Lecture 21
- 1. Recombination at the Molecular Level • three types – homologous recombination – site specific recombination – transposition
- 3. Nonreciprocal Homologous Recombination: Fox Model • incorporation of single strand of DNA into chromosome, forming heteroduplex DNA • thought to occur during bacterial transformation
- 4. Site-specific recombination • important in insertion of viral genomes into host chromosomes • there is only a small region of homology between inserted genetic material & host chromosome
- 5. transposition & transposable elements transposable elements = transposons = mobile genetic elements = “jumping genes”
- 6. Please note that due to differing operating systems, some animations will not appear until the presentation is viewed in Presentation Mode (Slide Show view). You may see blank slides in the “Normal” or “Slide Sorter” views. All animations will appear after viewing in Presentation Mode and playing each animation. Most animations will require the latest version of the Flash Player, which is available at http://get.adobe.com/flashplayer.
- 9. Please note that due to differing operating systems, some animations will not appear until the presentation is viewed in Presentation Mode (Slide Show view). You may see blank slides in the “Normal” or “Slide Sorter” views. All animations will appear after viewing in Presentation Mode and playing each animation. Most animations will require the latest version of the Flash Player, which is available at http://get.adobe.com/flashplayer.
- 12. Please note that due to differing operating systems, some animations will not appear until the presentation is viewed in Presentation Mode (Slide Show view). You may see blank slides in the “Normal” or “Slide Sorter” views. All animations will appear after viewing in Presentation Mode and playing each animation. Most animations will require the latest version of the Flash Player, which is available at http://get.adobe.com/flashplayer.
- 13. R plasmid w/ integrated Tn3 transposon
- 14. What are potential effects of transposons?
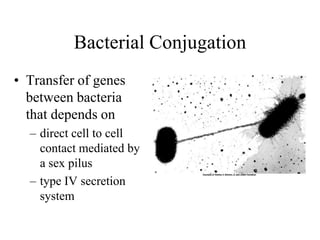
- 16. Bacterial Conjugation • Transfer of genes between bacteria that depends on – direct cell to cell contact mediated by a sex pilus – type IV secretion system
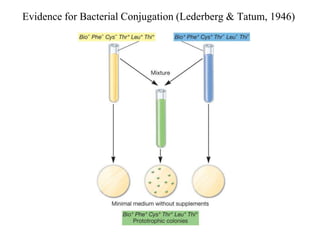
- 17. Evidence for Bacterial Conjugation (Lederberg & Tatum, 1946)
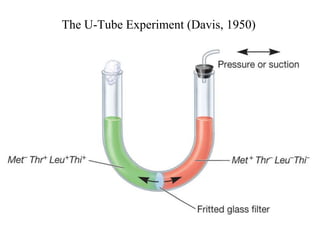
- 18. The U-Tube Experiment (Davis, 1950)
- 19. Types of Conjugation 1. F+ × F2. Hfr × F3. F’
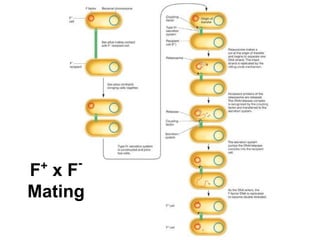
- 20. + - F x F Mating – copy of F factor is transferred to recipient & does not integrate into the host chromosome – donor genes usually not transferred
- 21. + - F xF Mating
- 23. Please note that due to differing operating systems, some animations will not appear until the presentation is viewed in Presentation Mode (Slide Show view). You may see blank slides in the “Normal” or “Slide Sorter” views. All animations will appear after viewing in Presentation Mode and playing each animation. Most animations will require the latest version of the Flash Player, which is available at http://get.adobe.com/flashplayer.
- 24. Hfr Conjugation – donor has F factor integrated into its chromosome (Hfr cell) – donor genes are transferred to recipient cell – complete copy of the F factor is usually not transferred
- 26. Figure 14.24a
- 27. Figure 14.24b
- 28. F’ Conjugation • F factor incorrectly leaves host chromosome • some of the F factor is left behind in host chromosome • some host genes have been removed along w/ some of the F factor – these genes can be transferred to a second host cell by conjugation
- 29. Figure 14.25
- 30. Bacterial Transformation • uptake of naked DNA by a competent cell followed by incorporation of the DNA into the recipient cell’s genome
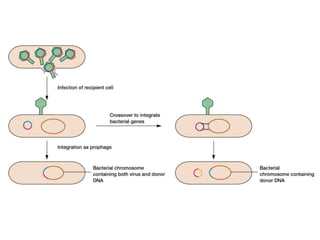
- 34. Transduction • transfer of bacterial genes by viruses • viruses (bacteriophages) can carry out the lytic cycle in which the host cell is destroyed or the viral DNA can integrate into the host genome, becoming a latent prophage
- 36. Generalized Transduction • any part of bacterial genome can be transferred • occurs during lytic cycle • during assembly, fragments of host DNA mistakenly packaged into phage head – generalized transducing particle
- 37. Generalized transduction abortive transductants = bacteria w/ nonintegrated transduced DNA
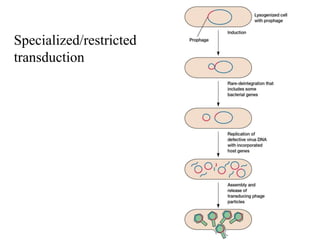
- 38. Specialized Transduction • a.k.a. restricted transduction • carried out only by lysogenic/temperate phages • only specific portion of bacterial genome is transferred • occurs when prophage incorrectly excises
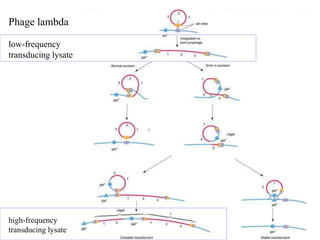
- 41. Phage lambda low-frequency transducing lysate insert Figure 13.21 high-frequency transducing lysate
- 42. For Tuesday: Read Ch 17 For Lab Next Week: Identify unknowns to Group level Collect materials needed for Team Projects