JavaFX in Action Part I
- 1. 1 JavaFX in Action Part I Hossein Rimaz K.N. Toosi University of Technology
- 2. 2 Table of Contents • Why JavaFX and Use Cases • JavaFX App Architecture • Hello World • JavaFX Shapes • Recursive Graphic • Quick Introduction to Java 8 Lambda • Event-Driven Programming • Design Patterns and Observer • Properties & Bindings • Simple Graph Editor
- 3. 3 Why JavaFX and Use Cases
- 4. 4 History of JavaFX Using Google Trends JavaFX Script 1.0 JavaFX 2.0 JavaFX 8
- 5. 5 Where can you use JavaFX? Basically everywhere! ● Desktop Applications ● Mobile (with Gluon Mobile) ● Web Application (require plug-ins but JPro doesn’t need any!) ● Embedded System (even ARM)
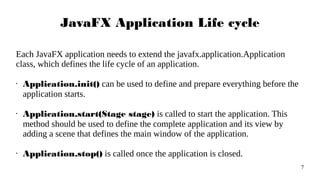
- 7. 7 JavaFX Application Life cycle Each JavaFX application needs to extend the javafx.application.Application class, which defines the life cycle of an application. • Application.init() can be used to define and prepare everything before the application starts. • Application.start(Stage stage) is called to start the application. This method should be used to define the complete application and its view by adding a scene that defines the main window of the application. • Application.stop() is called once the application is closed.
- 8. 8 Structure of a JavaFX Application
- 9. 9 Strange Names? Not at all! Think about it as a theater stage! You have a stage; actors (Nodes) come into the scene and going out of it. And well this is a play, scene goes in and goes out! Just as simple as it is!
- 10. 10 Hello World
- 11. 11 Creating a JavaFX Application
- 12. 12
- 13. 13
- 14. 14 Final Result That was a simple hello world that probably you have no idea about it! But the result is actually pretty!
- 15. 15 JavaFX Shapes
- 16. 16 JavaFX Shapes Well, let’s start a little bit simpler. ● Let’s just draw lines!
- 17. 17 Be careful about what package you are importing!
- 18. 18 JavaFX Shapes How about adding some loops?
- 19. 19 Final Result
- 20. 20 More Shapes
- 22. 22 Recursive Graphics ● You learned recursive programming and now you can apply those techniques to achieve stunning visual arts!
- 23. 23 Drawing a Tree Source code at: https://github.com/mhrimaz/RecursiveTreeFX
- 24. 24 Sierpinski Carpet Source code at : https://github.com/mhrimaz/SierpinskiCarpetFX
- 25. 25 Quick Introduction to Java 8 Lambda
- 26. 26 Java 8 New Features ● Lambda expressions ● Method references ● Default Methods (Defender methods) ● A new Stream API. ● Optional ● A new Date/Time API. ● Nashorn, the new JavaScript engine ● Removal of the Permanent Generation ● and more…
- 27. 27 Lambda Expression ● A primary goal of lambdas is to help address the lack in the Java language of a good way to express functional programming concepts.
- 28. 28 Syntax ● There are two ways to specify lambda expressions. The following simple examples illustrate the general forms: (param1, param2, ...) -> expression; (param1, param2, ...) -> { /* code statements */ }; ● Another thing to note is that parameters can be optionally typed. The compiler will infer the type of the parameters depending on the context.
- 29. 29 Why Lambda? ● In event handling lambda expressions will makes our codes shorter and more expressive. ● Now you can understand NetBeans starter code better.
- 31. 31 What is Event-Driven Programming? ● Until now, you may only wrote your programs in imperative way. Your code flow was deterministic and run line after another. ● Event-driven programming is a programming paradigm in which the flow of the program is determined by events such as user actions (mouse clicks, key presses), sensor outputs, or messages from other programs/threads. ● Event-driven programming is the dominant paradigm used in graphical user interfaces and other applications that are centered on performing certain actions in response to user input.
- 32. 32 Simple Example ● Simple scenario: mouse goes in, performs a double click and goes out.
- 33. 33 Design Patterns and Observer
- 34. 34 What is Design Pattern? ● In software engineering, a design pattern is a general repeatable solution to a commonly occurring problem in software design. A design pattern isn't a finished design that can be transformed directly into code. It is a description or template for how to solve a problem that can be used in many different situations. ● Design patterns can speed up the development process by providing tested, proven development paradigms. ● In addition, patterns allow developers to communicate using well- known, well understood names for software interactions.
- 35. 35 GoF 23 Design Patterns Creational patterns – Abstract Factory – Builder – Factory Method – Prototype – Singleton Structural patterns – Adapter – Bridge – Composite – Decorator – Façade – Flyweight – Proxy Behavioral patterns – Chain of responsibility – Command – Interpreter – Iterator – Mediator – Memento – Observer – State – Strategy – Template method – Visitor
- 36. 36 Design Pattern and JavaFX ● Well you’ve used many of them in your development without knowing their names. ● Knowing about observer design pattern can help you to understand JavaFX Properties & Bindings and It’s Observable collections better. ● If you want to learn more Please read this book: Java Design Patterns by Vaskaran Sarcar
- 37. 37 Observer Design Pattern ● GoF Definition: Define a one-to-many dependency between objects so that when one object changes state, all its dependents are notified and updated automatically. ● Concept: In this pattern, there are many observers (objects) which are observing a particular subject (object). Observers are basically interested and want to be notified when there is a change made inside that subject. So, they register themselves to that subject. When they lose interest in the subject they simply unregister from the subject. Sometimes this model is also referred to as the Publisher-Subscriber model.
- 38. 38 Computer World Example ● In the world of computer science, consider a simple UI-based example, where this UI is connected with some database (or business logic). A user can execute some query through that UI and after searching the database, the result is reflected back in the UI. In most of the cases we segregate the UI with the database. If a change occurs in the database, the UI should be notified so that it can update its display according to the change.
- 39. 39 UI Patterns ● Graphical user interfaces have become a familiar part of our software landscape, both as users and as developers. Looking at it from a design perspective they represent a particular set of problems in system design - problems that have led to a number of different but similar solutions. ● When developing GUI applications you will inevitably encounter UI architectural framework concepts such as model view controller (MVC), model view presenter (MVP), or model view view-model (MVVM).
- 41. 41 Properties & Bindings ● Properties are basically wrapper objects for JavaFX-based object attributes such as String or Integer. Properties allow developers to add listener code to respond when the wrapped value of an object has changed or is flagged as invalid. Also, property objects can be bound to one another. ● Binding behavior allows properties to update or synchronize their values based on a changed value from another property.
- 42. 42 Types of JavaFX Properties ● Read/Writable ● Read-Only ● JavaFX’s properties are wrapper objects holding actual values while providing change support, invalidation support, and binding capabilities. ● Some Property Classes: – javafx.beans.property.SimpleIntegerProperty – javafx.beans.property.ReadOnlyIntegerWrapper – javafx.beans.property.SimpleDoubleProperty – javafx.beans.property.ReadOnlyDoubleWrapper – javafx.beans.property.SimpleStringProperty – javafx.beans.property.ReadOnlyStringWrapper
- 43. 43 Example Output: StringProperty Value = password1 observable = StringProperty [value: 1234] oldValue = password1 newValue = 1234
- 44. 44 Bindings ● binding has the idea of at least two values (properties) being synchronized. This means that when a dependent variable changes, the other variable changes. ● JavaFX provides many binding options that enable the developer to synchronize between properties in domain objects and GUI controls.
- 45. 45 Types of JavaFX Bindings ● Simple Binding ● Bidirectional Binding
- 46. 46 Example ● Binding String length to a Integer Property
- 47. 47 Simple Graph Editor Source code at: https://github.com/mhrimaz/JavaFXWorkshop_01








































![43
Example
Output:
StringProperty Value = password1
observable = StringProperty [value: 1234]
oldValue = password1
newValue = 1234](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javafx-161219073222/85/JavaFX-in-Action-Part-I-43-320.jpg)



