Module 1 notes for IoT BETCK105H (VTU) Introduction to IoT
- 1. BASICS OF NETWORKING Prepared by Manjunatha I R ECE, CEC Mangalore
- 2. Life Simplified with Connected Devices IoT and its application in Smart Agriculture
- 3. Basics of Networking: Introduction, Network Types, Layered network models Emergence of IoT: Introduction, Evolution of IoT, Enabling IoT and the Complex Interdependence of Technologies, IoT Networking Components
- 4. BASIC COMPONENTS OF A COMPUTER NETWORK Server Client Transmission Media Network Interface card Hub Switch Router
- 5. Server: Computers that runs operating system and hold data that can be shared over a computer network. Client: Computer that is connected to other computers in the network and can receive data sent by other computers. Transmission Media wires, optical fiber cables, coaxial cables etc. Network Interface card: Each system or computer in a computer network must have a card called network interface card (NIC). The main purpose of NIC is to format the data, send the data and receive the data at the receiving node.
- 6. Hub: Hub acts as a device that connects all the computer in a network to each other. Switch: Switch is similar to hub however instead of broadcasting an incoming data request it uses the physical device address in the incoming request to transfer the request to correct server computer. Router: Router joins multiple computer networks to each other.
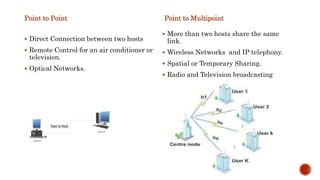
- 7. Type of Connection Point to Point Point to Multipoint Physical Topology Star Mesh Bus Ring Network Reachability Personal Area Networks(PAN) Local Area Networks(LAN) Metropolitan Area Networks(MAN) Wide Area Networks(WAN)
- 8. Point to Point Direct Connection between two hosts Remote Control for an air conditioner or television. Optical Networks. Point to Multipoint More than two hosts share the same link. Wireless Networks and IP telephony. Spatial or Temporary Sharing. Radio and Television broadcasting
- 10. Star Topology Central Hub Host B Host A Host D Host C Mesh Topology Host B Host C Host D Host A
- 11. Bus Host A Host B Host C Host E Host D Tap Drop Line Backbone Bus Ring Host A Host B Host C Host D Host E Host F
- 12. Topology Feature Advantage Disadvantage Star Point to Point Cheap, ease of installation; ease of fault identification. Single point of failure; traffic visible to network entities. Mesh Point to Point Resilient against single point of failures; scalable; traffic privacy and security ensured. Costly; complex connections. Bus Point to Multipoint Ease of installation; cheap Length of backbone cable limited; hard to localize faults. Ring Point to Point Ease of installation; cheap; ease of fault identification. Prone to single point of failure.
- 14. Personal Area Networks(PAN): Wireless Headphones, Wireless Speakers, Printers within a house Restricted to individual usage . Low range and low power technologies such as Bluetooth. Range: Few cm to few m. Local Area Networks(LAN) Collection of hosts linked to a single network through wired or wireless connections. Group of computers connected with each other in a small places such as school, hospital, apartment etc. . Speed can range anywhere from 100 to 100Mbps . Network Components – Servers, hubs, routers, switches , terminals and computers.
- 15. Metropolitan Area Networks(MAN): Connect various organizations or buildings within a given geographic location or city. Internet Service Provider. Network Components – Modems and Cables. MANs covers the larger area of a city or town Wide Area Networks(WAN) Connect diverse geographic locations. Provides long distance transmission of data The size of the WAN is larger than LAN and MAN. A WAN can cover country, continent or even a whole world. WAN are mobile broadband connections such as 3G, 4G etc
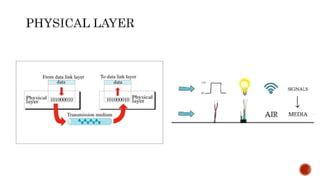
- 17. Application Layer Presentation Layer Session Layer Transport Layer Network Layer Data Link Layer Physical Layer Hardware Layers Software Layers Heart of OSI
- 20. Application Layer • Synonymous to collective functionalities of the OSI model’s session, presentation and application layers. • Defines the protocols for the data transfer. • HTTP,FTP,SMTP,DNS,RIP,SNMP-Core Protocols
- 22. Presentation Layer • Encoding and Decoding • Encryption and Decryption • Compress and Decompress
- 24. Session Management • Authentication • Autherization • Session Management
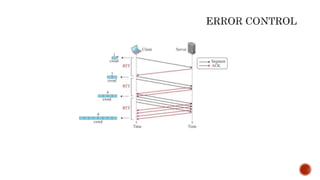
- 30. Transport Layer • Functions of error control, flow control, congestion control, segmentation. • User Datagram Protocol(UDP) • Transmission Control Protocol(TCP)
- 35. Framing -Physical Address Media Access Control
- 39. Layer Name Location PDU Function Examples 1 Physical Media Frames Communication over physical Medium. Ethernet, FDDI, B8ZS, V.35, V.24, RJ45 2 Data link Media Frame Reliability of communication over physical medium. IEEE 802.5/ 802.2, IEEE 802.3/802.2, PPP,HDLC, Frame Relay,ATM, FDDI 3 Network Media Packet Structuring of data and routing between multiple nodes. DDP, IP, AppleTalk, IPX 4 Transport Host Segment Reliability of communication over networks or between hosts. SPX, TCP, UDP Summery of the OSI Layers and their Features
- 40. Layer Name Location PDU Function Examples 5 Session Host Data Establishment, management, and termination of remote sessions. NetBios names, NFS, RPC, SQL 6 Presentatio n Host Data Syntactic conversion of data and encryption Encryption,ASCII,MID I,PICT,JPEG,TIFF,GIF 7 Application Host Data User Identification, authentication, privacy and quality of service SNMP,Telnet,WWW browsers,HTTP,NFS,F TP
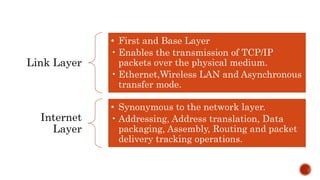
- 42. Link Layer Internet Layer Transport Layer Application Layer. The Internet protocol suite is yet another conceptual framework that provides levels of abstraction for ease of understanding and development of communication and networked systems on the Internet.
- 43. Link Layer • First and Base Layer • Enables the transmission of TCP/IP packets over the physical medium. • Ethernet,Wireless LAN and Asynchronous transfer mode. Internet Layer • Synonymous to the network layer. • Addressing, Address translation, Data packaging, Assembly, Routing and packet delivery tracking operations.
- 44. Transport Layer • Functions of error control, flow control, congestion control, segmentation. • User Datagram Protocol(UDP) • Transmission Control Protocol(TCP) Application Layer • Synonymous to collective functionalities of the OSI model’s session, presentation and application layers. • Defines the protocols for the data transfer. • HTTP,FTP,SMTP,DNS,RIP,SNMP-Core Protocols
- 45. NETWORKED COMMUNICATION BETWEEN TWO HOSTS FOLLOWING THE TCP/IP SUITE