Lecture 01 introduction to database
- 1. Lecture 1 File Systems and Databases
- 2. In this lecture, you will learn: What a database is, what it does, and why database design is important How modern databases evolved from files and file systems About flaws in file system data management What a DBMS is, what it does, and how it fits into the database system About types of database systems and database models
- 3. Introducing the Database Data versus Information Data constitute building blocks of information Information produced by processing data Information reveals meaning of data Good, timely, relevant information key to decision making Good decision making key to organizational survival
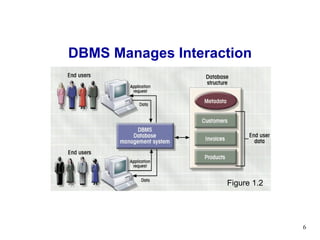
- 4. Database Management Database is shared, integrated computer structure housing: End user data Metadata Database Management System (DBMS) Manages Database structure Controls access to data Contains query language
- 5. Importance of DBMS Makes data management more efficient and effective Query language allows quick answers to ad hoc queries Provides better access to more and better-managed data Promotes integrated view of organization’s operations Reduces the probability of inconsistent data
- 6. DBMS Manages Interaction Figure 1.2
- 7. Database Design Importance of Good Design Poor design results in unwanted data redundancy Poor design generates errors leading to bad decisions Practical Approach Focus on principles and concepts of database design Importance of logical design
- 8. Historical Roots of Database First applications focused on clerical tasks Requests for information quickly followed File systems developed to address needs Data organized according to expected use Data Processing (DP) specialists computerized manual file systems
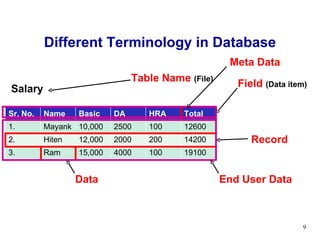
- 9. Different Terminology in Database Salary Table Name (File) Field (Data item) Record Data End User Data Meta Data Sr. No. Name Basic DA HRA Total 1. Mayank 10,000 2500 100 12600 2. Hiten 12,000 2000 200 14200 3. Ram 15,000 4000 100 19100
- 10. File Terminology Data Raw Facts Field Group of characters with specific meaning Record Logically connected fields that describe a person, place, or thing File Collection of related records
- 11. Simple File System Figure 1.5
- 12. File System Critique File System Data Management Requires extensive programming in third-generation language (3GL) Time consuming Makes ad hoc queries impossible Leads to islands of information
- 13. File System Critique (con’t.) Data Dependence Change in file’s data characteristics requires modification of data access programs Must tell program what to do and how Makes file systems cumbersome from programming and data management views Structural Dependence Change in file structure requires modification of related programs
- 14. File System Critique (con’t.) Field Definitions and Naming Conventions Flexible record definition anticipates reporting requirements Selection of proper field names important Attention to length of field names Use of unique record identifiers
- 15. File System Critique (con’t.) Data Redundancy Different and conflicting versions of same data Results of uncontrolled data redundancy Data anomalies Modification Insertion Deletion Data inconsistency Lack of data integrity
- 16. Database Systems Database consists of logically related data stored in a single repository Provides advantages over file system management approach Eliminates inconsistency, data anomalies, data dependency, and structural dependency problems Stores data structures, relationships, and access paths
- 17. Database vs. File Systems Figure 1.6
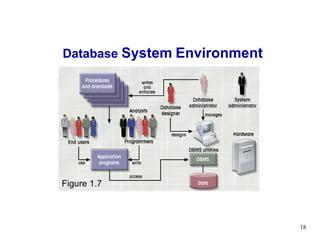
- 18. Database System Environment Figure 1.7
- 19. Database System Types Single-user vs. Multiuser Database Desktop Workgroup Enterprise Centralized vs. Distributed Use Production or transactional Decision support or data warehouse
- 20. DBMS Functions Data dictionary management Data storage management Data transformation and presentation Security management Multiuser access control Backup and recovery management Data integrity management Database language and application programming interfaces Database communication interfaces
- 21. Database Models Collection of logical constructs used to represent data structure and relationships within the database Conceptual models: logical nature of data representation Implementation models: emphasis on how the data are represented in the database
- 22. Relationships in Conceptual Models One-to-one (1:1) One-to-many (1:M) Many-to-many (M:N) Implementation Database Models Hierarchical Network Relational Database Models (con’t.)
- 23. Hierarchical Database Model Logically represented by an upside down tree Each parent can have many children Each child has only one parent Figure 1.8
- 24. Hierarchical Database Model Advantages Conceptual simplicity Database security and integrity Data independence Efficiency Disadvantages Complex implementation Difficult to manage and lack of standards Lacks structural independence Applications programming and use complexity Implementation limitations
- 25. Network Database Model Each record can have multiple parents Composed of sets Each set has owner record and member record Member may have several owners Figure 1.10
- 26. Network Database Model Advantages Conceptual simplicity Handles more relationship types Data access flexibility Promotes database integrity Data independence Conformance to standards Disadvantages System complexity Lack of structural independence
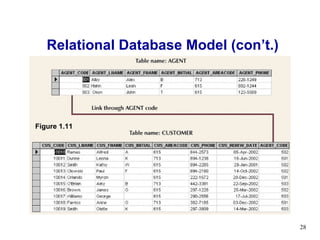
- 27. Relational Database Model Perceived by user as a collection of tables for data storage Tables are a series of row/column intersections Tables related by sharing common entity characteristic(s)
- 28. Relational Database Model (con’t.) Figure 1.11
- 29. Relational Database Model Advantages Structural independence Improved conceptual simplicity Easier database design, implementation, management, and use Ad hoc query capability with SQL Powerful database management system
- 30. Relational Database Model Disadvantages Substantial hardware and system software overhead Poor design and implementation is made easy May promote “islands of information” problems
- 31. Entity Relationship Database Model Complements the relational data model concepts Represented in an entity relationship diagram (ERD) Based on entities, attributes, and relationships Figure 1.13
- 32. Entity Relationship Database Model Advantages Exceptional conceptual simplicity Visual representation Effective communication tool Integrated with the relational database model Disadvantages Limited constraint representation Limited relationship representation No data manipulation language Loss of information content
- 33. Object-Oriented Database Model Objects or abstractions of real-world entities are stored Attributes describe properties Collection of similar objects is a class Methods represent real world actions of classes Classes are organized in a class hierarchy Inheritance is ability of object to inherit attributes and methods of classes above it
- 34. OO Data Model Advantages Adds semantic content Visual presentation includes semantic content Database integrity Both structural and data independence Disadvantages Lack of OODM Complex navigational data access Steep learning curve High system overhead slows transactions
- 35. Database Models and the Internet Characteristics of “Internet age” databases Flexible, efficient, and secure Internet access Easily used, developed, and supported Supports complex data types and relationships Seamless interfaces with multiple data sources and structures Simplicity of conceptual database model Many database design, implementation, and application development tools Powerful DBMS GUI make DBA job easier
Editor's Notes
- #23: 31