systems demand it (e.g., Swing) 6
- 7. Advantage of Java Multithreading 1) It doesn't block the user because threads are independent and you can perform multiple operations at same time. 2) You can perform many operations together so it saves time. 3) Threads are independent so it doesn't affect other threads if exception occur in a single thread.
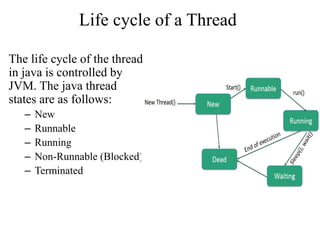
- 8. Life cycle of a Thread The life cycle of the thread in java is controlled by JVM. The java thread states are as follows: – New – Runnable – Running – Non-Runnable (Blocked) – Terminated
- 10. Life cycle of a Thread (Contd) • New: A new thread begins its life cycle in the new state. It remains in this state until the program starts the thread. It is also referred to as a born thread. • Runnable: After a newly born thread is started, the thread becomes runnable. A thread in this state is considered to be executing its task. • Waiting: Sometimes, a thread transitions to the waiting state while the thread waits for another thread to perform a task. A thread transitions back to the runnable state only when another thread signals the waiting thread to continue executing. • Timed waiting: A runnable thread can enter the timed waiting state for a specified interval of time. A thread in this state transitions back to the runnable state when that time interval expires or when the event it is waiting for occurs. • Terminated ( Dead ): A runnable thread enters the terminated state when it completes its task or otherwise terminates.
- 11. Daemon thread • Daemon thread is a low priority thread (in context of JVM) that runs in background to perform tasks such as garbage collection. • JVM terminates itself when all user threads (non-daemon threads) finish their execution, JVM does not care whether Daemon thread is running or not,
- 12. Thread Priority • When a Java thread is created, it inherits its priority from the thread that created it. • You can modify a thread’s priority at any time after its creation using the setPriority method. • Thread priorities are integers ranging between • MIN_PRIORITY (1) • NORM_PRIORITY (5) • MAX_PRIORITY (10)
- 13. Creating Threads • There are two ways to create our own Thread object – By extending Thread class – By implementing Runnable interface. • In both cases the run() method should be implemented
- 14. Commonly used Constructors of Thread class • Thread() • Thread(String name) • Thread(Runnable r) • Thread(Runnable r,String name)
- 15. Extending Thread SYNTAX class Mythread extends Thread { public void run(){ -------------- -------------- -------------- -------------- } } PROGRAM class Multi extends Thread{ public void run(){ System.out.println("thread is running ..."); } public static void main(String args[]){ Multi t1=new Multi(); t1.start(); } } Output: thread is running...
- 16. Thread Methods void start() – Creates a new thread and makes it runnable – This method can be called only once void run() – The new thread begins its life inside this method void stop() (deprecated) – The thread is being terminated
- 17. Thread Methods void yield() – Causes the currently executing thread object to temporarily pause and allow other threads to execute – Allow only threads of the same priority to run void sleep(int m) or sleep(int m, int n) – The thread sleeps for m milliseconds, plus n nanoseconds
- 18. Thread Methods • public void start() • public void run() • public final void setName(String name) • public final void setPriority(int priority) • public final void setDaemon(boolean on) • public final void join(long millisec) • public void interrupt() • public final boolean isAlive() • public static void yield() • public static void sleep(long millisec) • public static boolean holdsLock(Object x) • public static Thread currentThread() • public static void dumpStack()
- 19. Implementing Runnable class Multi3 implements Runnable{ public void run(){ System.out.println("thread is running..."); } public static void main(String args[]){ Multi3 m1=new Multi3(); Thread t1 =new Thread(m1); t1.start(); } } Output: thread is running...













![Extending Thread
SYNTAX
class Mythread extends Thread
{
public void run(){
--------------
--------------
--------------
--------------
}
}
PROGRAM
class Multi extends Thread{
public void run(){
System.out.println("thread is running
...");
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Multi t1=new Multi();
t1.start();
}
}
Output: thread is running...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javathreads-181116052046/85/Java-threads-15-320.jpg)



![Implementing Runnable
class Multi3 implements Runnable{
public void run(){
System.out.println("thread is running...");
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Multi3 m1=new Multi3();
Thread t1 =new Thread(m1);
t1.start();
}
}
Output: thread is running...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javathreads-181116052046/85/Java-threads-19-320.jpg)