Lecture 04 data resource management
- 1. DATA RESOURCE MANAGEMENT Presented by: Dr. Akhlas Ahmed Lecture # 04 Preston University
- 2. File Organization: Terms & Concept Binary: means composed of two pieces or two parts and may refer to: Mathematics: Binary number, a representation for numbers using only two digits (0 and 1) Binary relation, a mathematical relation involving two elements Binary function, a function in mathematics that takes two arguments Computing Binary file, composed of something other than human-readable text Executable, a type of binary file that contains machine code for the computer to execute Binary code, the digital representation of text and data
- 3. File Organization: Terms & Concept Multiples of bits Decimal Value 1000 10002 10003 10004 10005 10006 10007 10008 Value 1024 10242 10243 10244 10245 10246 10247 8 Metric kbit Mbit Gbit Tbit Pbit Ebit Zbit Ybit Kbit Mbit Gbit - kilobit megabit gigabit terabit petabit exabit zettabit yottabit Binary JEDEC kilobit megabit gigabit - Kibit Mibit Gibit Tibit Pibit Eibit Zibit IEC kibibit mebibit gibibit tebibit pebibit exbibit zebibit
- 4. File Organization: Terms & Concept • Bit: A bit is the basic unit of information in computing and digital communications. A bit can have only one of two values, and may therefore be physically implemented with a twostate device. The most common representation of these values are 0and1. The term bit is a contraction of binary digit. Smallest unit of data; binary digit (0,1) Byte: Group of bits that represents a single character Field: Group of words or a complete number
- 5. File Organization: Terms & Concept Record: Group of related fields File: Group of records of same type Database: Group of related files
- 6. Data Hierarchy: in a Computer System Figure 7-1
- 7. File Organization: Terms & Concept Entity: Person, place, thing, event about which information is maintained Attribute: Description of a particular entity Key field: Identifier field used to retrieve, update, sort a record
- 8. ORGANIZING DATA: IN A TRADITIONAL FILE ENVIRONMENT Figure 7-2
- 9. Problems with the Traditional File Environment Data redundancy Data redundancy occurs in database systems which have a field that is repeated in two or more tables. o Program-Data dependence A Flow dependency, also known as a data dependency or true dependency or read-after-write (RAW), occurs when an instruction depends on the result of a previous instruction: 1. A = 3 2. B = A 3. C = B Lack of flexibility Poor security Lack of data-sharing and availability
- 11. Database Management System (DBMS) • Creates and maintains databases • Eliminates requirement for data definition statements • Acts as interface between application programs and physical data files • Separates logical and physical views of data
- 13. Components of DBMS • Data definition language: Specifies content and structure of database and defines each data element • Data manipulation language: Manipulates data in a database • Data dictionary: Stores definitions of data elements, and data characteristics
- 14. Sample Data Dictionary Report Figure 7-5
- 15. Types of Databases • Relational DBMS • Hierarchical and Network DBMS • Object-Oriented Databases
- 16. Relational DBMS • Represents data as two-dimensional tables called relations • Relates data across tables based on common data element • Examples: DB2, Oracle, MS SQL Server
- 17. Relational Data Model Figure 7-6
- 18. Three Basic Operations in a Relational Database • Select: Creates subset of rows that meet specific criteria • Join: Combines relational tables to provide users with information • Project: Enables users to create new tables containing only relevant information
- 19. Three Basic Operations in a Relational Database Figure 7-7
- 20. Hierarchical and Network DBMS Hierarchical DBMS • Organizes data in a tree-like structure • Supports one-to-many parent-child relationships • Prevalent in large legacy systems
- 22. Hierarchical and Network DBMS Network DBMS • Depicts data logically as many-to-many relationships
- 24. Hierarchical and Network DBMS Disadvantages Outdated Less flexible compared to RDBMS Lack support for ad-hoc and English language-like queries
- 25. Object-Oriented Databases Object-oriented DBMS: Stores data and procedures as objects that can be retrieved and shared automatically Object-relational DBMS: Provides capabilities of both object-oriented and relational DBMS
- 26. Querying Databases: Elements of SQL Basic SQL Commands SELECT: FROM: Specifies columns Identifies tables or views WHERE: Specifies conditions
- 27. Results of SELECT Statement
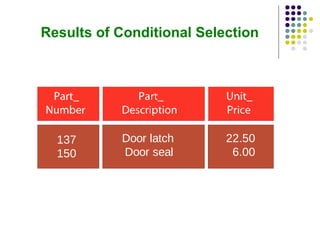
- 28. Results of Conditional Selection 137 150 Door latch Door seal 22.50 6.00
- 29. Projection from Joining PART and SUPPLIER Tables
- 30. Designing Databases Conceptual design: Abstract model of database from a business perspective Physical design: Detailed description of business information needs
- 31. Designing Databases Entity-relationship diagram: Methodology for documenting databases illustrating relationships between database entities Normalization: Process of creating small stable data structures from complex groups of data
- 34. CREATING A DATABASE ENVIRONMENT An Normalized Relation of ORDER Figure 7-15
- 35. Distributing Databases Centralized database Used by single central processor or multiple processors in client/server network
- 36. Distributing Databases Distributed database Stored in more than one physical location Partitioned database Duplicated database
- 38. Management Requirements for Database Systems Key elements in a database environment: Data Administration Data Planning and Modeling Methodology Database Technology and Management Users
- 39. Management Requirements for Database Systems Figure 7-17
- 40. Multidimensional Data Analysis On-line analytical processing (OLAP) Multidimensional data analysis Supports manipulation and analysis of large volumes of data from multiple dimensions/perspectives
- 41. Multidimensional Data Model Figure 7-18
- 42. Data Warehousing and Datamining Data warehouse Supports reporting and query tools Stores current and historical data Consolidates data for management analysis and decision making
- 43. Components of Data Warehouse Figure 7-19
- 44. Data Warehouse and data mining Data mart Subset of data warehouse Contains summarized or highly focused portion of data for a specified function or group of users
- 45. Data Warehouse and data mining Datamining Tools for analyzing large pools of data Find hidden patterns and infer rules to predict trends
- 46. Benefits of Data Warehouse Improved and easy accessibility to information Ability to model and remodel the data
- 47. Database and the web Hypermedia database • Organizes data as network of nodes • Links nodes in pattern specified by user • Supports text, graphic, sound, video and executable programs
- 48. Database Trends A Hypermedia Database Figure 7-20
- 49. Database Trends Databases and the Web Database server Computer in a client/server environment runs a DBMS to process SQL statements and perform database management tasks Application server Software handling all application operations
- 50. Database Trends Linking Internal Databases to the Web Figure 7-21
- 51. Thank You