lecture1.ppt instrumentation and sensors
- 1. LECTURE 1: INTRODUCTION Kamlesh T. Kahar Faculty of Elect. & Telecommunication Engineering SSGMCE
- 2. Instrumentation ◦ It is the branch of engineering that deals with measurement & control of process variables within a production/manufacturing area. Measurement ◦ A method to obtain information regarding the physical values of the variable. 2
- 3. Physical quantity: variable such as pressure, temperature, mass, length, etc. Data: Information obtained from the instrumentation/measurement system as a result of the measurements made of the physical quantities Information: Data that has a calibrated numeric relationship to the physical quantity. Parameter: Physical quantity within defined (numeric) limits. 3
- 4. 4 measurand Sensor, signal conditioning, display Man, tracking control etc
- 5. Measurand: Physical quantity being measured. Calibration: Implies that there is a numeric relationship throughout the whole instrumentation system and that it is directly related to an approved national or international standard. Test instrumentation: It is a branch of instrumentation and most closely associated with the task of gathering data during various development phases encountered in engineering, e.g. flight test instrumentation for testing and approving aircraft. 5 Terminology
- 6. Transducer: A device that converts one form of energy to another. Electronic transducer: It has an input or output that is electrical in nature (e.g., voltage, current or resistance). Sensor: Electronic transducer that converts physical quantity into an electrical signal. Actuator: Electronic transducer that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. 6
- 7. In the case of process industries and industrial manufacturing… ◦ To improve the quality of the product ◦ To improve the efficiency of production ◦ To maintain the proper operation. 7
- 8. To acquire data or information (hence data acquisition) about parameters, in terms of: ◦ putting the numerical values to the physical quantities ◦ making measurements otherwise inaccessible. ◦ producing data agreeable to analysis (mostly in electrical form) Data Acquisition Software (DAS) – data is acquired by the instrumentation system. 8
- 9. Direct comparison ◦ Easy to do but… less accurate e.g. to measure a steel bar Indirect comparison ◦ Calibrated system; consists of several devices to convert, process (amplification or filtering) and display the output e.g. to measure force from strain gages located in a structure 9
- 10. Stage 1: A detection-transducer or sensor-transducer, stage; e.g. Bourdon tube Stage 2: A signal conditioning stage; e.g. gearing, filters, bridges Stage 3: A terminating or readout-recording stage; e.g. printers, oscilloscope 10 General Structure of Measuring System
- 11. Passive Instruments ◦ the quantity being measured simply modulates (adapts to) the magnitude of some external power source. Active Instruments ◦ the instrument output is entirely produced by the quantity being measured Difference between active & passive instruments is the level of measurement resolution that can be obtained. 11
- 12. e.g. Float-type petrol tank level indicator 12
- 13. The change in petrol level moves a potentiometer arm, and the output signal consists of a proportion of the meter reading which varies according to the position of float. 13
- 14. e.g. Pressure-measuring device 14
- 15. The pressure of the fluid is translated into a movement of a pointer against scale. The energy expanded in moving the pointer is derived entirely from the change in pressure measured: there are no other energy inputs to the system. 15
- 16. An analogue instrument gives an output that varies continuously as the quantity being measured; e.g. Deflection-type of pressure gauge 16
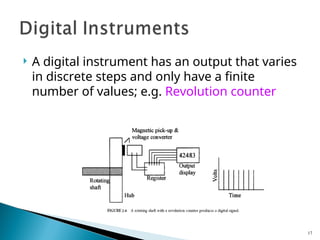
- 17. A digital instrument has an output that varies in discrete steps and only have a finite number of values; e.g. Revolution counter 17
- 18. Home ◦ Thermometer ◦ Barometer ◦ Watch Road vehicles ◦ speedometer ◦ fuel gauge Industry ◦ Automation ◦ Process control ◦ Boiler control 18
- 19. Unit-I : Basics of Transducers Transducer: Definition, Classification, Selection criteria. Errors, loading effects, Transducer Specifications, calibration, Generalized Instrumentation diagram. Static characteristics: Accuracy, Precision, Sensitivity, Threshold, Resolution, Repeatability and Hysteresis. Errors: Gross error, Systematic error, Random error, Limiting error. Statistical Parameters: Arithmetic mean Average deviation Standard deviation. Probable error, Histogram, Normal & Gaussian curve of errors. 19
- 20. Unit-II : Measurement of Displacement, Liquid Level Measurement of Displacement: Resistive, Capacitive, Inductive Measurement of Liquid Level: Resistive, Capacitive, Inductive, Ultrasonic, Gamma Rays. 20
- 21. Unit-III : Measurement of Temperature Measurement of Temperature: Resistance temperature detector (RTD): Principle, types, Configurations, construction and working of RTD, Material for RTD, advantages, disadvantages and applications of RTD. Thermistors: Principle, types (NTC and PTC), characteristics, Construction and working of Thermistor, Materials, specifications of Thermistor, applications. Thermocouples: Principle, thermoelectric effect, See beck effect, Peltier effect, laws of thermocouple, cold junction Compensation method, thermopile, thermocouple emf measurement method. Pyrometers: Principle, Construction and working of Radiation and optical pyrometers and its Applications, LM 335. 21
- 22. Unit-IV : Measurement of Pressure, Flow, Humidity. ◦ Measurement of Pressure: Primary pressure sensors - elastic elements like bourdon tube, diaphragm, and bellows. Electrical/Secondary Pressure ◦ Transducers: Capacitive, piezo-electric and its material, variable reluctance, LVDT. ◦ Differential pressure measurement: Capacitive. Low Pressure (Vacuum): Pirani gauge, thermocouple gauge, hot cathode ionization gauge. ◦ Flow Measurement: ultrasonic, electromagnetic & hotwire Anemometer. ◦ Flow Measurement: ultrasonic, electromagnetic & hotwire Anemometer. 22
- 23. Unit-V : Measurement of Velocity, Strain & Miscellaneous Sensors Velocity Measurement: Using photo detectors (both linear & angular velocity), Stroboscope. Strain Measurement: Introduction, types of strain gauge, gauge factor calculation, materials for strain gauge, resistance strain gauge bridges, temperature compensation and applications of strain gauges. Miscellaneous Sensors: Noise (sound) Sensors Characteristics of sound, levels of sound pressure, sound power and sound intensity. Smart sensors: Objective, block diagram, advantages and disadvantages. 23
- 24. Unit-VI : Data acquisition and applications of Electronic Instruments ◦ Analog & Digital data acquisition system.: Generalized block diagram of data acquisition system(DAS), objective of DAS, signal conditioning of inputs, single channel DAS, Multichannel DAS, computer based DAS ◦ Digital transducer: optical encoders, shaft encoders ◦ pH and blood pressure measurement. 24
- 25. Sr.No. Title Author Publications 1 A course in Electrical and Electronic Measurement and Instrumentation Sawhney A.K. Dhanpat Rai & Sons., Delhi 2 Electronics Instrumentation H. S. Kalsi Tata McGraw Hill, 2nd Edition 3 Instrumentation Measurement & analysis B C Nakra Tata Mc-Graw Hill. 4 Instrumentation, devices and systems Rangan Mani, Sharma Tata Mc-Graw Hill. 5 Electronics Instrumentation U.A. Bakshi & A. V. Bakshi Technical Publication 6 Modern Electronic Instrumentation and Measurement Tech Helfrick, Cooper Prentice hall 25