Learn Basics of chemistry myassignmenthelp.net
- 1. Basics Of Chemistry www.myassignmenthelp.net
- 2. Early Chemistry Early Chemists only believed in 1 element: Dirt Later Chemists believed in 4 elements: Air Earth Fire Water Various combinations of these produced various compounds www.myasignmenthelp.ne t
- 3. Basic Chemistry All Matter in universe is composed of Atoms. Elements are composed of only 1 type of atom. Atoms are mostly empty space. Atoms have Electrons which are very small and are negatively charged and have a negligible mass (mass = 0). Electrons move in orbits around the center of the atom - in relatively distinct areas called Energy Levels.(aka. Orbits or shells) The farther from the center an electron is the more energy it has. Electrons (& therefor atoms, can gain and lose energy) and do this by moving between energy levels. Atoms have a Nucleus which contain Protons & Neutrons. Protons are Positively Charged and have a mass=1 The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus determines what element it is Neutrons have no charge and are therefor called Neutral and have a mass = 1.
- 4. Summary of Subatomic Particles: Particle Name Location Charge Mass Electron Orbitals -1 ~0 Proton Nucleus +1 1 Neutron Nucleus No Charge 1
- 5. Periodic Table Notation: Chemical elements are represented on the periodic table using the following format. The letter is an abbreviation of Element Name Atomic Number is the number is the number of protons the atom has. It is the number of protons an element has which determines what element it is. Mass Number is the total mass of an atom in AMU. It is the same as the number of protons & neutrons of the element. One can calculate the number of neutrons an atom has by subtracting the atomic number (# protons) from the mass number. Mass number CAN change without changing the identity of the element.
- 6. Isotopes: Atoms having the same atomic numbers and different mass numbers are called Isotopes Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons (mass). They react chemically the same as the “normal” form of the element They are frequently radioactive Isotopes of Hydrogen
- 7. Interactions of matter: Atoms interact through the process of chemical bonding. Process is determined by the number of electrons found in the outermost energy level of an atom. Involves the transfer & sharing of electrons between atoms.
- 8. ELECTRON / ENERGY LEVEL RULES: Atoms in a neutral state have an equal number of protons and electrons. Atoms “fill up” their energy levels from the lowest to the highest. Electrons rarely “skip” levels. The 1st Energy level can only hold 2 electrons The 2nd (& all higher) energy levels can only hold 8 electrons Atoms seek to have a “full” outermost energy level. All chemical reactions happen to accomplish this
- 9. Chemical Bonds When a Chemical Reaction occurs atoms gain, lose or share electrons Atoms always want to have their outer energy level “full” of electrons When an atom has a different number of protons & electrons it is called an Ion. If an ion has more protons than electrons - it is Positively Charged If an atom has more electrons than protons it is Negatively Charged. Atoms of opposite charge are attracted to each other. There are three types of chemical bonds. Ionic bonds, Covalent Bonds, & Metallic Bonds.
- 10. Ionic Bonds: Ionic bonds form when 1 atom “gives” one or more electrons to another atom to complete their outer energy levels. This results in 1 positively charged ion & 1 negatively charged ion Since opposite charges attract, they come together and bond.
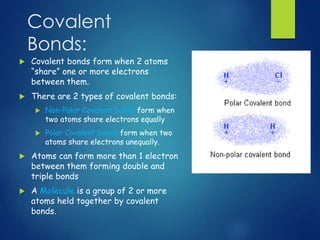
- 11. Covalent Bonds: Covalent bonds form when 2 atoms “share” one or more electrons between them. There are 2 types of covalent bonds: Non-Polar Covalent bonds form when two atoms share electrons equally Polar Covalent bonds form when two atoms share electrons unequally. Atoms can form more than 1 electron between them forming double and triple bonds A Molecule is a group of 2 or more atoms held together by covalent bonds.
- 12. Summary of Ionic & Covalent Bonds
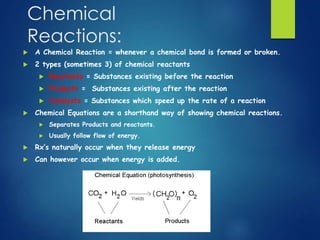
- 13. Chemical Reactions: A Chemical Reaction = whenever a chemical bond is formed or broken. 2 types (sometimes 3) of chemical reactants Reactants = Substances existing before the reaction Products = Substances existing after the reaction Catalysts = Substances which speed up the rate of a reaction Chemical Equations are a shorthand way of showing chemical reactions. Separates Products and reactants. Usually follow flow of energy. Rx’s naturally occur when they release energy Can however occur when energy is added.
- 14. Structural and Chemical Formulas: Chemical formulas show the number of and types of atoms in a molecule Structural Formulas are used to graphically represent a chemical formula Useful in visualizing how chemicals react and form new ones. When drawing them use the following rules: The Periodic table abbreviation is used to represent the atoms. A single strait line (---) represents a single bond Two parallel strait lines (==) represent double bonds
- 15. Example FCohermmicaul Nlaames: Chemical Formula Structural Formula Water H2O Carbon Dioxide CO2 Methane CH4 Glucose C6H12O6