Lecture 1_ EE 406 Introduction to Wireless Networking [Autosaved].pdf
- 1. SAINT AUGUSTINE UNIVERSITY OF TANZANIA FACULTY OF ENGINEERING ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING & INFORMATION SYSTEMS DEPARTMENT MODULE EE 406: WIRELESS TECHNOLOGY
- 2. Course Objective • To provide knowledge of different wireless technologies Expected outcomes: • Understand knowledge of different wireless technologies
- 3. Upon successful completion of the course, the student will be able to Comprehend concepts of all Wireless Communication techniques. Identify the Multiple Access Techniques for Wireless Communication. Illustrate the Development of wireless networks, WLAN &Bluetooth. Analyze the Wireless Data Services, Mobile IP and Wireless Access Protocol Illustrate the Mobile Data Networks, Wireless ATM & HiPER LAN.
- 4. Course Contents • Multiple Access Techniques For Wireless Communication: Introduction, FDMA, TDMA, Spread Spectrum, Multiple access, SDMA, Packet radio, Packet radio protocols, CSMA protocols, Reservation protocols • Introduction To Wireless Networking: Introduction, Difference between wireless and fixed telephone networks, Development of wireless networks, Traffic routing in wireless networks. • Wireless Data Services: CDPD, ARDIS, RMD, Common channel signalling, SS7, SS7 user part, signalling traffic in SS7.ISDN, BISDN and ATM, • Mobile Ip And Wireless Access Protocol: Mobile IP, Operation of mobile IP, Co-located address, Registration, Tunneling, WAP Architecture, overview, WML scripts, WAP service, WAP session protocol, wireless transaction, Wireless datagram protocol. • Wireless LAN Technology: Infrared LANs, Spread spectrum LANs, Narrow bank microwave LANs, IEEE 802 protocol Architecture, IEEE802 architecture and services, 802.11 medium access control, 802.11 physical layer. • Blue Tooth: Overview, Radio specification, Base band specification, Links manager specification, Logical link control and adaptation protocol. Introduction to WLL Technology. • Mobile Data Networks: Introduction, Data oriented CDPD Network, GPRS and higher data rates, Short messaging service in GSM, Mobile application protocol. • Wireless ATM & Hiper LAN: Introduction, Wireless ATM, HIPERLAN, Adhoc Networking and WPAN.
- 5. Recommended References/Textbooks 1. William Stallings, “Wireless Communication and Networking”, PHI, 2003. 2. Theodore, S. Rappaport, “Wireless Communications, Principles, Practice”, PHI, 2nd ed., 2002. 3. Kamilo Feher, “Wireless Digital Communications”, PHI, 1999. 4. Kaveh Pah Laven and P. Krishna Murthy, “Principles of Wireless Networks”, Pearson Education, 2002.
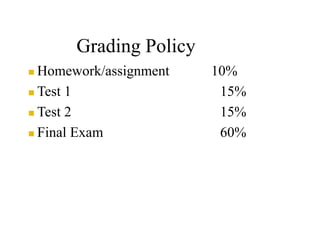
- 6. Grading Policy Homework/assignment 10% Test 1 15% Test 2 15% Final Exam 60%
- 7. What is communication Introduction •The word communication arises from the Latin word commūnicāre, which means “to share”. Communication is the basic step for exchange of information. •For example: – a baby in a cradle, communicates with a cry when she needs her mother. – A cow moos loudly when it is in danger. – A person communicates with the help of a language. – Communication is the bridge to share.
- 8. What is communication • The term communication (or telecommunication) means the transfer of some form of information by electrical means from one place (known as the source of information) to another place (known as the destination of information) using some system to do this function (known as a communication system). • Communication system is a system which describes the exchange of information or data between two stations, i.e. between transmitter and receiver.
- 9. What is communication System? • Communication system is a group (collection) of subsystems such us transmission subsystem, channel and receiver subsystem. They are designed and assembled in a proper manner for sending and receiving information signals. • Transmission subsystem: It is a group or collection of individual components and circuits such as information source, input transducer, modulator circuits (mixer, carrier signal generator and band pass filter), amplifiers and transmitting antenna etc. They are designed and assembled in a proper manner to convert the data/ information/ any physical quantity (carries some meaning of sense) into a suitable form for the transmission over the channel • Receiver subsystem: It is also a group or collection of individual components and circuits such as receiving antenna, amplifiers, demodulator circuits, low pass filter, output transducer and etc.
- 10. Basic Elements of Communication System
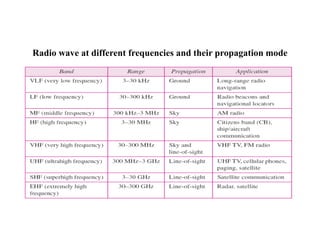
- 11. Radio wave at different frequencies and their propagation mode
- 12. Introduction to Wireless Networking M.D. Kabadi (Lecturer) 12
- 13. Agenda • Introduction to Wireless Communication • Wireless Technology • Wireless Networks • Wireless Wide Area Network( WWAN) • Wireless Metropolitan Area Network( WMAN) • Wireless Local Area Network( WLAN) • Wireless Person Area Network(WPAN) • Wireless Body Area Network ( WBAN) • Other wireless network such as Paging system and Cordless telephone systems • Trend on Wireless networks 13
- 14. What is the wireless communication ? • Any form of communication that does not require the physical contact between a transmitter and a receiver. Or the other words are the communication without wire • Mainly concerned with systems in the 300 MHz to 10 GHz range • Using the electromagnetic wave propagated through the – free space – Optical – laser, infrared – Radio Frequency – Acoustic – underwater communication 14
- 16. 16 Freq Spectrum Freq range Unit s Wavelength range Units VLF 3 30 Khz 100 10 Kilo meters Low freq 30 300 Khz 10 1 Kilo meters M4edium Frequency 300 3000 Khz 1 0.1 Kms High freq 3 30 MHz 100 10 meters VHF 30 300 MHz 10 1 meter UHF 300 3000 MHz 100 10 meter SHF 3 30 GHz 10 1 centi meter EHF 30 300 Ghz 10 1 milli meter Mobile communication is in UHF range Most frequently : 800/900 Mhz central frequency, and 1.8 Ghz
- 17. Wireless systems frequency spectrum 17
- 18. Spectrum Allocations for Existing Systems
- 19. Spectrum Allocations for Existing Systems The frequency bands are called ISM (Industrial, Scientific and Medical) bands.
- 20. Transmission modes • Simplex One way communication – Radio, TV, Satellite broadcasting • Half Duplex Two way communication but not the same time (one way at a time) – Walkie-Talkie, Push-to-Talk, As in 802.11, a device cannot simultaneously be transmitting and receiving • Full Duplex Two way communication – TDD – time division duplex – Users take turns on the channel – FDD – frequency division duplex – Users get two channels – one for each direction of communication – For example one channel for uplink (mobile to base station) another channel for downlink (base station to mobile) – Cellular phone 20
- 22. Why Wireless ? • User mobility • Reduced cost (Infrastructure is cheaper) • Flexibility and convenience • Increase the productivity 22
- 23. Why wireless • Mobility: – Example: talking on a cordless phone vs. cord phone. • Installation in difficult-to-Wire Areas: – rivers, freeways, old building – Hazard materials (such as asbestos particles) when drilling. – Right-of-way restrictions in some city to dig ground. • Reduced Installation Time: – It may take months to receive right-of-way approvals. • Increased Reliability: – cable vs. cable-less • Long-term savings: never need re-cabling
- 24. Difference between wired network and wireless network.
- 25. Advantages of Wireless Network Flexible: Radio waves can penetrate the obstacles. Sender and receiver can be placed any where. Mobility: Data can be access from any location. Robustness : Can survive in disaster (Earthquake, military operations) Scalable: Can be configured in variety of topologies. Easy Installation Less Cost Usage of ISM band: ISM (Industrial, Scientific and Medical) band (2.40GHz to 2.484 GHz, 5.725 GHz to 5.850 GHz) is available for use by anyone. No Planning: Only Wireless Ad hoc not required any planning.
- 26. Disadvantages of Wireless Network: Quality of Service: Lower Bandwidth Lower Data Transmission Rate High Error Rates Interference Higher Delay Restrictions: License-free frequency bands are not same worldwide. Safety and Security: Interference from other devices (e.g. Hospital. Eavesdropping is possible).
- 27. Major Challenges in Wireless • Limited Resources – Scarce and expensive spectrum (FCC-regulated) • Limited Bandwidth – 2-10 Mbps in the LAN, wired is 100 Mbps • Higher error rates – Can be as poor as 10^-2!! – Wired BER at 10^-12 • Limited Power – Short battery life – transmission and sensing are power-guzzling
- 28. Major Challenges in Wireless • Highly fluctuating channel conditions – Multipath fading, noise, signal attenuation – Time-varying changes – Dependent on environmental conditions – Impose severe limitations on range, data rates and reliability of communications – - e.g. a radio for an indoor user at walking speeds will support much higher data rates than an outdoor user channel that operates in the shadow of tall buildings and where the user moves at high speeds
- 30. And finally… • User mobility – Need to locate the user – Need to support routing to a moving user – Need to continuously track the change in the location and deliver data while the user is roaming – Need to manage the scarce resources in an fair and efficient manner while catering to varying user demands
- 31. Wireless Devices
- 34. Wireless Networks Wireless networks are classified depending on the geographic area (coverage area) within which a user may connect to the network – Wireless Body Area Network ( WBAN) – Wireless Personal area Network (WPAN) – Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) – Wireless Metropolitan Network( WMAN) – Wireless Wide area Network( WWAN) 34
- 35. WBAN • Wireless Body Area Network (WBAN) is such network that provides a continuous monitoring over or inside human body for a long period and can support transmission of real time traffic such as data, voice, video to observe the status of vital organs functionalities. • WBAN covers the full body and exchange data through wireless communication. • WBAN is designed with special purpose sensor which can autonomously connect with various sensors and appliances, located inside and outside of a human body. • Max. signal range 2 meters
- 36. WBAN Technologies • WBAN Technologies such as Low power WiFi, Bluetooth, ZigBee and IEEE 802.15.6. • IEEE 802.15.6 standard uses different frequency bands for data transmission including: – The Narrowband (NB) which includes the 400, 800, 900 MHz and the 2.3 and 2.4 GHz bands; – the Ultra Wideband (UWB) 4, which uses the 3.111.2 GHz; and the Human Body Communication (HBC) which uses the frequencies within the range of 1050 MHz – The channel access is handled using CSMA/CA or slotted Aloha access procedure.
- 37. General architecture for WBAN
- 38. WPAN • Wireless Personal area Network (WPANs) are short-range wireless networks that connect devices within a few meters(within 10m distance), such as Bluetooth headphones, keyboards, and smartwatches. • WPANs use low-power radio waves, low cost and Instrumental Scientific and Medical (ISM) frequency band of 2.4 GHz and have a data rate of up to 25 Mbps. • WPANs are suitable for personal use and small-scale applications, such as wireless printing, file sharing, and health monitoring 38
- 39. WPAN contd…. • using protocols like Bluetooth and Zigbee. Bluetooth enables hands-free phone calls, connects a phone to earpieces or transmits signals between smart devices. • WPAN Technologies – Bluetooth, IEEE 802.15.1 – Ultra Wide Band (UWB) (IEEE 802.15.3) – Zigbee (IEEE 802.15.4)
- 40. General architecture for WPAN
- 41. WLAN • Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) also known as Wireless Fidelity ( Wi- Fi) • WLAN are medium-range wireless networks that connect devices within a few hundred meters, such as Wi-Fi routers, laptops, smartphones, and tablets. • WLANs operates under unlicensed frequency radio waves in the 2.4 GHz, 3.6 GHz, 4.9 GHz, 5 GHz, and 5.9 GHz bands. • Coverage: limited to a distance less than 100m • Throughput: up to 54Mb/s 41
- 42. WLAN contd…. • use an access method known as Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance (CSMA/CA) which does not support real time voice traffic. • Mobility: with limited cell size support low speed mobility(pedestrian speed) • Handover: not designed to implement handover from WLAN to another WLAN. • WLANs are suitable for home, SME Private and Government Enterprises, Institutions, Public hotspots (i.e., hotels, airports, coffee shops) and office use to provide internet access, network security, and multimedia streaming. 42
- 43. General architecture for WLAN
- 44. WLAN Devices 44
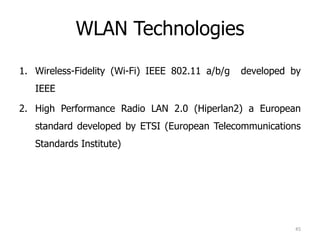
- 45. WLAN Technologies 1. Wireless-Fidelity (Wi-Fi) IEEE 802.11 a/b/g developed by IEEE 2. High Performance Radio LAN 2.0 (Hiperlan2) a European standard developed by ETSI (European Telecommunications Standards Institute) 45
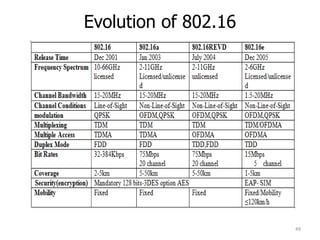
- 46. IEEE 802.11 series standards 46
- 47. WMAN • Wireless Metropolitan Network( WMAN) provides network access to buildings through exterior antennas communicating with central radio Base Stations (BS). • WMANs use radio waves in the 2.3 GHz, 2.5 GHz, 3.5 GHz, and 5.8 GHz bands and have a data rate of up to 1 Gbps. • WMANs are suitable for urban and rural use and provide broadband access, voice over IP, and video conferencing. • Wireless MAN are termed as Worldwide Interoperability of Microwave Access (WiMAX) • Broadband Wireless Access (BWA) – Fixed & Mobile • Common technology is WiMAX-IEEE 802.16 developed by Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE) 47
- 48. IEEE 802.16 WiMAX • Range up to 50 km. • Provide high speed connectivity that supports data, voice and video • Fast deployment, cost saving 48
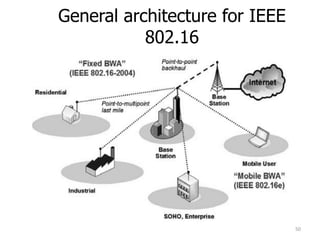
- 50. General architecture for IEEE 802.16 50
- 51. WWAN • Wireless Wide area Network (WWAN). Networks that provide connectivity over a wide geographical area that connect devices across the globe, such as cellular towers, satellites, and mobile phones • These connections are made using leased lines, circuit- switched and Packet-switched methods • WWANs use radio waves in the 700 MHz, 800 MHz, 900 MHz, 1.8 GHz, 1.9 GHz, 2.1 GHz, 2.6 GHz, and 3.5 GHz bands and have a data rate of up to 100 Mbps. • WWANs are suitable for mobile and remote use and provide voice, text, email, web browsing, and Global Position System (GPS) services. • Two technologies of WWAN – Satellite network – Mobile Network 51
- 52. WWAN
- 53. WWAN
- 54. Satellites Networks Another example of WWAN is satellite networks • Cover very large areas • require line of sight (LOS) • Different orbit heights • Geosynchronous Orbit (GEO) at 35,800 Km, Medium-Earth Orbit (MEO) at 5000-12,000 Km, Low-Earth Orbit (LEO) at 500 - 2000 Km and Very Small Aperture Satellite (VSAT • Optimized for one-way transmission( Simplex) • Radio ( DAB) and movie (SatTV) broadcasting 54
- 56. Transmission method of Satellite 56
- 57. Comparison Between LEO,MEO and GEO 57
- 59. Advantages of Satellite Networks • Can reach over large geographical area • Flexible (if transparent transponders) • Easy to install new circuits • Circuit costs independent of distance • Broadcast possibilities • Temporary applications (restoration) • User has control over own network • 1-for-N multipoint standby possibilities 59
- 60. Disadvantages of Satellite Network • Large up front capital costs (space segment and launch) • Interference and propagation delay • Congestion of frequencies and orbits 60