Managing Data at Scale - Microservices and Events
- 1. Managing Data at Scale Microservices and Events Randy Shoup @randyshoup linkedin.com/in/randyshoup
- 2. Evolution to Microservices • eBay • 5th generation today • Monolithic Perl Monolithic C++ Java microservices • Twitter • 3rd generation today • Monolithic Rails JS / Rails / Scala microservices • Amazon • Nth generation today • Monolithic Perl / C++ Java / Scala microservices @randyshoup linkedin.com/in/randyshoup
- 3. No one starts with microservices … Past a certain scale, everyone ends up with microservices
- 4. First Law of Distributed Object Design: Don’t distribute your objects! -- Martin Fowler
- 5. Managing Data at Scale • Migrating to Microservices • Challenges of Data in Microservices • Challenges of Event-Driven Systems
- 6. Managing Data at Scale • Migrating to Microservices • Challenges of Data in Microservices • Challenges of Event-Driven Systems
- 7. Microservices • Single-purpose • Simple, well-defined interface • Modular and independent • Isolated persistence (!) A C D E B
- 8. Extracting Microservices • Problem: Monolithic shared DB • Clients • Shipments • Items • Styles, SKUs • Warehouses • etc. stitchfix.com Styling app Warehouse app Merch app CS app Logistics app Payments service Profile service
- 9. Extracting Microservices • Decouple applications / services from shared DB • Clients • Shipments • Items • Styles, SKUs • Warehouses • etc. stitchfix.com Styling app Warehouse app Merch app CS app Logistics app Payments service Profile service
- 10. Extracting Microservices • Decouple applications / services from shared DB Styling app Warehouse app core_item core_sku core_client
- 11. Extracting Microservices • Step 1: Create a service Styling app Warehouse app core_item core_sku core_client client-service
- 12. Extracting Microservices • Step 2: Applications use the service Styling app Warehouse app core_item core_sku core_client client-service
- 13. Extracting Microservices • Step 3: Move data to private database Styling app Warehouse app core_item core_sku client-service core_client
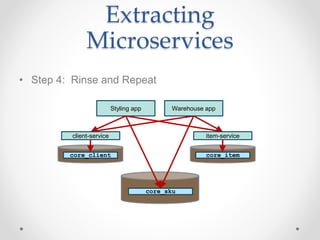
- 14. Extracting Microservices • Step 4: Rinse and Repeat Styling app Warehouse app core_sku client-service core_client item-service core_item
- 15. Extracting Microservices • Step 4: Rinse and Repeat Styling app Warehouse app client-service core_client item-service core_item style-service core_sku
- 16. Extracting Microservices • Step 4: Rinse and Repeat Styling app Warehouse app client-service core_client item-service core_item style-service core_sku
- 17. Managing Data at Scale • Migrating to Microservices • Challenges of Data in Microservices o Two Architectural Tools o Shared Data o Joins o Transactions • Challenges of Event-Driven Systems
- 18. Managing Data at Scale • Migrating to Microservices • Challenges of Data in Microservices o Two Architectural Tools o Shared Data o Joins o Transactions • Challenges of Event-Driven Systems
- 19. Service as System of Record • Single System of Record o Every piece of data is owned by a single service o That service is the canonical system of record for that data • Every other copy is a read-only, non-authoritative cache @randyshoup linkedin.com/in/randyshoup customer-service styling-service customer-search billing-service
- 20. Events as First-Class Construct • “A significant change in state” o Statement that some interesting thing occurred • Traditional 3-tier system o Presentation interface / interaction o Application stateless business logic o Persistence database • Fourth fundamental building block o State changes events o 0 | 1 | N consumers subscribe to the event, typically asynchronously @randyshoup linkedin.com/in/randyshoup
- 21. Microservices and Events • Events are a first-class part of a service interface • A service interface includes o Synchronous request-response (REST, gRPC, etc) o Events the service produces o Events the service consumes o Bulk reads and writes (ETL) • The interface includes any mechanism for getting data in or out of the service (!) @randyshoup linkedin.com/in/randyshoup
- 22. Managing Data at Scale • Migrating to Microservices • Challenges of Data in Microservices o Two Architectural Tools o Shared Data o Joins o Transactions • Challenges of Event-Driven Systems
- 23. Data in Microservices: Shared Data • Monolithic database makes it easy to leverage shared data • Where does shared data go in a microservices world? @randyshoup linkedin.com/in/randyshoup
- 24. Data in Microservices: Shared Data Option 1: Synchronous Lookup o Customer service owns customer data o Fulfillment service calls customer service in real time fulfillment-service customer-service @randyshoup linkedin.com/in/randyshoup
- 25. Data in Microservices: Shared Data Option 2: Async event + local cache o Customer service owns customer data o Customer service sends address-updated event when customer address changes o Fulfillment service caches current customer address fulfillment-servicecustomer-service @randyshoup linkedin.com/in/randyshoup
- 26. Data in Microservices: Shared Data Option 3: Shared metadata library o Read-only metadata, basically immutable o E.g., size schemas, colors, fabrics, US States, etc. receiving-serviceitem-service style-service
- 27. Managing Data at Scale • Migrating to Microservices • Challenges of Data in Microservices o Two Architectural Tools o Shared Data o Joins o Transactions • Challenges of Event-Driven Systems
- 28. Data in Microservices: Joins • Monolithic database makes it easy to join tables • Splitting the data across microservices makes joins very hard @randyshoup linkedin.com/in/randyshoup SELECT FROM A INNER JOIN B ON …
- 29. Data in Microservices: Joins Option 1: Join in Client Application o Get a single customer from customer-service o Query matching orders for that customer from order-service Customers Orders order-history-page customer-service order-service
- 30. Data in Microservices: Joins Option 2: Service that “Materializes the View” o Listen to events from item-service, events from order-service o Maintain denormalized join of items and orders together in local storage Items Order Feedback item-feedback-service item-service order-feedback-service
- 31. Data in Microservices: Joins • Many common systems do this o “Materialized view” in database systems o Most NoSQL systems o Search engines o Analytic systems @randyshoup linkedin.com/in/randyshoup
- 32. Managing Data at Scale • Migrating to Microservices • Challenges of Data in Microservices o Two Architectural Tools o Shared Data o Joins o Transactions • Challenges of Event-Driven Systems
- 33. Data in Microservices: Transactions • Monolithic database makes transactions across multiple entities easy • Splitting data across services makes transactions very hard @randyshoup linkedin.com/in/randyshoup BEGIN; INSERT INTO A …; UPDATE B...; COMMIT;
- 34. “In general, application developers simply do not implement large scalable applications assuming distributed transactions.” -- Pat Helland Life After Distributed Transactions: An Apostate’s Opinion, 2007
- 35. “Grownups don’t use distributed transactions” -- Pat Helland
- 36. Data in Microservices: Workflows and Sagas • Transaction Saga o Model the transaction as a state machine of atomic events • Reimplement as a workflow • Roll back by applying compensating operations in reverse A B C A B C @randyshoup linkedin.com/in/randyshoup
- 37. Data in Microservices: Workflows and Sagas • Many common systems do this o Payment processing o Expense approval o Travel o Any multi-step workflow @randyshoup linkedin.com/in/randyshoup
- 38. Data in Microservices: Workflows and Sagas • Simple event-driven processing o Very lightweight logic o Stateless o Triggered by an event • Consider Function-as-a-Service (“Serverless”) A B C A B C @randyshoup linkedin.com/in/randyshoup ƛ ƛ ƛ ƛ ƛ ƛ
- 39. Managing Data at Scale • Migrating to Microservices • Challenges of Data in Microservices • Challenges of Event-Driven Systems o Event Duplication o Event Ordering
- 40. Managing Data at Scale • Migrating to Microservices • Challenges of Data in Microservices • Challenges of Event-Driven Systems o Event Duplication o Event Ordering
- 41. Event Duplication • Problem: The same event will be delivered more than once o Network issues o Redelivery @randyshoup linkedin.com/in/randyshoup Producer ConsumerTransport • Event-1 • Event-2 • Event-3 • Event-1 • Event-2 • Event-2 • Event-3
- 42. Event Duplication • The consumer must process an event correctly regardless of how many times it receives it @randyshoup linkedin.com/in/randyshoup Producer ConsumerTransport • Event-1 • Event-2 • Event-3 • Event-1 • Event-2 • Event-2 • Event-3 • Event-1 • Event-2 • Event-3
- 43. Event Duplication: (A) Exactly Once Delivery Message bus buffers messages o Message bus remembers events it has delivered, identified by message id o Only deliver event if not yet delivered @randyshoup linkedin.com/in/randyshoup Producer ConsumerTransport • Event-1 • Event-2 • Event-3 • Event-1 [1] • Event-2 [2] • Event-3 [3] • Event-1 [1] • Event-2 [2] • Event-2 [2] • Event-3 [3] • Event-1 [1] • Event-2 [2] • Event-3 [3]
- 44. Event Duplication: (B) Idempotent Processing Option 1: Idempotency key o Remember previously processed events, identified by idempotency key o Before processing, check whether you have processed it already o E.g., counter @randyshoup linkedin.com/in/randyshoup Producer ConsumerTransport • Event-1 [aaa] • Event-2 [bbb] • Event-3 [ccc] • Event-1 [aaa] • Event-2 [bbb] • Event-2 [bbb] • Event-3 [ccc] • Event-1 • Event-2 • <nothing> • Event-3 aaa aaa,bbb aaa,bbb aaa,bbb,ccc
- 45. Event Duplication: (B) Idempotent Processing Option 2: Processing is inherently idempotent o Simply do the processing N times for N events o E.g., “set X to 10”, UPSERT @randyshoup linkedin.com/in/randyshoup Producer ConsumerTransport • Event-1 • Event-2 • Event-3 • Event-1 • Event-2 • Event-2 • Event-3 • Set x:=1 • Set x:=2 • Set x:=2 • Set x:=3
- 46. Event Duplication: (B) Idempotent Processing Option 3: Conflict-free Replicated Datatypes (CRDTs) o Achieve agreement without explicit coordination o Custom data structures, composable processing steps o Many implementations, but still an area of active research Common techniques o Remember what you saw (request id, idempotency key) o Remember that an item was deleted (“tombstone”) (Do *NOT* roll your own from first principles) @randyshoup linkedin.com/in/randyshoup
- 47. Managing Data at Scale • Migrating to Microservices • Challenges of Data in Microservices • Challenges of Event-Driven Systems o Event Duplication o Event Ordering
- 48. Event Ordering • Problem: Events will arrive out of order o Network issues o Processing time o Redelivery @randyshoup linkedin.com/in/randyshoup Producer ConsumerTransport • Event-1 • Event-2 • Event-3 • Event-2 • Event-1 • Event-3
- 49. Event Ordering • The consumer must process events correctly regardless of the order in which they arrive @randyshoup linkedin.com/in/randyshoup Producer ConsumerTransport • Event-1 • Event-2 • Event-3 • Event-2 • Event-1 • Event-3 • Event-1 • Event-2 • Event-3
- 50. Event Ordering: (A) Impose Order Option 1: Sequence + Reorder in the message bus o Sequence number at the producer o Message bus queues messages, waits for gaps o Bus sends to consumer in order @randyshoup linkedin.com/in/randyshoup Producer ConsumerTransport • Event-1 [1] • Event-2 [2] • Event-3 [3] • Event-1 [1] • Event-2 [2] • Event-3 [3] • Event-1 [1] • Event-2 [2] • Event-3 [3] • Event-2 [2] • Event-1 [1] • Event-3 [3]
- 51. Event Ordering: (A) Impose Order Option 2: Sequence + Reorder in the consumer o Sequence number / timestamp at the producer o Consumer reorders before processing @randyshoup linkedin.com/in/randyshoup Producer ConsumerTransport • Event-1 [1] • Event-2 [2] • Event-3 [3] • Event-2 [2] • Event-1 [1] • Event-3 [3] • Event-1 [1] • Event-2 [2] • Event-3 [3]
- 52. Event Ordering: (B) Order-Independence Option 1: Order-independent semantics o E.g., count number of events @randyshoup linkedin.com/in/randyshoup Producer ConsumerTransport • Event-1 • Event-2 • Event-3 • Event-2 • Event-1 • Event-3 • +1 • +1 • +1
- 53. Event Ordering: (B) Order-Independence Option 2: Notification + Read-back o Event is a notification: object id + type of change o Consumer “reads back” to the source service to get current state @randyshoup linkedin.com/in/randyshoup Producer ConsumerTransport • Event-1 • Event-2 • Event-3 • Event-2 • Event-1 • Event-3 • State = 2 • State = 2 • State = 3
- 54. Event Ordering: (B) Order-Independence Option 3: Event Sourcing o Store all events in a log o Process / interpret later @randyshoup linkedin.com/in/randyshoup Producer ConsumerTransport • Event-1 • Event-2 • Event-3 • Event-2 • Event-1 • Event-3 Event-2 Event-1 Event-3 • Event-1 • Event-2 • Event-3
- 55. Managing Data at Scale • Migrating to Microservices • Challenges of Data in Microservices • Challenges of Event-Driven Systems










































![Event Duplication:
(A) Exactly Once Delivery
Message bus buffers messages
o Message bus remembers events it has delivered, identified by message id
o Only deliver event if not yet delivered
@randyshoup linkedin.com/in/randyshoup
Producer ConsumerTransport
• Event-1
• Event-2
• Event-3
• Event-1 [1]
• Event-2 [2]
• Event-3 [3]
• Event-1 [1]
• Event-2 [2]
• Event-2 [2]
• Event-3 [3]
• Event-1 [1]
• Event-2 [2]
• Event-3 [3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildstuffes2018-managingdataatscale-microservicesandevents-180505170707/85/Managing-Data-at-Scale-Microservices-and-Events-43-320.jpg)
![Event Duplication:
(B) Idempotent Processing
Option 1: Idempotency key
o Remember previously processed events, identified by idempotency key
o Before processing, check whether you have processed it already
o E.g., counter
@randyshoup linkedin.com/in/randyshoup
Producer ConsumerTransport
• Event-1 [aaa]
• Event-2 [bbb]
• Event-3 [ccc]
• Event-1 [aaa]
• Event-2 [bbb]
• Event-2 [bbb]
• Event-3 [ccc]
• Event-1
• Event-2
• <nothing>
• Event-3
aaa
aaa,bbb
aaa,bbb
aaa,bbb,ccc](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildstuffes2018-managingdataatscale-microservicesandevents-180505170707/85/Managing-Data-at-Scale-Microservices-and-Events-44-320.jpg)





![Event Ordering:
(A) Impose Order
Option 1: Sequence + Reorder in the message bus
o Sequence number at the producer
o Message bus queues messages, waits for gaps
o Bus sends to consumer in order
@randyshoup linkedin.com/in/randyshoup
Producer ConsumerTransport
• Event-1 [1]
• Event-2 [2]
• Event-3 [3]
• Event-1 [1]
• Event-2 [2]
• Event-3 [3]
• Event-1 [1]
• Event-2 [2]
• Event-3 [3]
• Event-2 [2]
• Event-1 [1]
• Event-3 [3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildstuffes2018-managingdataatscale-microservicesandevents-180505170707/85/Managing-Data-at-Scale-Microservices-and-Events-50-320.jpg)
![Event Ordering:
(A) Impose Order
Option 2: Sequence + Reorder in the consumer
o Sequence number / timestamp at the producer
o Consumer reorders before processing
@randyshoup linkedin.com/in/randyshoup
Producer ConsumerTransport
• Event-1 [1]
• Event-2 [2]
• Event-3 [3]
• Event-2 [2]
• Event-1 [1]
• Event-3 [3]
• Event-1 [1]
• Event-2 [2]
• Event-3 [3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildstuffes2018-managingdataatscale-microservicesandevents-180505170707/85/Managing-Data-at-Scale-Microservices-and-Events-51-320.jpg)




