Large scale agile development practices
- 1. EXPERIENCE REPORT: LARGE SCALE AGILE DEVELOPMENT PRACTICES Daphne Chong (@daphnechong) Niall Connaughton (@nconnaughton)
- 2. What was the project? C# Winforms SQL Server database Large CRUD system App deployed to client sites Started in 2001 Market leading product
- 3. What was the project? Low volume Performance important, but not critical Goal was a stable, consistent, feature-rich app Rapid release cycle (after any successful build)
- 4. In 2006… 60 Developers 5 million lines of code (including tests) ~100 solutions, 250 projects 300+ db tables 160,000 automated tests
- 5. Today… 60 Developers ~10 million lines of code 485 solutions 470 db tables 343,090 automated tests
- 6. The Pit of Success We want our customers to simply fall into winning practices by using our platform and frameworks – Rico Mariani Build platforms [where] developers just fall into doing the “right thing”... Types should be defined with a clear contact that communicates effectively how they are to be used (and how not to) – Brad Abrams
- 7. Pit of Success – Technical Factors Inheritance Template Method pattern Strict naming conventions Common reusable controls Own type system Single generic repository – handled common scenarios in CRUD, transactions, referential integrity, caching, persistence
- 8. Pit of Success Tried to avoid too much divergence in code Made it difficult for people to stray from the “true path”
- 12. Consistency 70 % of a dev’s time is understanding existing code – Peter Hallam [2] If you can reduce that even by a small amount, it’s significant productivity gain
- 13. Consistency Consistent approach to everything Naming conventions – project, solutions, file locations, namespaces, class names, methods, database tables and columns Formatting UI look and feel (achieved through base controls) Patterns of design
- 14. Consistency Standardised on a core set of technologies that best fit the application Avoided “technology soup” support and maintenance Reduced learning curve for new developers
- 15. Insane things we did 60 devs, no feature branches! SourceSafe Highly sensitive to the build breaking True continuous integration Mitigated by clients opting in to “alpha”, “beta” or “stable” versions Two large re-writes of architecture Result was more suited to our needs than if we had kept the first and refactored it progressively
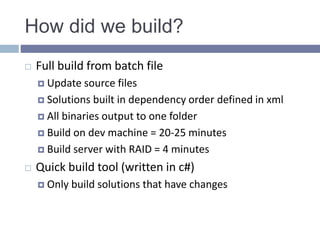
- 16. How did we build? Full build from batch file Update source files Solutions built in dependency order defined in xml All binaries output to one folder Build on dev machine = 20-25 minutes Build server with RAID = 4 minutes Quick build tool (written in c#) Only build solutions that have changes
- 17. Development - Architecture Built our own architecture Re-usable controls Comprehensive base classes Own type system Primitive types as well as Custom types Could define helper methods .IsEmpty, .SubstringSafe() , IsInRange()
- 18. Development - Architecture Architecture constantly extended Approach was always unified though the architecture Enabled good ideas to have widespread effect
- 19. Development – Technical debt Management support for improving bad code Aggressive attitude to technical debt Very little dead code Example: methods with 7 overloads that can’t be deleted because don’t know who’s consuming them
- 20. Development – Technical debt Constant small amount of pain Rare occurrences of large amounts of pain Once a hard cost has been paid, make sure that nobody ever has to pay the cost again
- 21. Development - Custom Tools Automated repetitive and error prone tasks Custom ORM generator Database upgrading tool GUI binding helpers to ensure targets exist Build monitor system tray application Code Generators for new modules Automated deployment tool
- 22. Testing Two types of tests Business Tests: user functionality Meta Tests: code design and contracts
- 23. Testing Most of our tests were actually integration tests of varying scope Didn’t use a mocking framework (not yet well known) Created our own stubs by inheriting from the concrete class and overriding any methods that used resources, etc.
- 24. Business Tests Generally state based logic Easy to read and write Fairly resilient throughout refactoring Derived from a base TestCase with ~25 basic tests Array properties don’t return null Properties don’t throw NullReferenceExceptions Don’t alter the state of the object before shown in GUI
- 25. Business Tests - Example
- 26. Meta Tests Don’t test direct functionality Enforced consistency, patterns and code contracts Implemented using reflection and attributes Slow to run, but very valuable
- 27. Meta Tests – Examples Check code conforms to conventions and contracts Public constructor with a specific parameter exists Assemblies are strong named Check for memory leaks Check that each model had an associated test [TestsSubclassesOf(typeof(BusinessBase))] public abstract class BusinessBaseTest { // contract tests here }
- 28. Meta Tests The Meta Tests help to enforce the rules, rather than having a “bad cop” in your team Not political or personal Once established, it gave power to the rest of the team to contribute new tests and rules
- 29. Meta Tests Allowed the architecture to grow rapidly Already know the code conforms to a particular standard
- 30. How do you run 343,000 tests? Initial approach similar to CruiseControl One machine building and running all tests Results emailed after completion … stalled once we hit 25,000 tests … Took 4 hrs to run Feedback cycle wasn’t fast enough
- 31. Growth of Tests
- 32. Distributed Testing Framework Highly customised Tests distributed to up to 60 agents Build time around 1 hour if built on single agent = 30-40 hours Package on successful build Agents ran on idle developer machines Ran 24/7
- 34. Distributed Testing Framework Developer submitted builds could be processed (i.e. pre-checkin) Task tray to signal progress Red light = broken tests, broken build or checkin embargo Green light = OK to check in
- 35. Team Very Flat structure 6-8 devs in architecture team (“Blue Code”) Business & GUI architecture Development tools Testing framework Database development Upgrading code Most other developers building business rules into software (“Red Code”)
- 36. Architecture vs Business teams
- 37. Team - Architecture Made up less than 20% of team Improved productivity by much more than 20% Allowed devs to focus on smaller slice of stack and get quicker feedback cycles
- 38. Team - Business Low barrier to entry for development Junior or new developers could be productive very quickly Varied skill sets in the team were utilitsed accordingly Technically minded people drawn to architecture Business minded people focused on implementing customer requirements
- 39. Team – Sharing Information Free flowing collaboration Some development overhead in helping other people Some information silo-ing
- 40. Team – Pair Programming Initially strict pairing Became “organic” Not enforced Never discouraged
- 41. Team – Work Ethic People took a lot of responsibility and accountability of their own accord Boy scout rule – leave things cleaner than when you found it Always fix broken windows
- 42. Work satisfaction Low turnover rates for first 4 years Lots of smart people to work with More meritocracy than political Developers took pride in their work Ability to implement large scale change open to everyone
- 43. Work Satisfaction – flip side Hard to have interesting work for 60 developers Could be pigeon-holed into the business layer More stress than an average agile environment Long work hours implied because there’s only one build – responsibility to keep the dev machine going. No leaving the build broken or failing tests throughout lunch or overnight.
- 44. Conclusion Team made a lot of investment in design and conformity Easy to do with a CRUD system, harder with other types of business software Project has expanded and moved on, but the architecture has evolved with it and is still in use
- 45. Thanks to… Zubin Appoo Senior Manager, Product Development www.cargowise.com
- 46. References [1] Brad Abrams, The Pit of Success http://blogs.msdn.com/b/brada/archive/2003/10/02/50420.aspx [2] Peter Hallam, What do Programmers Really do Anyway? http://blogs.msdn.com/b/peterhal/archive/2006/01/04/509302.aspx
Editor's Notes
- #40: \






![The Pit of Success
We want our customers to simply fall into winning
practices by using our platform and frameworks
– Rico Mariani
Build platforms [where] developers just fall into
doing the “right thing”... Types should be defined
with a clear contact that communicates effectively
how they are to be used (and how not to)
– Brad Abrams](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/largescaleagiledevelopmentpractices-101130103104-phpapp02/85/Large-scale-agile-development-practices-6-320.jpg)





![Consistency
70 % of a dev’s time is understanding existing code
– Peter Hallam [2]
If you can reduce that even by a small amount, it’s
significant productivity gain](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/largescaleagiledevelopmentpractices-101130103104-phpapp02/85/Large-scale-agile-development-practices-12-320.jpg)













![Meta Tests – Examples
Check code conforms to conventions and contracts
Public constructor with a specific parameter exists
Assemblies are strong named
Check for memory leaks
Check that each model had an associated test
[TestsSubclassesOf(typeof(BusinessBase))]
public abstract class BusinessBaseTest
{
// contract tests here
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/largescaleagiledevelopmentpractices-101130103104-phpapp02/85/Large-scale-agile-development-practices-27-320.jpg)


















![References
[1] Brad Abrams, The Pit of Success
http://blogs.msdn.com/b/brada/archive/2003/10/02/50420.aspx
[2] Peter Hallam, What do Programmers Really do Anyway?
http://blogs.msdn.com/b/peterhal/archive/2006/01/04/509302.aspx](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/largescaleagiledevelopmentpractices-101130103104-phpapp02/85/Large-scale-agile-development-practices-46-320.jpg)