Lecture -Introduction to Flutter and Dart.pptx
- 1. Duration: 65 min High School Grades: 9 - 12 CCSS, NGSS Mobile Application Development Introduction to Flutter & Dart Instructor: Engr. Farhan Ghafoor Associate Professor, Software Engineering Dept, CoE
- 2. Learning OUTCOMES At the end of this lesson, learners should be able to: Describe what is Flutter Explain what is a Flutter widget Understanding of Stateless and Stateful widgets Design a Flutter mobile app using Scaffold widgets
- 3. What is Flutter? Flutter is a user interface toolkit developed by Google that can be used for developing mobile applications. Developers use Dart programming language to create a Flutter mobile app. Dart is an object-oriented, open-source, and general-purpose programming language Dart is a general-purpose, object-oriented, open-source programming language with C-style syntax that was also developed by Google.
- 4. Technical Overview What is flutter SDK? An app SDK capable of providing high performance applications for iOS & Android, Web (Hummingbird – work in progress) Even Desktop (Work in progress). High Performance Applications that will have same natural feel as if it was written on the same platform Apps are written in Dart language
- 5. What is Dart? An object-oriented language. Supports Ahead-of-Time (AOT) and Just-in-Time (JIT) compilation C-style syntax Statically Type
- 6. Dart Basics Dart Pad Editor: https://dartpad.dev/? Functions Variables and Values Types Classes
- 7. Mobile App Architecture Presentation Layer (PL) • This Layer focuses on UI Components (View and Controller) • Defines the way, the mobile app will present itself in front of the end user • On this Layer, just focus on features and their locations
- 8. Mobile App Architecture Business Layer (BL) Focuses on Business logic Includes workflow, Business components Service Layer and Domain Layer Service Layer: Defines a common set of application functions that will be available to the client and end users Domain Layer: Focuses on the domain specific problems
- 9. Mobile App Architecture Data Layer (DL) It’s the final layer! data access components (DAC), Data Helpers/Utilities Service Agents These three components control the — Persistence Layer(Backend) / Network Call Since now we know the basic architecture, here comes the question! Why we want to use flutter ? Or why we should use it ?
- 10. Why Learn Flutter and Dart? Benefits associated with: It’s highly productive! It is Perfect for an MVP! Develops iOS and Android applications from single code base Prototype and iterate easily: — Experimental feature can reflect instantly by hot reload, fix crashes and continue debugging from where the app left off Creates beautiful, highly customized user experiences (has its own rendering engine) Consistent UIs across devices and manufacturers Superb performance
- 11. Why Learn Flutter and Dart? Benefits associated with Flutter Material Design and Cupertino available for iOS widgets Resembles React Native No need to use a JavaScript bridge, which improves app startup times and overall performance. Once your UI works, it just works. And keeps working. Manufacturers / OS versions / different devices can’t break it Dart achieves this thanks to Ahead-of-Time (AOT), compilation. Dart also makes use of Just-in-Time, or JIT, compilation.
- 12. Why Learn Flutter and Dart? Flutter includes: A modern react-style framework, A 2-D rendering engine, Ready-to use widgets, and Development tools. Flutter basically provides all those components which are required to build a Highly interactive and Personalized application for fast development Especially Android APIs require a lot of ceremony for simple things Flutter was able to start from scratch and avoid previously made pitfalls
- 13. Platform SDKs (Android and IOS)
- 15. Flutter SDK
- 16. Flutter vs React Native Base image from: https://speakerdeck.com/passsy/flutter-60-fps-ui-of-the-future Our cross-platform code Native land ● Also fast performance here, however: ○ Expensive to travel to ● We can’t afford to go here too often, just like we can’t afford beach vacations every week ● Everything in our control ● Things we do here have fantastic performance and are cheap ● We should stay here as much as possible
- 17. Flutter - Native Plugins Allow access to every native platform API Bluetooth, geolocation, sensors, fingerprint, camera, etc. Both official and community-driven plugins available Some plugins missing or in early stages There’s a community-driven geolocation plugin with really limited API There’s a community-driven Bluetooth plugin that doesn’t work with iOS just yet If a plugin for your use case doesn’t exist, you’ll have to make it yourself This is where other frameworks like React Native & Xamarin currently shine and Flutter takes the loss Situation expected to be solved with time
- 19. Widgets
- 20. Introduction to Widgets Flutter widgets are built using a modern framework that takes inspiration from React. Building blocks of UI in Flutter The whole app is a Widget. A screen is a Widget that contains Widgets. What is a widget? Widgets can be compared to LEGO blocks. Advanced widgets are made by combining basic widgets. Widgets describe what their view should look like given their current configuration and state.
- 21. Widgets The whole app is a Widget. A screen is a Widget that contains Widgets. Can represent UI element, such as Text, Button, BottomNavigationBar, TextField, etc. Layout element, such as Padding, Center, Stack, Column, etc. Completely new screen (Activity/ViewController equivalent)
- 22. Widgets Each widget is an immutable declaration of the user interface. Widgets are configurations for different parts of the UI. Placing the widgets together creates the widget tree Like an Architect draws a blue-print of a house.
- 23. Widgets Widgets create a widget tree. When a widget’s state changes, the widget rebuilds its description, Which the framework differentiates against the previous description Why? To determine the minimal changes needed in the underlying render tree to transition from one state to the next.
- 24. Widget Tree
- 28. Widget Catalog – Material Design Widgets https://docs.flutter.dev/developme nt/ui/widgets/material
- 29. Widgets Flutter has widgets with: Structuring elements such as a list, grid, text, and button Input elements such as a form, form fields, and keyboard listeners Styling elements such as font type, size, weight, color, border, and shadow to lay out the UI such as row, column, stack, centering, and padding Interactive elements that respond to touch, gestures, dragging, and dismissible Animation and motion elements such as hero animation, animated container, Animated crossfade, fade transition, rotation, scale, size, slide, and opacity Elements like assets, images, and icons Widgets that can be nested together to create the UI needed Custom widgets you can create yourself
- 31. Stateless Widgets - Lifecyle
- 32. Stateful Widgets
- 33. Stateful Widgets
- 34. Stateful Widgets - State
- 35. Flutter architectural overview Flutter is a cross-platform UI toolkit It is designed to allow code reuse across operating systems such as iOS and Android, while also allowing applications to interface directly with underlying platform services. To enable developers to deliver high-performance apps that feel natural on different platforms, embracing differences where they exist while sharing as much code as possible.
- 36. Flutter architectural overview During development: Flutter apps run in a VM that offers stateful hot reload of changes without needing a full recompile. For release: Flutter apps are compiled directly to machine code, whether Intel x64 or ARM instructions, Or to JavaScript if targeting the web. The framework is open source, with a permissive BSD license, Has a thriving ecosystem of third-party packages that supplement the core library functionality.
- 37. Flutter architectural overview This overview is divided into a number of sections: 1. The layer model: The pieces from which Flutter is constructed. 2. Reactive user interfaces: A core concept for Flutter user interface development. 3. An introduction to widgets: The fundamental building blocks of Flutter user interfaces. 4. The rendering process: How Flutter turns UI code into pixels. 5. An overview of the platform embedders: The code that lets mobile and desktop OSes execute Flutter apps. 6. Integrating Flutter with other code: Information about different techniques available to Flutter apps. 7. Support for the web: Concluding remarks about the characteristics of Flutter in a browser environment.
- 38. 1. Architectural layers Designed as an extensible, layered system. Exists as a series of independent libraries that each depend on the underlying layer. No layer has privileged access to the layer below Every part of the framework level is designed to be optional and replaceable.
- 39. 1. Architectural layers - Embedder To the underlying OS, Flutter applications are packaged in the same way as any other native application. A platform-specific embedder provides an entry point; coordinates with the underlying operating system for access to services like rendering surfaces, accessibility, and Input manages the message event loop. The embedder is written in a language that is appropriate for the platform: Java and C++ for Android, Objective-C/Objective-C++ for iOS and macOS, C++ for Windows and Linux.
- 40. 1. Architectural layers - Embedder Using the embedder, Flutter code can be integrated into an existing application as a module, Or the code may be the entire content of the application. Flutter includes a number of embedders for common target platforms, but other embedders also exist.
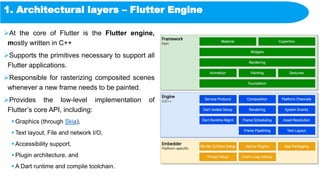
- 41. 1. Architectural layers – Flutter Engine At the core of Flutter is the Flutter engine, mostly written in C++ Supports the primitives necessary to support all Flutter applications. Responsible for rasterizing composited scenes whenever a new frame needs to be painted. Provides the low-level implementation of Flutter’s core API, including: Graphics (through Skia), Text layout, File and network I/O, Accessibility support, Plugin architecture, and A Dart runtime and compile toolchain.
- 42. 1. Architectural layers – Flutter Engine The engine is exposed to the Flutter framework through dart:ui dart:ui wraps the underlying C++ code in Dart classes. This library exposes the lowest-level primitives, such as: Classes for driving input Graphics Text rendering subsystems
- 43. 1. Architectural layers – Flutter Framework Developers interact with Flutter through the Flutter framework, Provides a modern, reactive framework written in the Dart language. Includes a rich set of platform, layout, and foundational libraries, composed of a series of layers.
- 44. 1. Architectural layers – Flutter Framework Working from the bottom to the top, we have:
- 45. 1. Architectural layers – Conclusion Flutter framework is relatively small Many higher-level features are implemented as packages, including Platform plugins like camera and webview, Platform-agnostic features like characters, http, and animations that build upon the core Dart and Flutter libraries. Some of these packages come from the broader ecosystem, covering services like in-app payments, Apple authentication, and Animations.
- 46. Mobile Application Development - Flutter
- 47. Thank you Mobile Application Development - Flutter