Logical link protocols and service data.pptx
- 2. Logical link control protocols There are 3 types of LLC protocols. 1.Pure ALOHA 2.Slotted ALOHA 3.HDLC
- 3. ALOHA • Aloha, also called the Aloha method, refers to a simple communications scheme in which each source (transmitter) in a network sends data whenever there is a frame to send.
- 4. PURE ALOHA • It allows the stations to transmit data at any time whenever they want. • After transmitting the data packet, station waits for some time. • Then, following 2 cases are possible Case-01: • Transmitting station receives an acknowledgement from the receiving station. • In this case, transmitting station assumes that the transmission is successful. Case-02: • Transmitting station does not receive any acknowledgement within specified time from the receiving station. • In this case, transmitting station assumes that the transmission is unsuccessful. • Transmitting station uses a Back Off Strategy and waits for some random amount of time. • After back off time, it transmits the data packet again. • It keeps trying until the back off limit is reached after which it aborts the transmission.
- 6. Pure (unslotted) ALOHA • unslotted Aloha: simpler, no synchronization • pkt needs transmission: • send without awaiting for beginning of slot • collision probability increases: • pkt sent at t0 collide with other pkts sent in [t0-1, t0+1]
- 7. SLOTTED ALOHA • Slotted Aloha divides the time of shared channel into discrete intervals called as time slots. • Any station can transmit its data in any time slot. • The only condition is that station must start its transmission from the beginning of the time slot. • If the beginning of the slot is missed, then station has to wait until the beginning of the next time slot. • A collision may occur if two or more stations try to transmit data at the beginning of the same time slot
- 8. Slotted Aloha • time is divided into equal size slots (= pkt trans. time) • node with new pkt: transmit at beginning of next slot • if collision: retransmit pkt in future slots with probability p, until successful. Success (S), Collision (C), Empty (E) slots
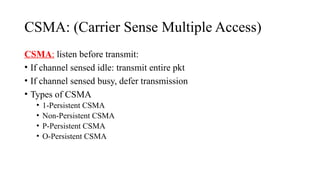
- 10. CSMA: (Carrier Sense Multiple Access) CSMA: listen before transmit: • If channel sensed idle: transmit entire pkt • If channel sensed busy, defer transmission • Types of CSMA • 1-Persistent CSMA • Non-Persistent CSMA • P-Persistent CSMA • O-Persistent CSMA
- 11. CSMA/CD (Collision Detection) CSMA/CD: carrier sensing, deferral as in CSMA • collisions detected within short time • colliding transmissions aborted, reducing channel wastage • persistent or non-persistent retransmission • collision detection: • easy in wired LANs: measure signal strengths, compare transmitted, received signals • difficult in wireless LANs: receiver shut off while transmitting
- 12. Token Ring • Used in bus and ring network topologies (token ring) • Each computer in the network can only send its data if it has the token. This prevents collisions that occur when data is sent at the same time over the network • The token is a special pattern of bits/bit in a frame that is directly detectible by each node in the network • A computer may only transmit information if it is in possession of the token • The message is sent to all other computers in the network
- 13. Operation of Token Ring
- 14. FDDI (Fiber Distributed Data Interface) • FDDI is a standard developed by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) for transmitting data on optical fibers • Supports transmission rates of up to 200 Mbps • Uses a dual ring • First ring used to carry data at 100 Mbps • Second ring used for primary backup in case first ring fails • If no backup is needed, second ring can also carry data, increasing the data rate up to 200 Mbps • Supports up to 1000 nodes • Has a range of up to 200 km
- 17. Ethernet • Most successful local area networking technology of last 20 years. • Developed in the mid-1970s by researchers at the Xerox Palo Alto Research Centers (PARC). • Uses CSMA/CD technology • Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection. • A set of nodes send and receive frames over a shared link. • Carrier sense means that all nodes can distinguish between an idle and a busy link. • Collision detection means that a node listens as it transmits and can therefore detect when a frame it is transmitting has collided with a frame transmitted by another node.
- 18. Ethernet • Multiple Ethernet segments can be joined together by repeaters. • A repeater is a device that forwards digital signals. • No more than four repeaters may be positioned between any pair of hosts. • An Ethernet has a total reach of only 2500 m.
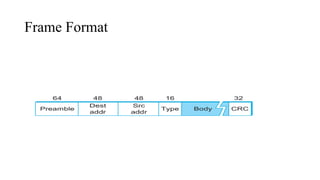
- 19. Frame Format
- 21. • Worst-case scenario: (a) A sends a frame at time t; (b) A’s frame arrives • at B at time t + d; (c) B begins transmitting at time t + d and collides with A’s frame; • (d) B’s runt (32-bit) frame arrives at A at time t + 2d.
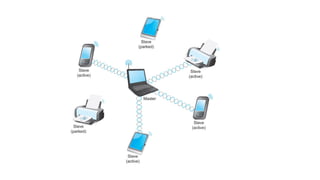
- 22. Bluetooth • The basic Bluetooth network configuration is called a piconet • Consists of a master device and up to seven slave devices • Any communication is between the master and a slave • The slaves do not communicate directly with each other • A slave can be parked: set to an inactive, low-power state
- 24. 802.11
- 25. IEEE 802.11 • Also known as Wi-Fi • Like its Ethernet and token ring siblings, 802.11 is designed for use in a limited geographical area (homes, office buildings, campuses) • Primary challenge is to mediate access to a shared communication medium – in this case, signals propagating through space • 802.11 supports additional features • power management and • security mechanisms
- 26. • Consider the situation shown in the following figure when node C moves from the cell serviced by AP-1 to the cell serviced by AP-2. • As it moves, it sends Probe frames, which eventually result in Probe Responses from AP-2. • At some point, C prefers AP-2 over AP-1 , and so it associates itself with that access point. • This is called active scanning since the node is actively searching for an access point IEEE 802.11 – Distribution System Node Mobility
- 27. IEEE





![Pure (unslotted) ALOHA
• unslotted Aloha: simpler, no synchronization
• pkt needs transmission:
• send without awaiting for beginning of slot
• collision probability increases:
• pkt sent at t0 collide with other pkts sent in [t0-1, t0+1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/logicallinkprotocols-250110092339-e5803cb2/85/Logical-link-protocols-and-service-data-pptx-6-320.jpg)