Modulation techniques matlab_code
- 1. 1 | P a g e COMSATS-Lancaster Dual Degree Programme . CIIT, 1.5KM Defence Road, Off Raiwind Road, Lahore. Name : Ahmed Daud Registration Number : CIIT/DDP-FA10-BTE-002/LHR Email : [email protected] Semester : 6 Section : DDP Department : Electrical Engineering Course Title : Lab Data Communication and Computer Networks Course Code : EEE314 Assignment Number : 2 Assignment Topic : Modulation Techniques Course Book : Data and Computer Communications Submission Date : April 02, 2013 Submitted To : Mr. Owais Javed
- 2. 2 | P a g e TABLE OF CONTENTS QUESTION # PAGE # Q # 1 ASK 3 Q # 2 BPSK 5 Q # 3 FSK 7 Q # 4 Line Coding 11 References 14
- 3. 3 | P a g e Write the MATLAB code for Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK) Modulation. SOLUTION: Amplitude-shift keying (ASK) is a form of modulation that represents digital data as variations in the amplitude of a carrier wave. MATLAB Code: clear all; clc; close all; F1=input('Enter the frequency of carrier='); F2=input('Enter the frequency of pulse='); A=3;%Amplitude t=0:0.001:1; x=A.*sin(2*pi*F1*t);%Carrier Sine wave u=A/2.*square(2*pi*F2*t)+(A/2);%Square wave message v=x.*u; subplot(3,1,1); plot(t,x); xlabel('Time'); ylabel('Amplitude'); title('Carrier'); grid on; subplot(3,1,2); plot(t,u); xlabel('Time'); ylabel('Amplitude'); title('Square Pulses'); grid on;subplot(3,1,3); plot(t,v); xlabel('Time'); ylabel('Amplitude'); title('ASK Signal'); grid on;
- 4. 4 | P a g e OUTPUT: Enter the frequency of carrier=100 Enter the frequency of pulse=10
- 5. 5 | P a g e Write the MATLAB code for Binary Phase Shift Keying (BPSK) Modulation. SOLUTION: BPSK (also sometimes called PRK, Phase Reversal Keying, or 2PSK) is the simplest form of phase shift keying (PSK). It uses two phases which are separated by 180 degrees and so can also be termed 2- PSK. It does not particularly matter exactly where the constellation points are positioned and in this figure they are shown on the real axis, at 0 degrees and 180 degrees. MATLAB Code: clear all; clc; close all; set(0,'defaultlinelinewidth',2); A=5; t=0:.001:1; f1=input('Carrier Sine wave frequency ='); f2=input('Message frequency ='); x=A.*sin(2*pi*f1*t);%Carrier Sine subplot(3,1,1); plot(t,x); xlabel('time'); ylabel('Amplitude'); title('Carrier'); grid on; u=square(2*pi*f2*t);%Message signal subplot(3,1,2); plot(t,u); xlabel('time'); ylabel('Amplitude'); title('Message Signal'); grid on; v=x.*u;%Sine wave multiplied with square wave subplot(3,1,3); plot(t,v); axis([0 1 -6 6]); xlabel('t');
- 6. 6 | P a g e ylabel('y'); title('PSK'); grid on; OUTPUT: Carrier Sine wave frequency =20 Message frequency =5
- 7. 7 | P a g e Write the MATLAB code for Frequency-shift keying (FSK) Modulation. SOLUTION: Frequency-shift keying (FSK) is a frequency modulation scheme in which digital information is transmitted through discrete frequency changes of a carrier wave. The simplest FSK is binary FSK (BFSK). BFSK uses a pair of discrete frequencies to transmit binary (0s and 1s) information. MATLAB Code: clc; close all; clear all; x=input('enter the binary input = '); l=length(x); for i=1:1:l m(((i-1)*100)+1:i*100)=x(i); end figure; subplot(4,1,1); plot(m); xlabel('time'); ylabel('amplitude'); title('modulating signal'); f=100; t=0:(1/f):(l-(1/f)); f1=10; f2=5; c1=sin(2*pi*f1*t); y1=m.*c1; subplot(4,1,2); plot(t,y1); xlabel('time'); ylabel('amplitude'); for j=1:l if x(j)==1 x(j)=0; else x(j)=1;
- 8. 8 | P a g e end m1((j-1)*100+1:j*100)=x(j); end c2=sin(2*pi*f2*t); y2=m1.*c2; subplot(4,1,3); plot(t,y2); xlabel('time'); ylabel('amplitude'); y=y1+y2; subplot(4,1,4); plot(t,y); xlabel('time'); ylabel('amplitude'); title('FSK modulated wave'); r=randn(size(y)); F=y+r; figure; subplot(3,1,1); plot(F); xlabel('time'); ylabel('amplitude'); title('noise added FSK signal'); l1=length(F); t1=0:0.01:.99; r1=sin(2*pi*f1*t1); r1=fliplr(r1); l2=length(r1); l3=l1+l2-1; u=fft(F,l3); v=fft(r1,l3); k1=u.*v; k11=ifft(k1,l3); r2=sin(2*pi*f2*t1); r2=fliplr(r2); w=fft(r2,l3); k2=u.*w; k22=ifft(k2,l3); k=k11-k22; subplot(3,1,2); plot(k); xlabel('time'); ylabel('amplitude');
- 9. 9 | P a g e title('correlated signal'); for z=1:l t(z)=k(z*100); if t(z)>0 s(z)=1; else s(z)=0; end end subplot(3,1,3); stem(s); xlabel('time'); ylabel('amplitude'); title('Demodulated output signal'); OUTPUT: enter the binary input = 101
- 10. 10 | P a g e
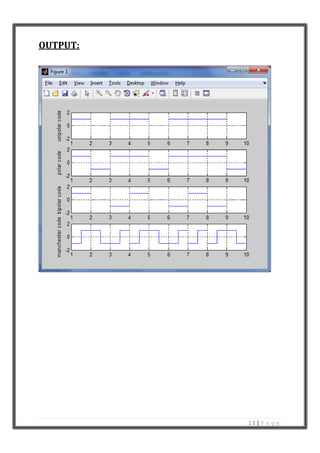
- 11. 11 | P a g e Write the MATLAB code for line coding. SOLUTION: Line coding consists of representing the digital signal to be transported by an amplitude- and time- discrete signal that is optimally tuned for the specific properties of the physical channel (and of the receiving equipment). The waveform pattern of voltage or current used to represent the 1s and 0s of a digital data on a transmission link is called line encoding. The common types of line encoding are unipolar, polar, bipolar, and Manchester encoding. MATLAB Code: clc; close all; clear all; x=[1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 0]; nx=size(x,2); sign=1; i=1; while i<nx+1 t = i:0.001:i+1-0.001; if x(i)==1 unipolar_code=square(t*2*pi,100); polar_code=square(t*2*pi,100); bipolar_code=sign*square(t*2*pi,100); sign=sign*-1; manchester_code=-square(t*2*pi,50); else unipolar_code=0; polar_code=-square(t*2*pi,100); bipolar_code=0; manchester_code=square(t*2*pi,50); end subplot(4,1,1); plot(t,unipolar_code); ylabel('unipolar code'); hold on; grid on;
- 12. 12 | P a g e axis([1 10 -2 2]); subplot(4,1,2); plot(t,polar_code); ylabel('polar code'); hold on; grid on; axis([1 10 -2 2]); subplot(4,1,3); plot(t,bipolar_code); ylabel('bipolar code'); hold on; grid on; axis([1 10 -2 2]); subplot(4,1,4); plot(t,manchester_code); ylabel('manchester code'); hold on; grid on; axis([1 10 -2 2]); i=i+1; end
- 13. 13 | P a g e OUTPUT:
- 14. 14 | P a g e Artech House - A Professionals Guide to Data Communication in a TCP-IP World – 2006 Computer Networks (4th Ed 2003) - Andrew Tanenbaum Prentice Hall Data Communications and Networking - Behrouz A 4th Edition Data and Computer Communications by William Stallings, 7th Edition, Prentice Hall Computer Networking- A Top-Down Approach Featuring the Internet by Kurose & Ross, 3rd Edition, Pearson Education Data Communications And Computer Networks By Prakash C. Gupta Data Communication And Computer Networks, 1E by B B Tiwari R Agarwal Understanding Data Communications, 7/E by Held Data Communications and Computer Networks: A Business User's Approach by Curt M. White Data Communication System by Monika Khurana Understanding Data Communications and Networks by William A. Shay Computer Networks and Internets with Internet Applications, 4/e by Comer Data and Network Communications by Michael A. Miller Basics of computer networking by Thomas G. Robertazzi www.google.com www.wikipedia.com http://ocw.mit.edu/ http://see.stanford.edu/ http://mycourses.med.harvard.edu/public/ https://sites.google.com/a/ciitlahore.edu.pk/eee314/ http://libweb.lancs.ac.uk/ http://www.mathworks.com




![5 | P a g e
Write the MATLAB code for Binary Phase Shift Keying (BPSK) Modulation.
SOLUTION:
BPSK (also sometimes called PRK, Phase Reversal Keying, or 2PSK) is the simplest form of phase shift
keying (PSK). It uses two phases which are separated by 180 degrees and so can also be termed 2-
PSK. It does not particularly matter exactly where the constellation points are positioned and in this
figure they are shown on the real axis, at 0 degrees and 180 degrees.
MATLAB Code:
clear all;
clc;
close all;
set(0,'defaultlinelinewidth',2);
A=5;
t=0:.001:1;
f1=input('Carrier Sine wave frequency =');
f2=input('Message frequency =');
x=A.*sin(2*pi*f1*t);%Carrier Sine
subplot(3,1,1);
plot(t,x);
xlabel('time');
ylabel('Amplitude');
title('Carrier');
grid on;
u=square(2*pi*f2*t);%Message signal
subplot(3,1,2);
plot(t,u);
xlabel('time');
ylabel('Amplitude');
title('Message Signal');
grid on;
v=x.*u;%Sine wave multiplied with square wave
subplot(3,1,3);
plot(t,v);
axis([0 1 -6 6]);
xlabel('t');](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulationtechniquesmatlabcode-141022000931-conversion-gate02/85/Modulation-techniques-matlab_code-5-320.jpg)





![11 | P a g e
Write the MATLAB code for line coding.
SOLUTION:
Line coding consists of representing the digital signal to be transported by an amplitude- and time-
discrete signal that is optimally tuned for the specific properties of the physical channel (and of the
receiving equipment). The waveform pattern of voltage or current used to represent the 1s and 0s of
a digital data on a transmission link is called line encoding. The common types of line encoding are
unipolar, polar, bipolar, and Manchester encoding.
MATLAB Code:
clc;
close all;
clear all;
x=[1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 0];
nx=size(x,2);
sign=1;
i=1;
while i<nx+1
t = i:0.001:i+1-0.001;
if x(i)==1
unipolar_code=square(t*2*pi,100);
polar_code=square(t*2*pi,100);
bipolar_code=sign*square(t*2*pi,100);
sign=sign*-1;
manchester_code=-square(t*2*pi,50);
else
unipolar_code=0;
polar_code=-square(t*2*pi,100);
bipolar_code=0;
manchester_code=square(t*2*pi,50);
end
subplot(4,1,1);
plot(t,unipolar_code);
ylabel('unipolar code');
hold on;
grid on;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulationtechniquesmatlabcode-141022000931-conversion-gate02/85/Modulation-techniques-matlab_code-11-320.jpg)
![12 | P a g e
axis([1 10 -2 2]);
subplot(4,1,2);
plot(t,polar_code);
ylabel('polar code');
hold on;
grid on;
axis([1 10 -2 2]);
subplot(4,1,3);
plot(t,bipolar_code);
ylabel('bipolar code');
hold on;
grid on;
axis([1 10 -2 2]);
subplot(4,1,4);
plot(t,manchester_code);
ylabel('manchester code');
hold on;
grid on;
axis([1 10 -2 2]);
i=i+1;
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulationtechniquesmatlabcode-141022000931-conversion-gate02/85/Modulation-techniques-matlab_code-12-320.jpg)