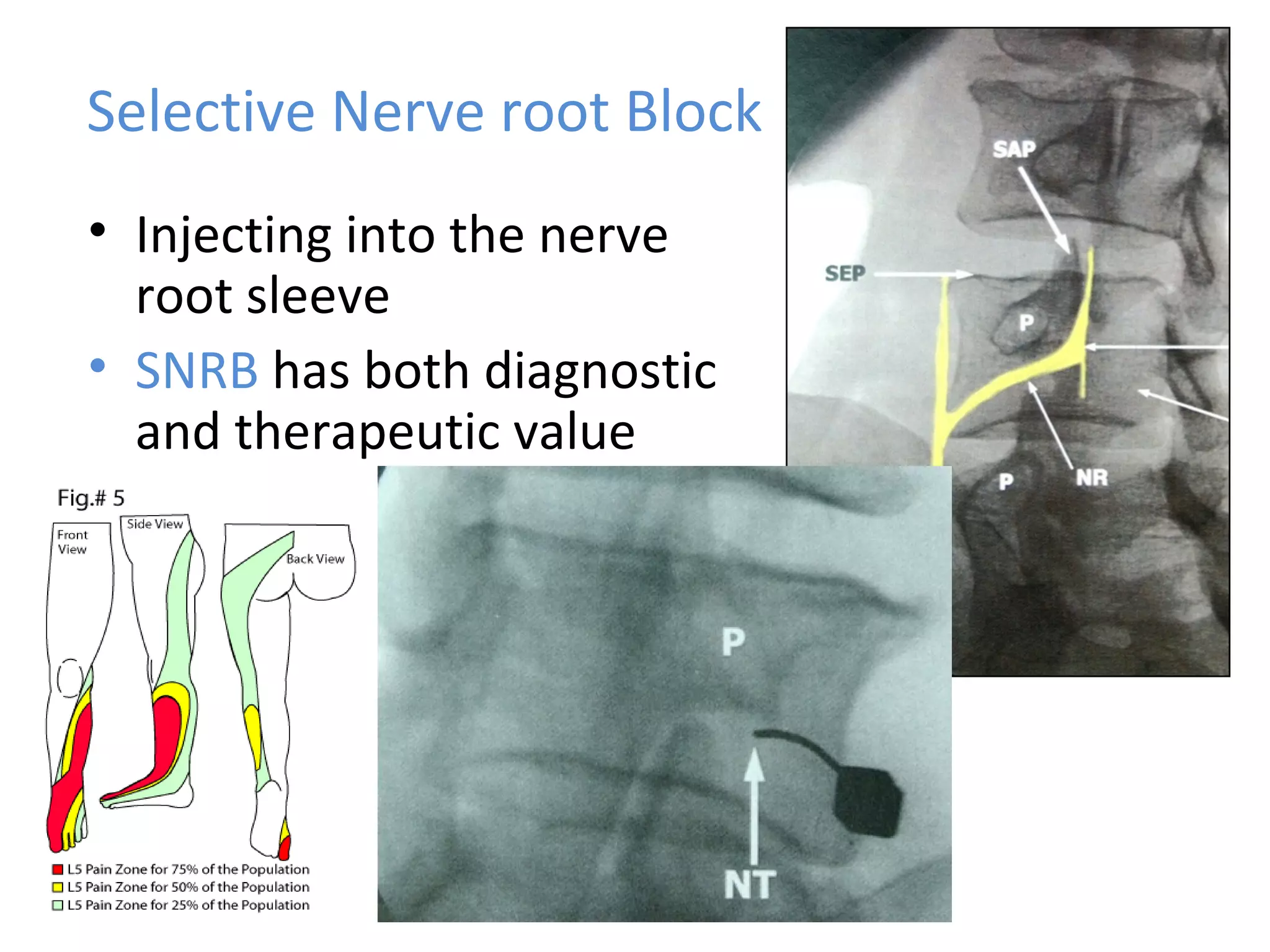
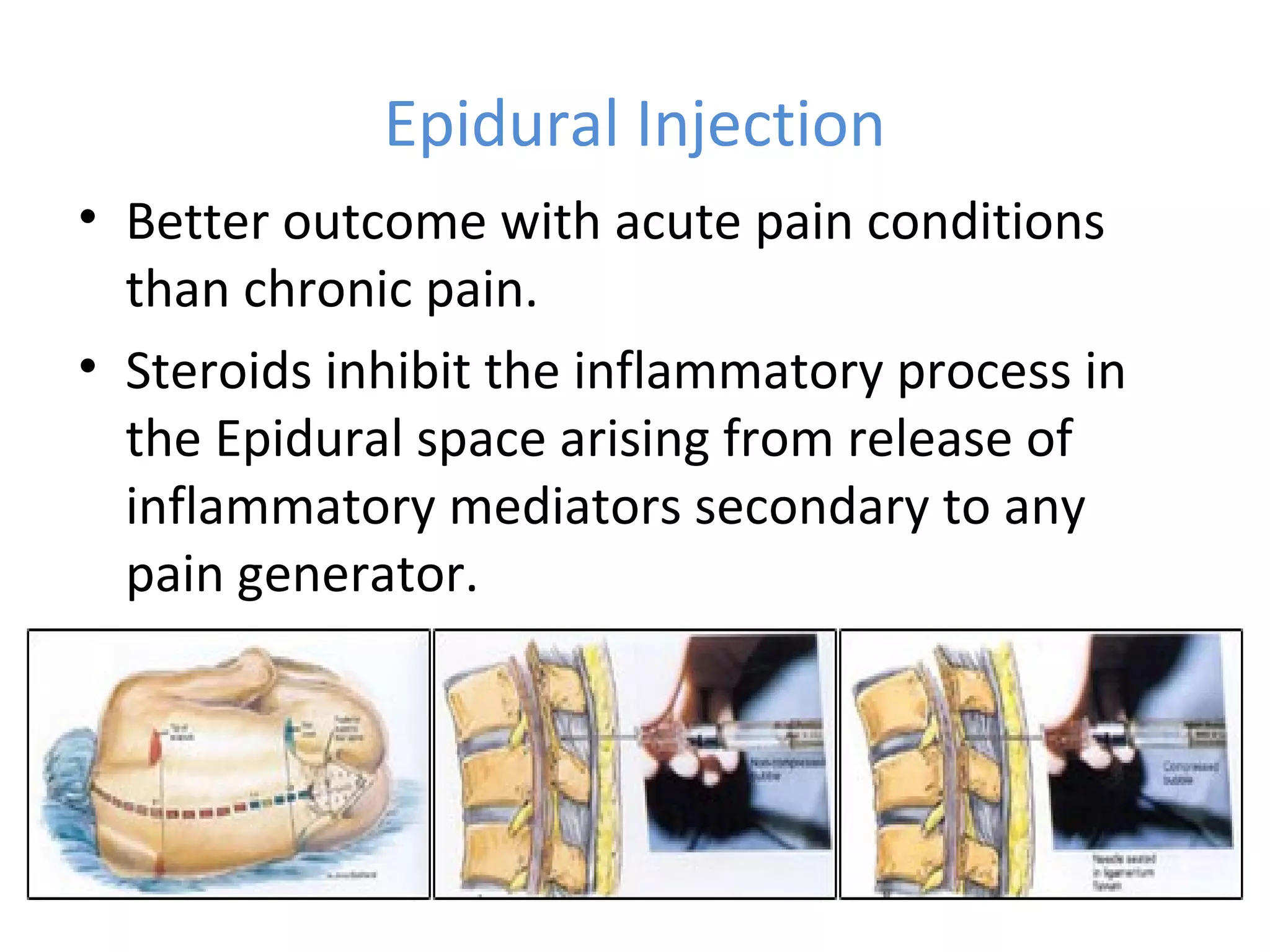
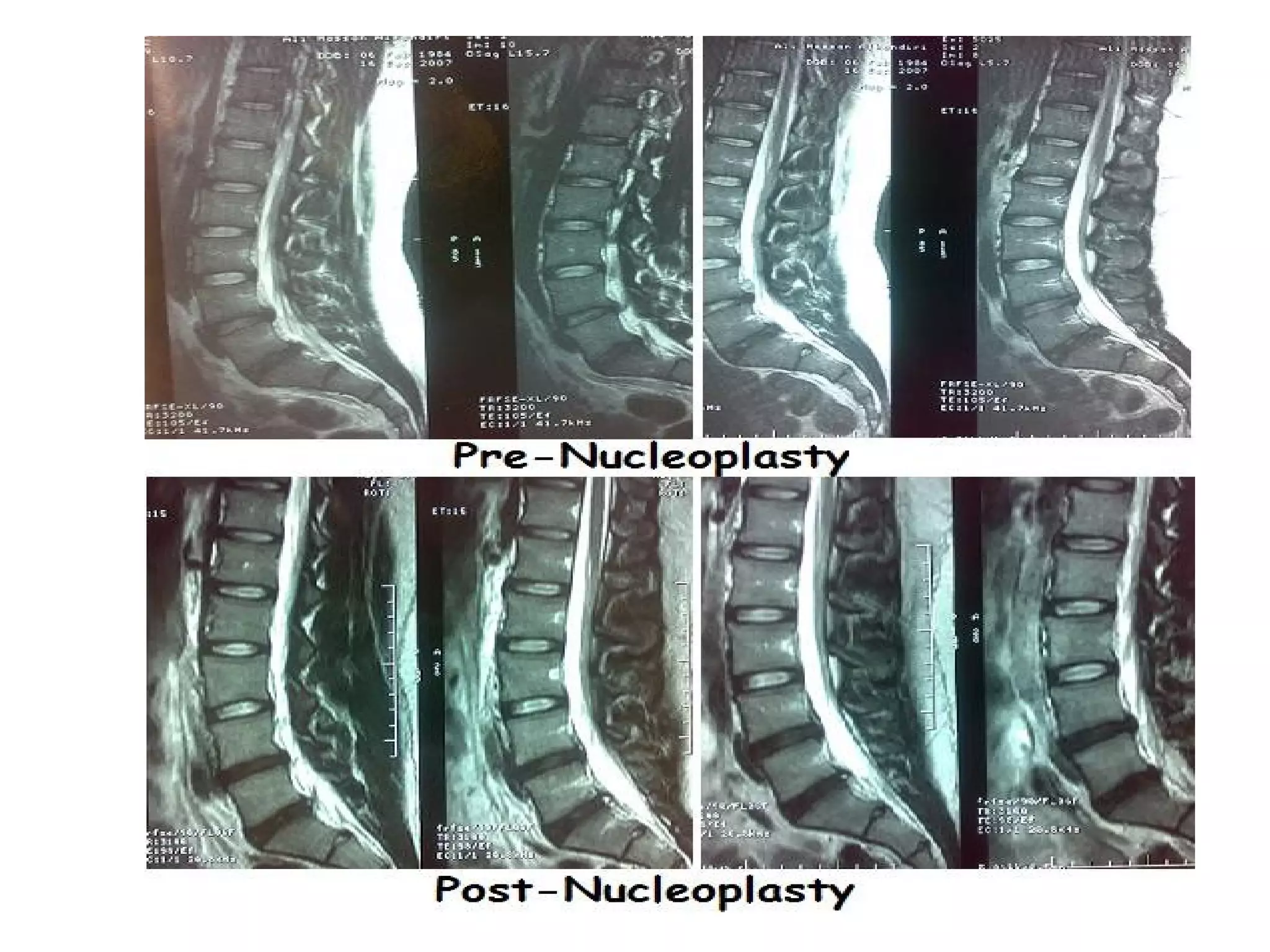
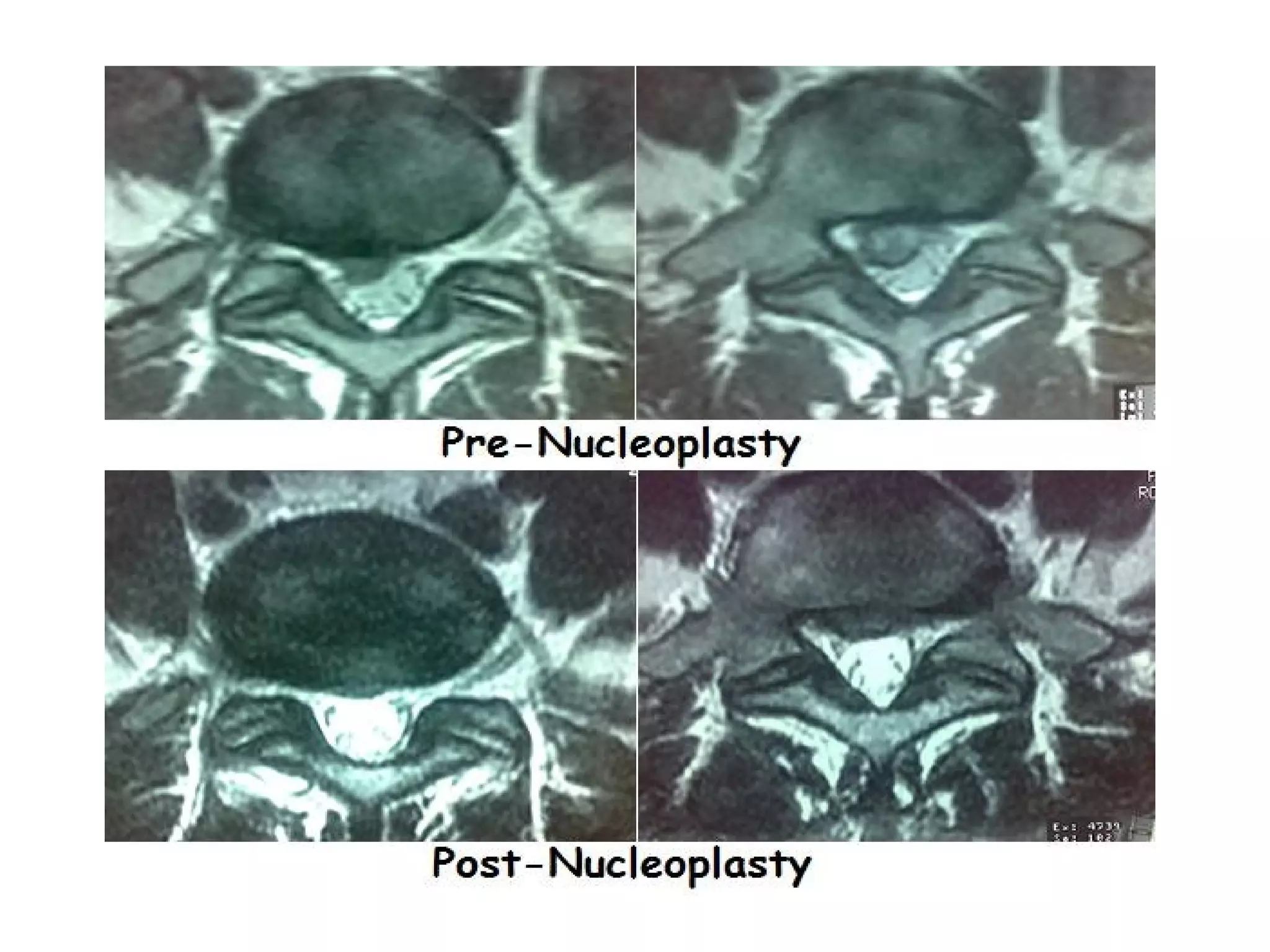
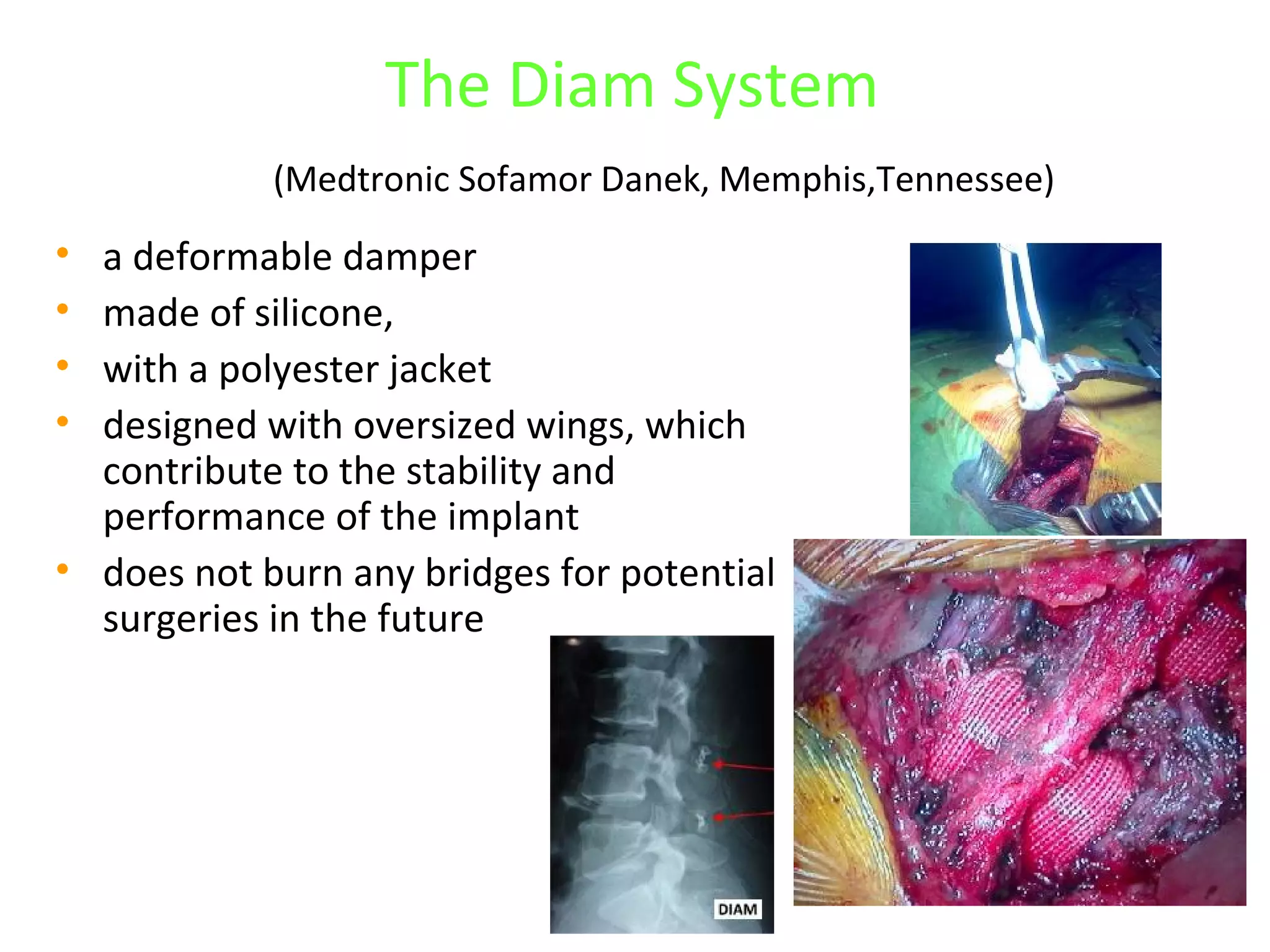
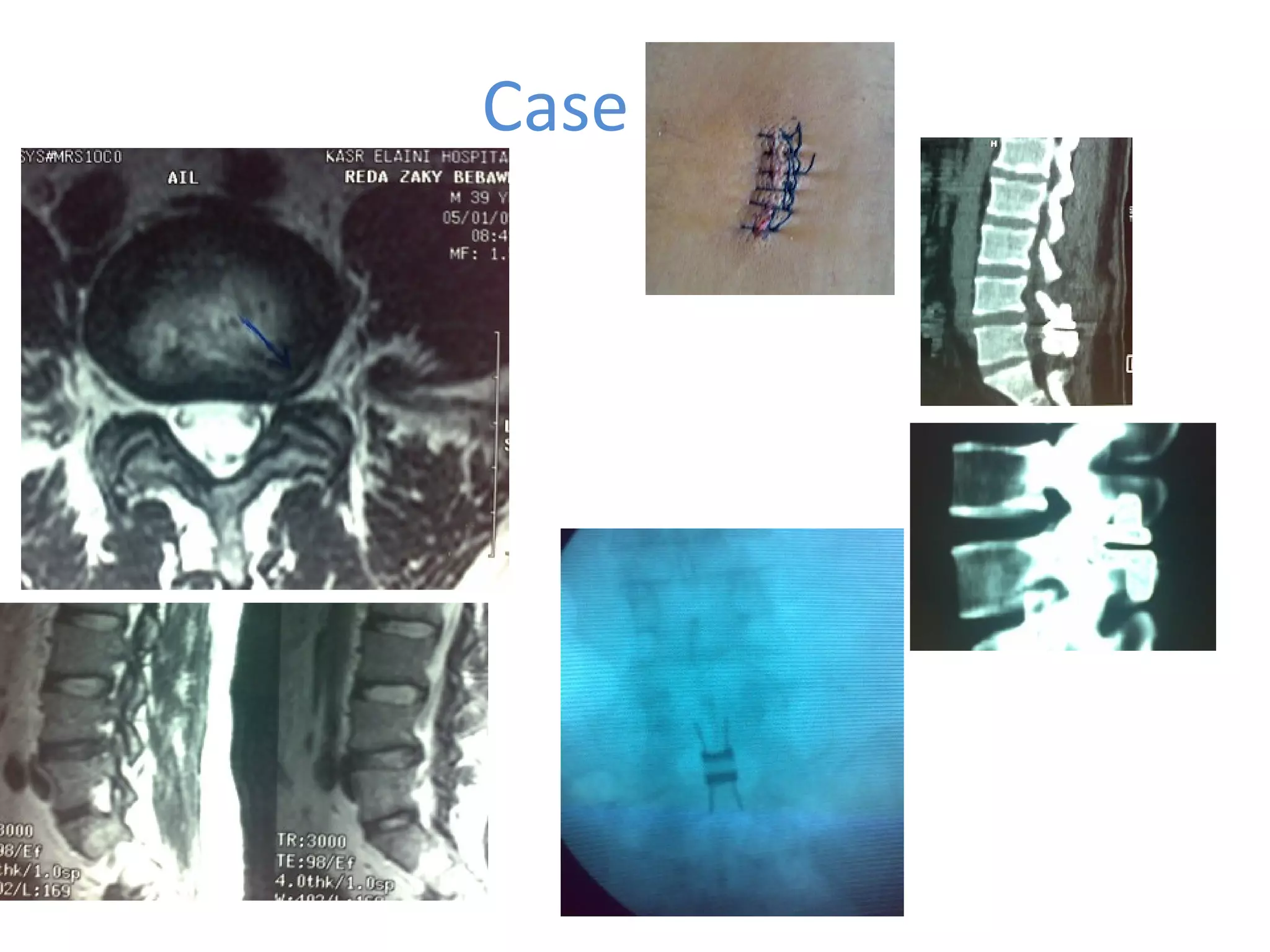
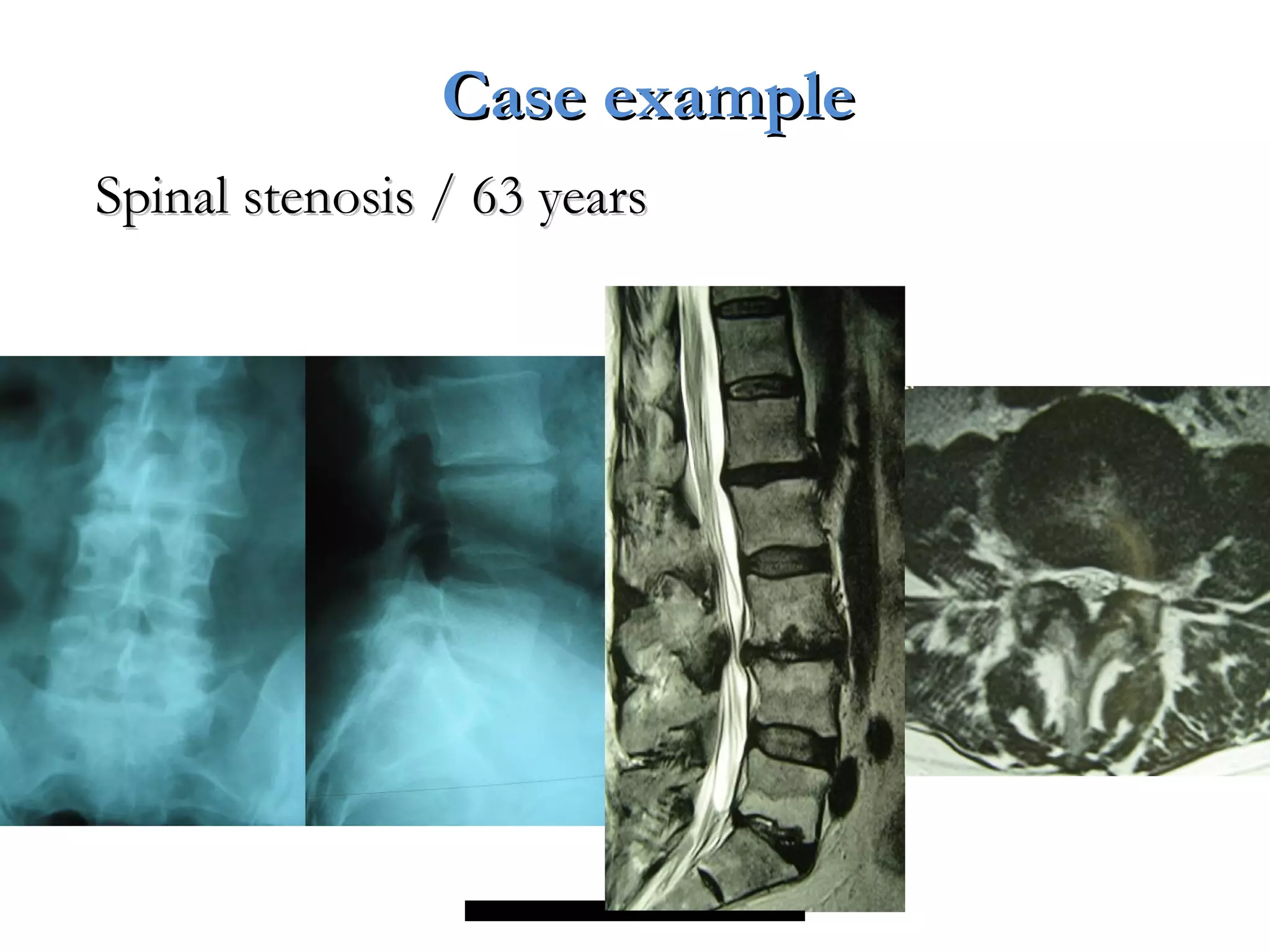
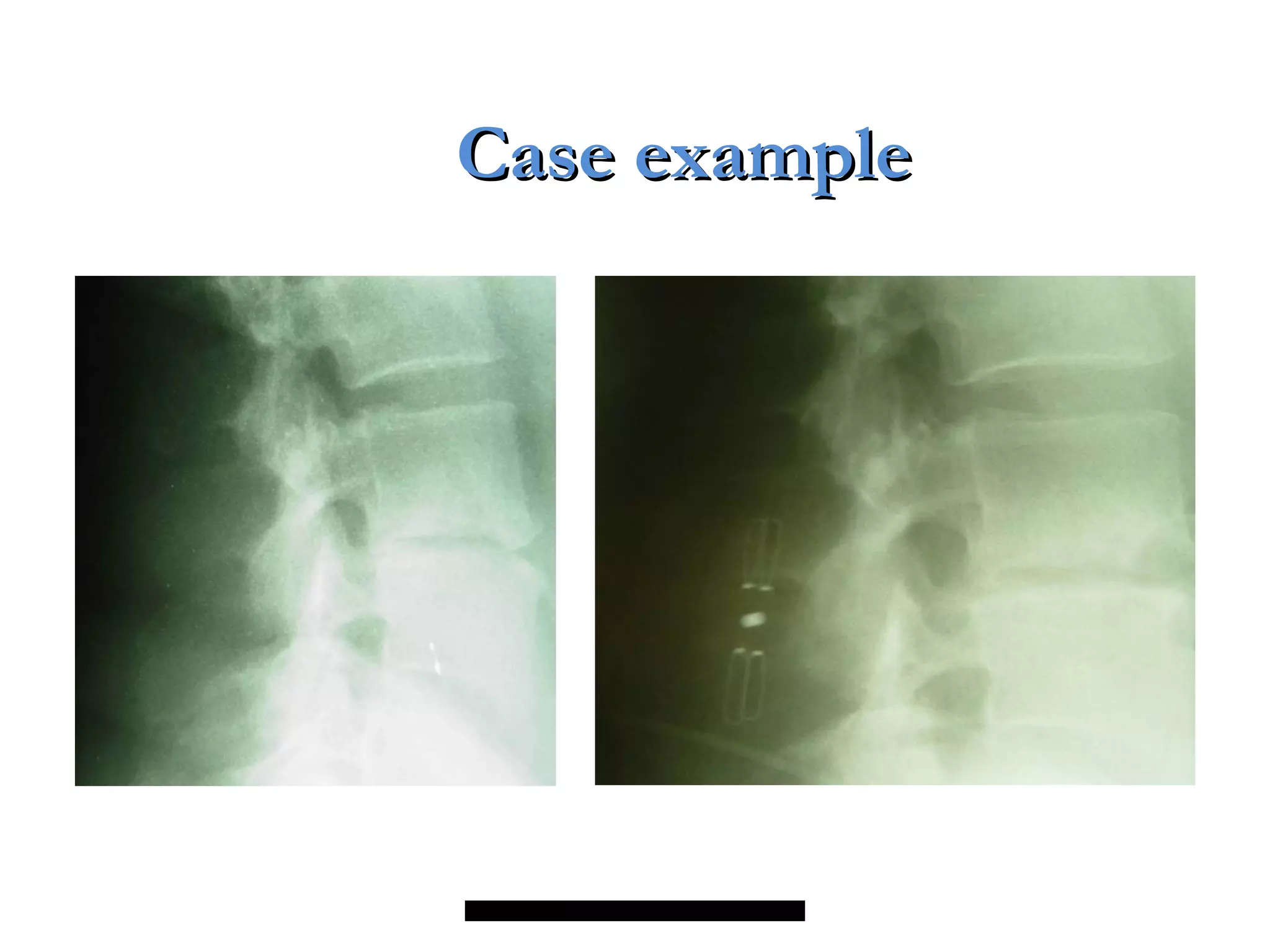
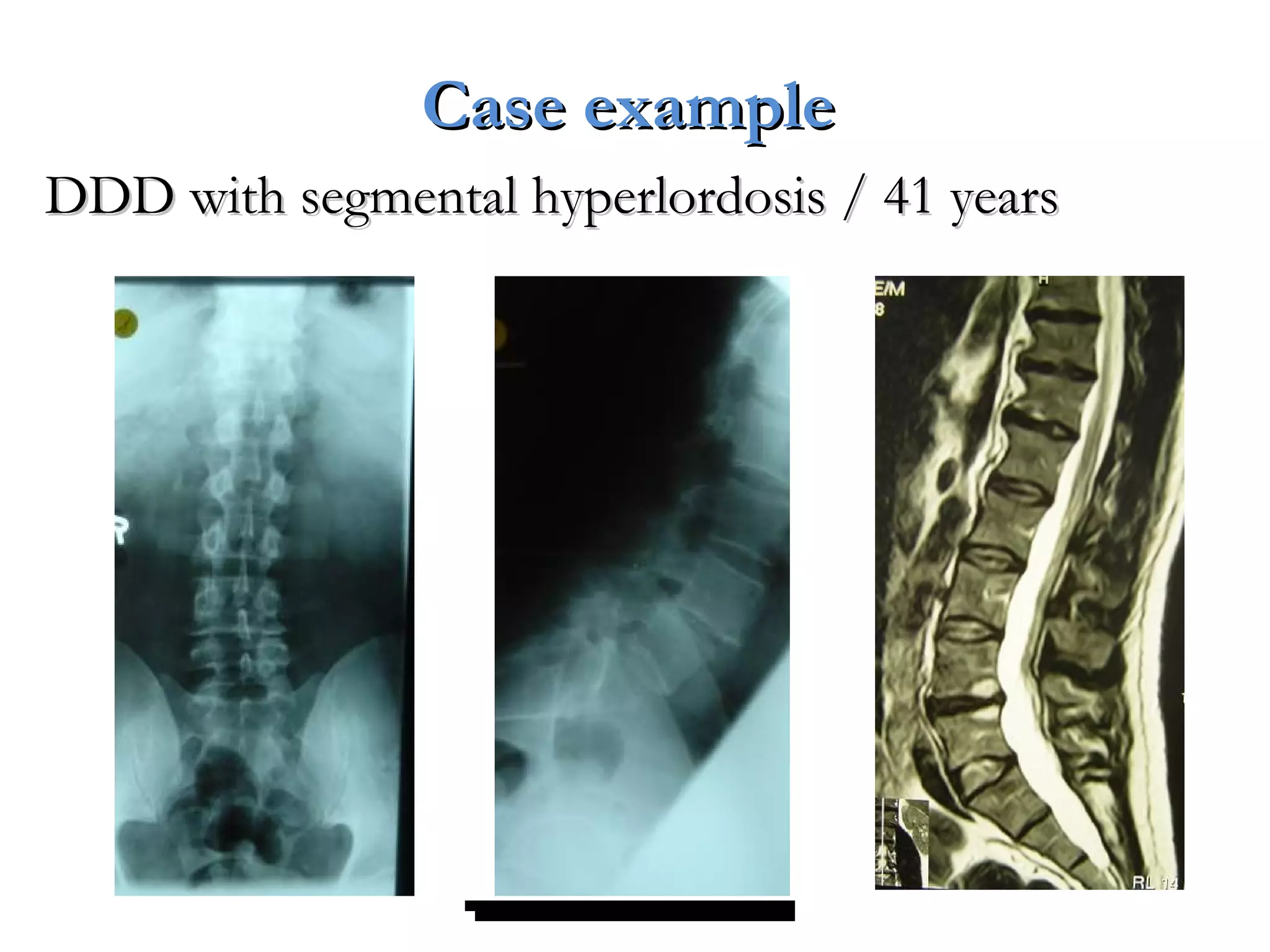
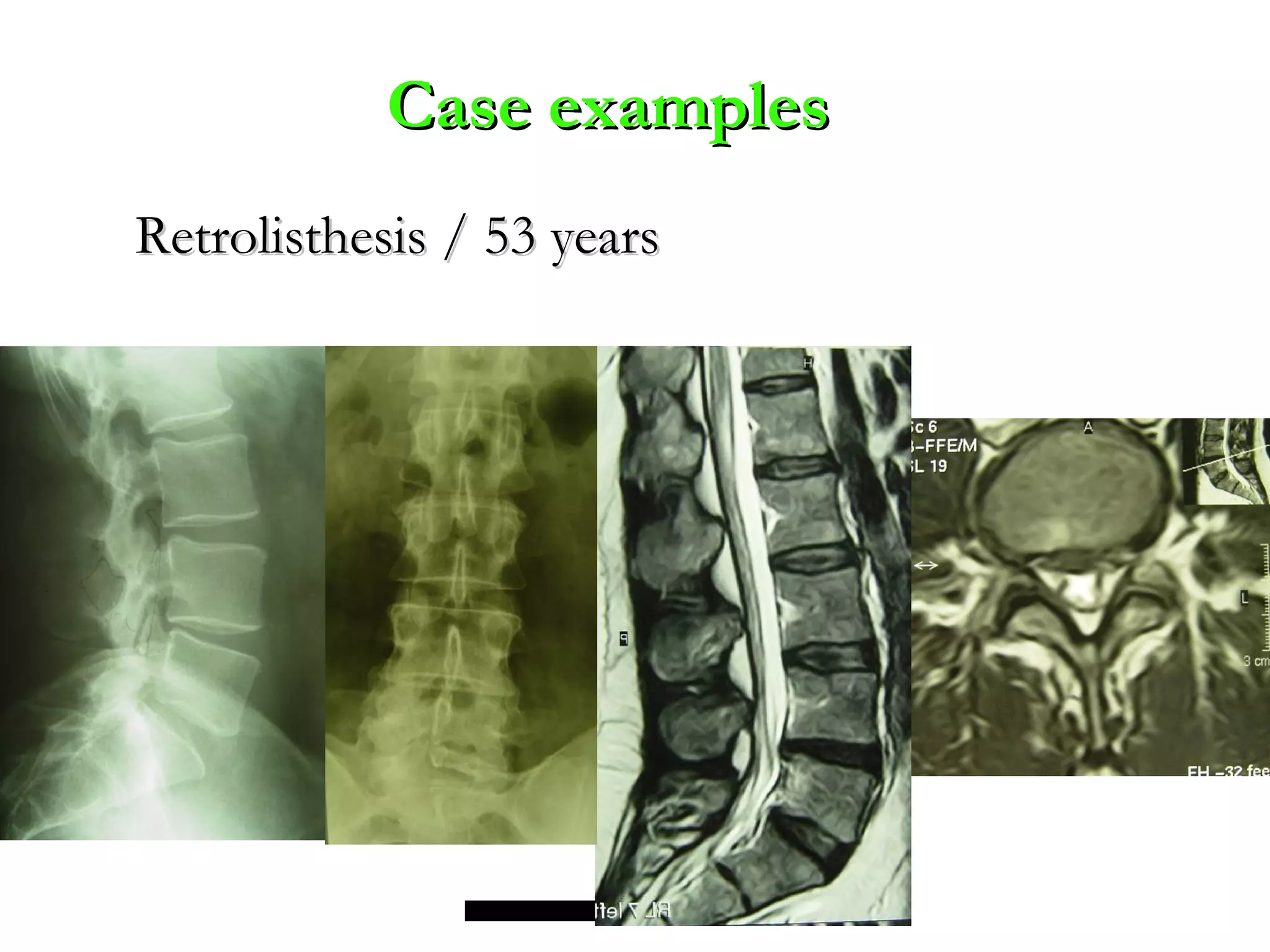
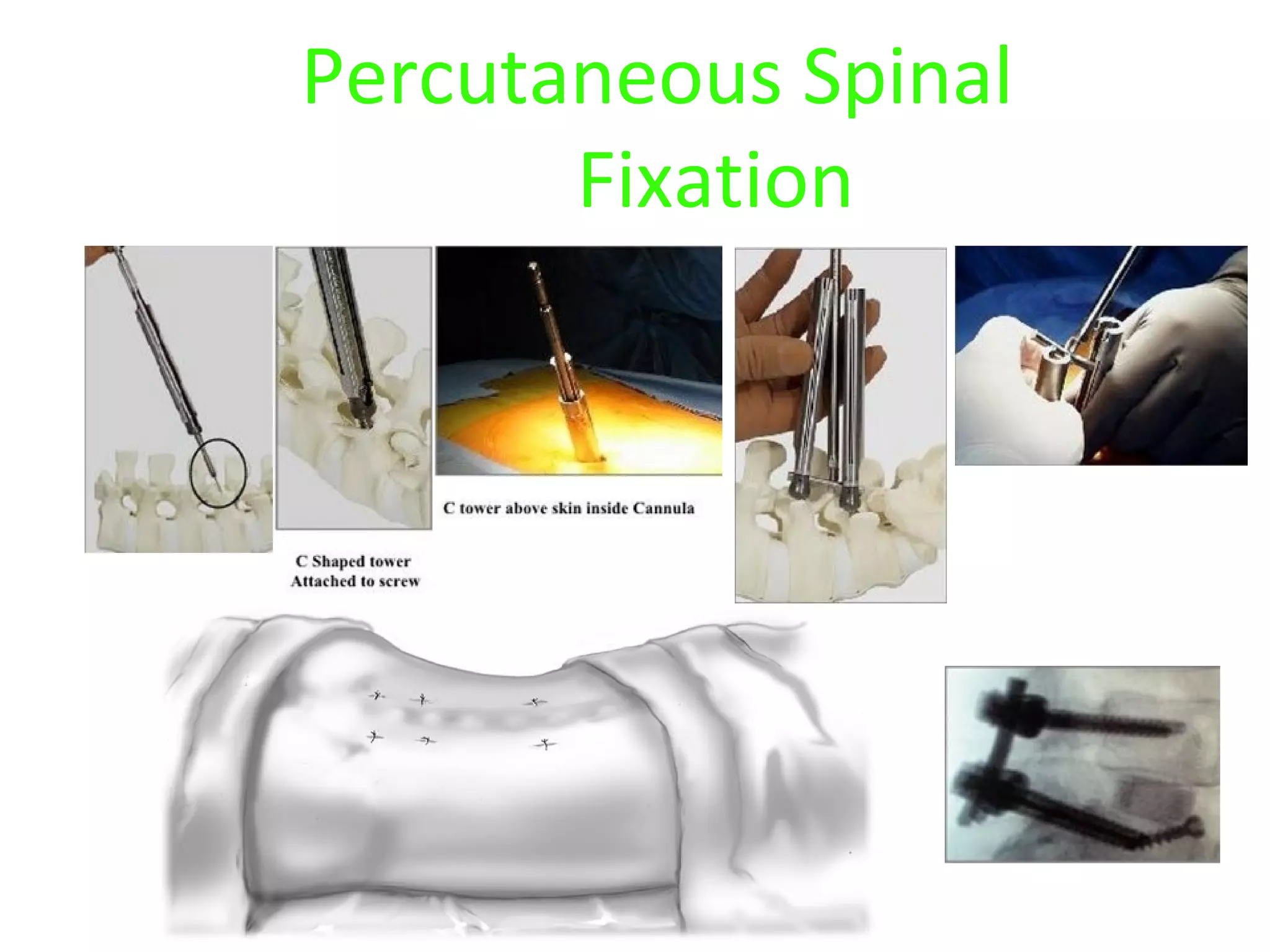
Minimally invasive techniques (MIT) are increasingly used to treat lumbar disc disease. They offer advantages over open surgery such as smaller incisions, less tissue damage, shorter recovery times, and lower risks. MITs include discography, epidural injections, facet/nerve blocks, nucleoplasty, kyphoplasty, tumor debulking, and interspinous spacers. They aim to diagnose and treat back pain conditions under local anesthesia or mild sedation using fluoroscopy guidance. MITs are generally low risk and allow many patients to be treated as outpatients or with only overnight hospitalization.