Lecture 6.1 flow control selection
- 2. 2 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Topics • Basic Concepts: Why Selection and Repetition • Selection (Branching) • Basic concepts • Case study: Paper Scissor Rock • Syntax • Examples in Python • Repetition (Looping) • Basic concepts: for and while • Syntax: while • The range function • Syntax: for • Nested loops • break, continue, and pass • Case Study: Visual Example - Path of a projectile
- 3. 3 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Basic Concepts • The Power of Computer Programs • Program Execution • Why Selection? • Why Repetition? • What is Flow Control / Control Flow?
- 4. 4 of 66Module 6 : Flow control The Power of Computer Programs • Help automation • Can repeat computation (which may be routine job) with high reliability and reusability • Reliability – low error rate (compared to human) • Reusability – same piece of code run again and again • Can be embedded to enhance many daily life devices: phone, TV, fridge, cooker, etc. • How many computers you now have?
- 5. 5 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Program Execution • Given a computer program, CPU runs its instructions one by one This program can automate the computation of circle area and circumference; no matter how many times we run it, it can reliably do the same computation consistently
- 6. 6 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Program Execution • But… This program only shows a basic kind of control flow, called “sequence” • If we only have “sequence” in programming… Is it enough? What cannot be done? Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 ……
- 7. 7 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Sequence alone? If I ask you to write a program for … 1. Computing the average height of students in a class? 2. A simple computer game such as paper scissor rock?
- 8. 8 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Sequence alone? 1) Computing the average height of students in a class? • Basic idea for the algorithm: Sum all height values and Divide it by total • If we only have sequence… We need to repeat certain instruction, e.g., accumulate height of students, exactly N times, where N is the total number of students
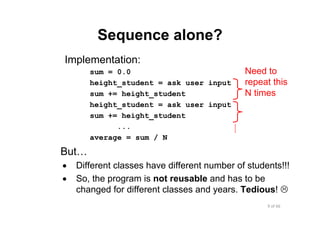
- 9. 9 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Sequence alone? Implementation: sum = 0.0 height_student = ask user input sum += height_student height_student = ask user input sum += height_student ... average = sum / N But… • Different classes have different number of students!!! • So, the program is not reusable and has to be changed for different classes and years. Tedious! Need to repeat this N times
- 10. 10 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Sequence alone? 2) A simple computer game such as paper scissor rock? • Basic idea for the algorithm here: 1. First, the computer program has to randomize a choice out of the three 2. Then get user input (user’s choice) 3. Finally, the computer program compares the two choices and determines who wins
- 11. 11 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Sequence alone? But… in the final step… • How can a computer program compare and tell who wins? • With “sequence” …Every step is pre-planned and fixed; there is ONLY one possible consequence (control flow) in the program • But… sometimes human wins; sometimes computer wins...
- 12. 12 of 66Module 6 : Flow control So… we need • Selection – A computer program can dynamically choose which instruction(s) to be executed next based on certain condition(s) during the program runtime • Different instructions can be selected to run at different time • BUT the program is the same (we do not need to change and compile it again for different situations; we already define possible program responses for different cases when writing the program)
- 13. 13 of 66Module 6 : Flow control So… we need • Looping – A computer program can dynamically choose how many times it repeats certain instruction(s) during the program runtime • Program instructions can be repeated dynamically; sometimes 3 times, sometimes 1000 times, or sometimes even 0 times • Again, the program is the same (we do not need to change it for different number of repetitions)
- 14. 14 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Computational thinking - Looping 1) To compute the average height of the students in a class • We may repeat the height accumulation based on the value of N sum = 0.0 REPEAT N times ASK user for next student’s height sum += height END of REPEAT average = sum / N Same program can work no matter how many students; more reusable
- 15. 15 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Computational thinking - Selection 2) Game: paper scissor rock • A program can compare choices from human and computer, and then determine who wins IF user_choice == paper and computer_choice == scissor print("computer wins") IF user_choice == scissor and computer_choice == paper print("human wins") ... # for other cases
- 16. 16 of 66Module 6 : Flow control What is Flow Control / Control Flow? • It is to control which instruction to be executed next • By default, it is defined by the “sequence” concept, i.e., one after the other • But selection and repetition can alter the flow… When you write/read a program, make sure you understand the flow!!! i.e., what is to be executed next for every step… The flow control in a program -> Its Logic!!!
- 17. 17 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Topics • Basic Concepts: Why Selection and Repetition • Selection (Branching) • Basic concepts • Case study: Paper Scissor Rock • Syntax • Examples in Python • Repetition (Looping) • Basic concepts: for and while • Syntax: while • The range function • Syntax: for • Nested loops • break, continue, and pass • Case Study: Visual Example - Path of a projectile
- 18. 18 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Basic Concept: IF • Form #1: IF statement IF condition is True THEN DO THIS END IF …… Hence… Program can make decisions!!! Whether to execute it or not depends on the condition during program runtime After that, continue the sequence and execute the next instructionan IF statement
- 19. 19 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Basic Concept: IF • Form #1: IF statement IF condition is True THEN DO THIS END IF …… Adopted in many programming languages with proper indentation! Python forces you!!! We usually indent these statement(s) to improve the code readability that this part becomes to the true condition
- 20. 20 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Examples • Example #1 IF body temperature > 37.5 THEN print("Fever!") print("Time to see doctor!") END IF …… The power of IF statement is that the program can selectively run the block based on the runtime condition!!! Sometimes run it! Sometimes skip it! In Python, this group of indented statement(s) is called a suite/block. (compound statement: a set of statements being used as a group)
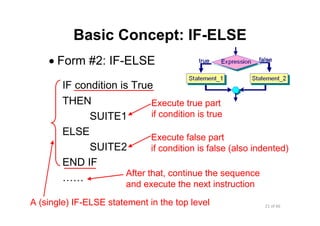
- 21. 21 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Basic Concept: IF-ELSE • Form #2: IF-ELSE IF condition is True THEN SUITE1 ELSE SUITE2 END IF …… Execute true part if condition is true After that, continue the sequence and execute the next instruction Execute false part if condition is false (also indented) A (single) IF-ELSE statement in the top level
- 22. 22 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Examples • Example #2.1 IF body temperature > 37.5 THEN print("Fever! See doctor") END IF IF body temperature <= 37.5 THEN print("Normal!") END IF …… Here we use two consecutive IF statements for true and false sides Any issue? Efficiency? Redundancy?
- 23. 23 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Examples • Example #2.2 IF body temperature > 37.5 THEN print("Fever! See doctor") ELSE print("Normal!") END IF …… The power of IF-ELSE statement is that the program becomes more efficient! JUST ONE checking (temperature > 37.5) can let us know which way to go!! Avoid redundant check!
- 24. 24 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Basic Concept: IF-ELIF-ELSE • Form #3: IF-ELIF-ELSE IF condition1 is True THEN DO SUITE A ELIF condition2 is True THEN DO SUITE B ELSE DO SUITE C END IF …… Execute A if condition 1 is true then skip B and C No matter after which case, we continue here (sequence concept) Execute B if condition 1 is false and condition 2 is true, then skip C Execute C if both conditions 1 and 2 are false Else if The whole statement
- 25. 25 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Basic Concept: IF-ELIF-ELSE • Form #3: IF-ELIF-ELSE IF condition1 is True THEN DO SUITE A ELIF condition2 is True THEN DO SUITE B ELSE DO SUITE C END IF ……
- 26. 26 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Basic Concept: IF-ELIF-ELSE • Form #3: IF-ELIF-…-ELSE statement IF condition1 is True THEN DO SUITE A ELIF condition2 is True THEN DO SUITE B ELIF condition3 is True THEN DO SUITE C ELSE DO SUITE D # conditions 1,2,3 are all false END IF …… You may have many … many ELIF blocks The whole statement
- 27. 27 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Examples • Example #3 Let’s write a simple number guessing game. The computer program randomly pick a number in-between 0 and 50 (inclusively). You can make a guess and the computer can tell you whether your guess is the same, too large, or too small.
- 28. 28 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Examples • Example #3.1 …… IF my_guess > computer_num THEN print("Your guess is too large") END IF IF my_guess < computer_num THEN print("Your guess is too small") END IF IF my_guess == computer_num THEN print("Bingo!!! Correct") END IF …… 1) Is this program logically correct? 2) Efficient? Any redundant check? Three consecutive IF statements
- 29. 29 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Examples • Example #3.2 …… IF my_guess > computer_num THEN print("Your guess is too large") ELIF my_guess < computer_num THEN print("Your guess is too small") ELIF my_guess == computer_num THEN print("Bingo!!! Correct") END IF …… 1. Is it better? If condition 1 is true, no need to check others (they must be F) 2. But can you make it even better?
- 30. 30 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Examples • Example #3.3 IF my_guess > computer_num THEN print("Your guess is too large") ELIF my_guess < computer_num THEN print("Your guess is too small") ELSE print("Bingo!!! Correct") END IF …… When comparing two numbers, there are only three possibilities!!! If it is not the first two cases, must be the third case!!!
- 31. 31 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Basic Concept: Nested IF • Form #4: Nested IF statement • Recall that for each IF statement, there is an associated block for its TRUE part IF condition1 is True THEN DO THIS SUITE END IF ……
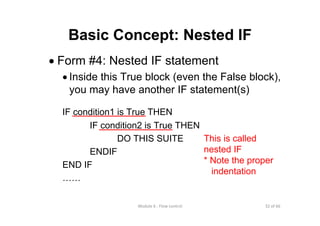
- 32. 32 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Basic Concept: Nested IF • Form #4: Nested IF statement • Inside this True block (even the False block), you may have another IF statement(s) IF condition1 is True THEN IF condition2 is True THEN DO THIS SUITE ENDIF END IF …… This is called nested IF * Note the proper indentation
- 33. 33 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Basic Concept: Nested IF • Form #4: Nested IF statement • And… inside the TRUE block of the TRUE block, you may still use IF statement(s) IF condition1 is True THEN IF condition2 is True THEN IF condition3 is True THEN DO THIS ENDIF ENDIF END IF We DO THIS only if condition 1 is true, condition 2 is true, and condition 3 is true SIMILAR to AND’ed
- 34. 34 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Basic Concept: Nested IF • Form #4: Nested IF statement • Or even with ELSE inside… IF condition1 is True THEN IF condition2 is True THEN DO SUITE A ELSE DO SUITE B END IF END IF
- 35. 35 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Basic Concept: Nested IF • Form #4: Nested IF statement • Or use it on the False side… IF condition1 is True THEN DO SUITE A ELSE IF condition2 is True THEN DO SUITE B ELSE DO SUITE C END IF END IF Which one to use? It’s all about the logic for problem solving
- 36. 36 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Topics • Basic Concepts: Why Selection and Repetition • Selection (Branching) • Basic concepts • Case study: Paper Scissor Rock • Syntax • Examples in Python • Repetition (Looping) • Basic concepts: for and while • Syntax: while • The range function • Syntax: for • Nested loops • break, continue, and pass • Case Study: Visual Example - Path of a projectile
- 37. 37 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Case Study: paper scissor rock • Recall our paper scissor rock game • Assume: Variable comp_choice stores computer’s choice on paper, scissor, or rock, while Variable your_choice stores your choice
- 38. 38 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Case Study: paper scissor rock • Let’s analyze the problem… • Without using IF-ELSE and nested-IF, if we only use IF statements, how many possible combinations of choices? There are 3 x 3 possible combinations
- 39. 39 of 66Module 6 : Flow control 1st attempt • So… Pseudo code #4.1 IF comp_choice == paper and your_choice == paper THEN print("draw") END IF IF comp_choice == paper and your_choice == rock THEN print("computer wins") END IF IF comp_choice == paper and your_choice == scissor THEN print("you win") END IF …… # just continue with the # remaining six cases …. Is it logically correct? Good program? Efficient? We exhaust all possible combinations of input
- 40. 40 of 66Module 6 : Flow control 1st attempt • So… Pseudo code #4.1 IF comp_choice == paper and your_choice == paper THEN print("draw") END IF IF comp_choice == paper and your_choice == rock THEN print("computer wins") END IF IF comp_choice == paper and your_choice == scissor THEN print("you win") END IF …… Notice anything in common? … the first three IF statements? Do we check them redundantly
- 41. 41 of 66Module 6 : Flow control 2nd attempt • Pseudo code #4.2 IF comp_choice == paper THEN IF your_choice == paper THEN print("draw") END IF IF your_choice == rock THEN print("computer wins") END IF IF your_choice == scissor THEN print("you win") END IF END IF …… We can combine them by using nested IF… then, can avoid redundant comparison!!! Exercise: Draw the flowchart
- 42. 42 of 66Module 6 : Flow control 3rd attempt • Pseudo code #4.3 IF comp_choice == paper THEN IF your_choice == paper THEN print("draw") ELIF your_choice == rock THEN print("computer wins") ELIF your_choice == scissor THEN print("you win") END IF END IF …… Further use ELIF (else if) to avoid redundant checks! What check(s) may be avoided? Exercise: Draw the flowchart
- 43. 43 of 66Module 6 : Flow control 4th attempt • Pseudo code #4.4 IF comp_choice == paper THEN IF your_choice == paper THEN print("draw") ELIF your_choice == rock THEN print("computer wins") ELSE print("you win") END IF END IF …… Further use ELSE to avoid one more redundant check! Exercise: Draw the flowchart (it slightly differs from previous two)
- 44. 44 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Another approach - 5th attempt • Pseudo code #4.5 IF ( comp_choice == paper and your_choice == paper ) or ( comp_choice == rock and your_choice == rock ) or ( comp_choice == scissor and your_choice == scissor ) THEN print("draw") ELIF ( comp_choice == paper and your_choice == rock ) or ( comp_choice == rock and your_choice == scissor ) or ( comp_choice == scissor and your_choice == paper ) THEN print("computer wins") ELSE print("you win") END IF We may have many other solutions! Different ways of computational thinking! Think: based on possible outcomes
- 45. 45 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Another approach - 6th attempt • Pseudo code #4.6… Even better IF comp_choice == your_choice THEN print("draw") ELIF ( comp_choice == paper and your_choice == rock ) or ( comp_choice == rock and your_choice == scissor ) or ( comp_choice == scissor and your_choice == paper ) THEN print("computer wins") ELSE print("you win") END IF Hope that you enjoy computational thinking and programming… (note: we are not using Python yet) Further simplified
- 46. 46 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Topics • Basic Concepts: Why Selection and Repetition • Selection (Branching) • Basic concepts • Case study: Paper Scissor Rock • Syntax • Examples in Python • Repetition (Looping) • Basic concepts: for and while • Syntax: while • The range function • Syntax: for • Nested loops • break, continue, and pass • Case Study: Visual Example - Path of a projectile
- 47. 47 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Python Syntax Now… let’s look at how Python implements • IF statement • IF-ELSE statement • IF-ELIF-ELSE statement • Nested IF
- 48. 48 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Syntax #1 • IF statement in Python Syntax: if <a boolean expression> : one or more indented statements Example: if a > b: print( "a > b" ) MUST use colon here MUST use indentation for the entire true block
- 49. 49 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Syntax #1 cont. Note: 1) Colon : marks the beginning of a block! 2) In Python, indentation -- not just for readability but also for defining the scope of a block! 3) Number of whitespaces for indentation is flexible but should be consistent for the same level in the same program More keywords in Python • else (see syntax #2) • elif (see syntax #3)
- 50. 50 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Syntax #2 • IF-ELSE statement if a > b: print("a > b") else: print("a <= b") In Python, always Remember that colon marks the beginning of a block/suite *** Don’t forget it!!! else syntax error
- 51. 51 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Syntax #3 • IF-ELIF-ELSE statement if a > b: print("a > b") print("case 1 here") elif a < b: print("a < b") print("case 2 here") else: print("a == b") print("case 3 here") In Python, indentation defines a block!!! So if you continue to use the same amount of indentation, it is still in the same block
- 52. 52 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Nested IF – No new syntax • Comparing a, b, and c: if a >= b: if a >= c: print("maximum value is ",a) else print("maximum value is ",c) else if b >= c: print("maximum value is ",b) else print("maximum value is ",c) end Any bug(s) here? (no logic error)
- 53. 53 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Bugs fixed • Nested IF if a >= b: if a >= c: print("maximum value is ",a) else: print("maximum value is ",c) else: if b >= c: print("maximum value is ",b) else: print("maximum value is ",c) six syntax errors fixed! need proper indentation
- 54. 54 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Syntax #4 • In Python • 0, ‘’, [ ] or other “empty” objects are equivalent to False; anything else is equivalent to True Run it More info: http://docs.python.org/library/stdtypes.html#truth-value-testing
- 55. 55 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Topics • Basic Concepts: Why Selection and Repetition • Selection (Branching) • Basic concepts • Case study: Paper Scissor Rock • Syntax • Examples in Python • Repetition (Looping) • Basic concepts: for and while • Syntax: while • The range function • Syntax: for • Nested loops • break, continue, and pass • Case Study: Visual Example - Path of a projectile
- 56. 56 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Python Implementation • Now… Let’s revisit the examples we went through in real Python code • See the beauty and simplicity of Python
- 57. 57 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Examples Revisit in Python • Example #1 - Compare with the pseudo code we saw previously - Python code is simple and clear
- 58. 58 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Examples Revisit in Python • Example #2.2 - Remember to put colon also for else! (it marks the beginning of a block)
- 59. 59 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Examples Revisit in Python • Example #3.3 Use this print() temporarily for code testing when there is a random scenario; When done, just comment it Note:
- 60. 60 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Examples Revisit in Python • Example #4.1 Very tedious
- 61. 61 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Examples Revisit in Python • Example #4.4 Code Simplified
- 62. 62 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Examples Revisit in Python • Example #4.6 By analyzing the pattern, we can further simplify the code statement continuity
- 63. 63 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Exercises! Trace these code carefully and understand its control flow. Can you draw the flow charts for these code? What is/are the conditions for reaching each print()? Note: condition_A, condition_B, etc., are boolean variables
- 65. 65 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Take Home Messages • Computational thinking or algorithm design requires the careful and thoughtful applications of sequence, selection (branching) and repetition (looping) to control the flow • #1 Understand: be able to trace code and understand the control flow inside a given program • #2 Analysis: Given a problem, think and analyze carefully different possibilities/combinations and the logic • #3 Apply: Furthermore, transform the logic appropriately into IF-ELSE, IF-ELIF-ELSE and nested IF • #4 Test: Lastly, use sufficient test data to evaluate your program with different consequences Last word… practice practice practice
- 66. 66 of 66Module 6 : Flow control Reading Assignment • Textbook Chapter 2: Control 2.1 to 2.4 Note: Though some material (2.3 and 2.4) in textbook is not directly related to the lecture material, you can learn more from them.
![1 of 66Module 6 : Flow control
Introduction to
Computational Thinking
Module 6 : Flow control #1
Asst Prof Chi‐Wing FU, Philip
Office: N4‐02c‐104
email: cwfu[at]ntu.edu.sg](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture6-1flowcontrolselection-130525013943-phpapp01/85/Lecture-6-1-flow-control-selection-1-320.jpg)

















































![54 of 66Module 6 : Flow control
Syntax #4
• In Python
• 0, ‘’, [ ] or other “empty” objects are equivalent
to False; anything else is equivalent to True
Run it
More info: http://docs.python.org/library/stdtypes.html#truth-value-testing](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture6-1flowcontrolselection-130525013943-phpapp01/85/Lecture-6-1-flow-control-selection-54-320.jpg)











