Multiplication algorithm
- 1. PRESENTED BY:- Gaurav Raj Khaiwal 110101097 Gaurav Subham 110101099 Harsha Mehra 110101103
- 2. A multiplication algorithm is an algorithm (or method) to multiply two numbers. Depending on the size of the numbers, different algorithms are in use. Efficient multiplication algorithms have existed since the advent of the decimal system.
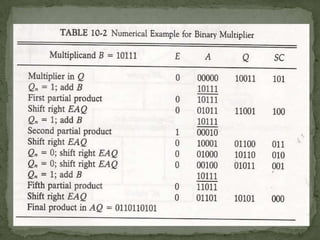
- 3. 1) instead of as many number of registers as there are bits in multiplier, it is convenient to provide an adder for the summation of only two successive binary numbers. 2)Instead of shifting the multiplicand to the left , the partial product will be shifted to the right. 3) when the corresponding bit of multiplier is 0, there is no need to add all zeros to the partial product. EX:- 10011 X 11 10011 10011 shifting the bits of multiplicand left OR first right shift the partial product 10011 partial product is shifted to the left 10011
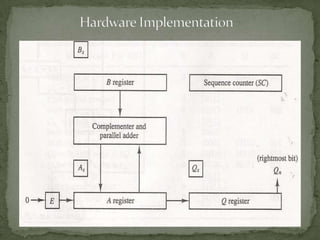
- 5. The multiplicand is in register B and multiplier is in Q. The SC is initially set a number equal to the number of bits in multiplier. The counter is decremented by 1 after forming each partial product. The sum of A and B forms a partial product which is transferred to the EA register. Both the partial product and multiplier are shifted to the right. shrEAQ. The LSB of A is shifted into MSB of Q, The bit from E is shifted into MSB of A, and 0 is shifted into E. In this manner the right most bit of the multiplier will be the one which must be inspected next.
- 8. Booth's multiplication algorithm is a multiplication algorithm that multiplies two signed binary numbers in two's complement notation. The algorithm was invented by Andrew Donald Booth in 1950
- 10. Sign bits are not separated. Qn designate the least significant bit of the mulltiplier in register QR. An extra flip flop Qn+1 is appended to QR to facilitate a double bit inspection of the multiplier.
- 12. AC, SC, Qn+1 are initialized by zero. The two bits of the multiplier in Qn and Qn+1 are inspected If they are 10 subtraction of multiplicand from partial product 01 addition of multiplicand in partial product. When the two bits are same, partial product does not change. The next step is to shift right the partial product and multiplier(including bit Q n+1). This is an arithmetic right shift operation.
- 13. The arithmetic shift right leaves the sign bit unchanged and shifts the number including the sign bit to the right. 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0