Library Automation A - Z Guide: A Hands on Module
- 1. Library Automation A - Z Guide: A Hands on Module Ashok Kumar Satapathy Asst. Librarian, IMIS, Bhubaneswar E-mail: [email protected] Contact No. : 919437040513
- 2. Chapter for Discussion : What is library automation Need for library automation Basic features & functions of Library Management System in a automated environment The role of standards in library automation and resource sharing A suitable design or plan for library automation Integrated library management system (Evaluation) Organise and implementation of effective strategy
- 3. Area of Automation & its Scope : Acquisition System Cataloguing System Circulation System Serial Control System OPAC Add-on Module
- 4. What is Library Automation : “ Library Automation” is a buzz word in the contemporary environment. It refers to the implementation of information and communications technologies (ICT) in the libraries & information centers. In other words, conversion of manual system into a specific MARC format which makes it suitable for cooperative networking and resource sharing among the libraries and information centers.
- 5. Need for Library Automation : Increased operational efficiencies of the library staff. Improve the quality, speed, accuracy, and effectiveness of services. Get better access to other networks and systems, on the Web, etc. Facilitate wider access to information for their clients. Smooth the progress of wider dissemination of information products and services.
- 6. Library Management System : A library management system refers to the implementation of software, that has been developed to handle the basic housekeeping functions of a library. Single Function. Integrated Function Identifying the important role, that the library management system will play, in planning and implementing library automation projects. In this situation, it is necessary to educate ourselves through proper training and development.
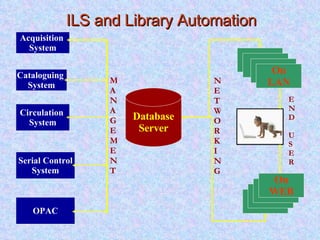
- 7. ILS and Library Automation OPAC OPAC OPAC OPAC On WEB MANAGEMENT END USER Cataloguing System Database Server Circulation System Serial Control System OPAC Acquisition System OPAC OPAC On LAN NETWORKING
- 8. Features of an ILS Functional modules (as per requirement) Basic modules - acquisition, cataloging, circulation, & OPAC Add on modules - serial control, interlibrary loan (ILL), and Web OPAC, etc. Operating systems Preferably Windows, Linux environment. Database systems Oracle, Informix, MS SQL, MS Access, etc… Network architecture Client-server architecture that uses TCP-IP to communicate across networks (LANs and WANs) User interface Graphical user interface (GUI), it is easier to work with and it allows a wide range of tasks to be accomplished with a click. Library automation standards A compatible standards such as MARC and Z39.50 protocol
- 9. Automation Standards The standards adopted by the library and its community that facilitate data interchange between libraries & information centers through a unique format which are supported by all systems, for example MARC (Machine Readable Cataloguing) standards and Z39.50, the information search and retrieve protocol standard.
- 10. Why MARC The MARC standard allows libraries to share bibliographic resources with other information centers. It also enables libraries to easily migrate to commercially available library automation systems, a majority of which support only the MARC standard. A bibliographic record in MARC format will allow the application system or library automation system to: Format the information correctly for printing a set of catalog cards or for displaying the information on computer screen Search for and retrieve certain types of information within specific fields (Keyword Searching) Display lists of items as required by the search .
- 11. Z39.50 Protocol Z39.50 is generally defined as the information search and retrieve protocol standard used primarily by library and information related systems. The standard specifies a client / server-based protocol for searching and retrieving information from remote databases simultaneously using a single interface.
- 12. The OPAC Cataloging activities using an Automated ILS, produces an electronic catalog. Providing access to the catalog for users which is limited to search and display, is called an “Online Public Access Catalog” or OPAC. An OPAC is usually offered as an add-on module that is inter-related with the cataloging module. The specific search and display features of an OPAC vary from system to system.
- 13. OPAC & More… OPAC can also be linked to the Circulation Module so that users can find out the status of any item (whether it is on loan, on-shelf, etc.), as well as making a self-reservation, self check-in/check-out, etc. Through the development in ICTs we can enable our libraries to publish their catalogs on the Web and making them accessible remotely, as Web OPAC.
- 14. ABOUT MODULES
- 15. Acquisitions Module Automates the acquisition process like : ordering, receiving, claiming material from vendors / suppliers, & also cancellations of library material at the time of order for purchase. Used to maintain statistics, and in some cases manage accounting activities. Acquisition can be done online if system is linked to an external network .
- 16. Cataloging Module Creation, Storage, Retrieval and Management of bibliographic records and / or indexes. Defines the record in a specific format used in the database and provides for authority control (author, subject headings etc.) Usually there are two different interfaces for search and retrieval of the electronic catalog : For catalogers: that allows them to maintain the library database (main cataloging module) , For users: that allows them to search and display the results on (OPAC)
- 17. Circulation Module Handles circulation activities such as: lending, return, renewal, place on hold, and reservation etc. Manage library material - circulation type, location and status; patron database - patron type, profiles, privileges; and other transactions such as computation and payment of overdue fines, lost books, etc. We may be added value functions like: import, export, backup and restore functions for the databases; inventory; report generation; and support for MARC, Z39.50, ILL standards. This may support integration with security systems that complement the self-check-in and check-out features of the circulation module. etc.
- 18. Serials Control Module In an ILS, serial control is playing an omnipotent role. Organising & managing the orders to the respective vendors, keep tracking on accounting part and preparing statistical information as per requirement. Provides a expert system for tracking over un-received (due) periodicals and simultaneously generate claim, etc.
- 19. Add-on Module The vendor usually offer additional functions and features as optional to the basic functions or as an integral part of a module. For Ex. inventory, ILL, short loan transactions, import / export of records through MARC formats, Web OPAC, and security systems linked to or integrated with the cataloging / circulation module, etc.
- 20. Library Automation: Steps Involved Engagement of Subject Expert Technology Plan Selection and Acquisition of ILMS Implementation Post-Analysis
- 21. Engagement of Subject Expect Experienced guide is more essential initially, for the development of a new concept. It is necessary because “learn from the mistake” concept is their. The expert should be engaged from the beginning of the proposal for automation. In a automation system most important thing is the “staff literacy”, who will work from the start to implementation & take part in post-analysis.
- 22. Technology Plan and Project Proposal In planning and implementing library automation, a thorough study of the library’s existing system as well as the library’s vision is necessary to enable the environment to prepare a good technology plan and project proposal. Steps: Vision Present Status Requirement Feasibility Study Technology Plan Project Proposal
- 23. Vision A vision is a future dream. It is a vivid picture of what you would like your library to become in the near future. It is based on the mission of your library, the needs of our users and on the changing trends of library service. A vision provides direction and a philosophy for the library.
- 24. Analysis of Present Status A systems study is conducted to assess the library’s status and needs. It involves gathering data about the library’s operations, capacity, facilities, collections, procedures, and staff expertise, etc. In general, the assessment should involve gathering information about user needs and wants and matching these with what the library can presently offer.
- 25. Feasibility Study The Purpose of the study is to state, analyse, and document the data needed to make an informed and intelligent decision. The points are: Technical Feasibility: It deals with technical issues, like (Hardware, Software, etc.) Operational Feasibility: It will examine the proposed project or system will work when it is developed or installed or related problems (barrier) Economic Feasibility: It will call for greater attention. In actual sense it deals with the budget factor / Money involvement.
- 26. Technological Plan Library Automation is depend on a specific technological plan, it includes: Hardware Software Supported Peripherals for Automation (scanner, & printer, etc.) IT literacy & software related T.D. of Library Staffs.
- 27. Project Proposal It is based on the technological plan. It will help to study the present environment of the library, and able to create or develop a vision for successful automation. Help to prepare Request for Proposal (RFP) and so on…
- 28. Basic Requirements Gathering of Statistical DATA Staff Profile Patron Profile Policies and Procedures Functional Specifications Staff Coordination and T.D.
- 29. Selection and Acquisition of ILMS In House: The software developed by own or in by the institution / organisation. Commercial software: Software purchased from vendor. Out side from the organisation. For the selection of the best package for library, analyse and identify your needs and match it with the features and functions of integrated library systems.
- 30. Need for evaluation of ILS Evaluating the Integrated Library Systems is necessary to choose the most appropriate library management system that will answer the needs of the library in automating its operations for further development. The task of selecting software packages requires careful planning. To reach an informed decision you will have to study several systems.
- 31. Lastly, Steps in the RFP Process Writing the RFP (Request for Proposal) Engagement of subject expert Approval Submitting to vendor Receiving proposals from vendors Evaluating proposals Preparing a short list of vendors Requesting a demo of the system Purchasing the system Preparing the contract Proper training support Implementing the system Evaluating the implemented system
- 32. Dreaming for automation is a night issue, but it consumed several nights without any dream…