Natural Language Processing Topics for Engineering students
- 2. Distinction between language processing applications and Data processing Systems- Knowledge of Language Eg: use of wc in Linux Usage of data processing - count bytes and lines Usage of knowledge- count the words in a file(needs a knowledge about what it means to be a word)
- 3. Eg:HAL, conversational agent Able to recognize words from an audio signal(speech recognition) and generate audio signal from a sequence of words(speech synthesis). Knowledge required: phonetics, phonology How words are pronounced How sounds are realized acoustically
- 4. Morphology: producing and recognizing variations of individual words(like singular and plural) Structural knowledge(syntax): properly string together the words that constitute its response. Semantics: knowledge of meaning Lexical semantics(meaning of all words, like silk, export in the following eg) Compositional semantics(what does end mean when combined with 18th century) Eg: how much Chinese silk was exported to western Europe by the end of 18th century?
- 5. Pragmatics: Knowledge of the relationship of meaning to the goals and intentions of the speaker. Example: Request: John, open the front door. statement: John, the front door is open. Information Question: John, is the front door open? Knowledge about kind of actions that speakers intend by their use of sentences. Also known as dialogue knowledge.
- 6. Discourse :Knowledge about linguistic units larger than a single utterance. Example: How many students were in classroom that time? To interpret words like that year ,a QA System needs to examine the earlier questions that were asked,for example in above context,qn may be ISRO Scientist came to the CSE class room for the motivational speech by last week of January.
- 7. The use of knowledge about how words like that or pronouns like it or she refer to previous parts of the discourse known as coreference resolution.
- 8. If multiple, alternative linguistic structures can be built for an input – it is ambiguous. Example: John went to the bank. (The bank may be edge of the river or financial bank.)
- 9. Part of speech tagging: deciding whether the word is noun or verb. Word sense disambiguation: deciding the correct sense based on context. Speech act interpretation: Determining whether a sentence is a statement or question. Probabilistic parsing: for addressing syntactic disambiguation.
- 10. various kinds of linguistic knowledge can be captured through formal models or theories. state machines(formal models that consists of states, transitions among states, and an input representation.) Rule systems(Regular grammars, context free grammars) Logic Probabilistic models Vector space models
- 11. Models in turn lend themselves to a small number of algorithms. State space search Dynamic Programming Machine learning Algorithms Classifiers Expectation-Maximization
- 12. Truly intelligent machines-Ability of computer to process language skilfully as humans do. First and major work by-Alan Turing Turing Test-game in which computer’s use of language would form the basis for determining if the machine could think. If the machine could win the game, it would be judged intelligent.
- 13. Three participants are there in turing’s game. Two people and a computer. One of the people is contestant and plays the role of interrogator. To win, interrogator have to determine which of the other participant is the machine by asking a series of questions. Turing System helped a lot in the invention of ELIZA(natural language processing system capable of carrying on a limited form of conversation with a user.)
- 14. ELIZA is a simple program that uses pattern matching to process the input and translate it into suitable outputs. Many people interacted with ELIZA believed that it can understood them and their problems. Even after the program operation have explained to them, still the people were continue their belief in ELIZA. These facts lead to the design of conversational agents.
- 15. Regular expression is one way of describing finite automata. FSA Finite-state automata are the theoretical foundation of a good deal of the computational work. Any regular expression can be implemented as a Finite state automaton. Symmetrically, any finite-state automaton can be described with a regular expression.
- 17. We can represent the automaton as a directed graph: a finite set of vertices (also called nodes), together with a set of directed links between pairs of vertices called arcs. We’ll represent vertices with circles and arcs with arrows. The automaton has five STATES, which are represented by nodes in the graph. State 0 is the start state. State 4 is the final state or accepting state, which we represent by the double circle. It also has four transitions, which we represent by arcs in the graph.
- 18. the sheep language can be defined as any string from the following (infinite) set: baa! baaa! baaaa! baaaaa! baaaaaa! ------.
- 20. FSA can be used for recognizing (we also say accepting) strings in the following way. First, think of the input as being written on a long tape broken up into cells, with one symbol written in each cell of the tape, as the following figure shows.
- 22. The machine starts in the start state (q0), and iterates the following process: Check the next letter of the input. If it matches the symbol on an arc leaving the current state, then cross that arc, move to the next state, and also advance one symbol in the input. If we are in the accepting state (q4) when we run out of input, the machine has successfully recognized an instance of sheeptalk.
- 23. If the machine never gets to the final state, either because it runs out of input, or it gets some input that doesn’t match an arc, or if it just happens to get stuck in some non-final state, we say the machine rejects or fails REJECTS to accept an input.
- 24. We can represent Automaton with a state transition table. the state-transition table represents the start state, the accepting states, and what transitions leave each state with which symbols.
- 26. marked state 4 with a colon to indicate that it’s a final state (you can have as many final states as you want), and the /0 indicates an illegal or missing transition. We can read the first row as “if we’re in state 0 and we see the input b we must go to state 1. If we’re in state 0 and we see the input a or !, we fail”.
- 28. Algorithm for recognizing a string using a state-transition table. The algorithm is called D-RECOGNIZE for “deterministic recognizer”. A deterministic algorithm is one that has no choice points; the algorithm always knows what to do for any input.
- 31. The algorithm will fail whenever there is no legal transition for a given combination of state and input. We can think of “empty” elements in the table as if they all pointed at one “empty” state, which we might call the fail state or sink state.
- 33. A model which can both generate and recognize all and only the strings of a formal language acts as a definition of the formal language. A formal language is a set of strings, each string composed of symbols from a ALPHABET finite symbol-set called an alphabet.
- 34. So the formal language defined by our sheeptalk automaton m in Fig. 2.10 (and Fig. 2.12) is the infinite set: (2.1) L(m) = {baa!,baaa!,baaaa!,baaaaa!,baaaaaa!, . . .}
- 35. A formal language is a set of strings, each string composed of symbols from a finite symbol-set called an alphabet. we can use L(m) to mean “the formal language characterized by m”. Example: The alphabet for the sheep language is the set S = {a,b, !}. So the formal language defined by our sheep talk automaton m is the infinite set: L(m) = {baa!,baaa!,baaaa!,baaaaa!,baaaaaa!, . . .}
- 36. Formal languages are not the same as natural languages, which are the kind of languages that real people speak. a formal language may bear no resemblance at all to a real language. But we often use a formal language to model part of a natural language.
- 37. In Deterministic FSAs each of its transactions is uniquely determined by its source state and input symbol. But in NFSA, for some state and input symbol, the next state may be nothing or one or two or more possible state.
- 39. Here, we get in state2,if we seen an a, we don’t know whether to remain in state2 or go on to state 3.Automata with decision points like these are called NFSA. NFSA have been generalized in multiple ways: ◦ NFSA with Epsilon moves ◦ Finite State Transducers ◦ Push Down Automata ◦ Probabilistic Automata
- 40. Since there is more than one choice point in NFAs may lead to a wrong choice. There are 3 solutions to the problem of this non determinism: ◦ Backup: Whenever we come to a choice point, we could put a marker to mark where we were in the input, and what state the automaton was in. Then if it turns out that we took the wrong choice, we could back up and try another path. ◦ Look-ahead: We could look ahead in the input to help us decide which path to take. ◦ Parallelism: Whenever we come to a choice point, we could look at every alternative path in parallel.
- 41. ND-RECOGNIZE accomplishes the task of recognizing strings in a regular language by providing a way to systematically explore all the possible paths through a machine. If this exploration yields a path ending in an accept state, it accepts the string, otherwise it rejects it.
- 42. Algorithms which operates by systematically searching for solutions are known as state space search algorithms. Goal is to explore the space of possible solutions, return answer when one is found, or rejects the input when the space has been exhaustively explored. Effectiveness depends on the order in which the state in the space are considered.
- 43. Depth First Search or Last In First Out Breadth First Search or First In First Out
- 44. Consider an ordering strategy where the states that are considered next are the most recently created ones. Such a policy can be implemented by placing newly created states at the front of the agenda and having NEXT return the state at the front of the agenda when called. Thus the agenda is implemented by a stack.
- 46. The second way to order the states in the search space is to consider states in the order in which they are created. Such a policy can be implemented by placing newly created states at the back of the agenda and still have NEXT return front of the agenda. Thus the agenda is implemented via a queue. This is commonly referred to as a breadth-first search or First In First Out (FIFO) strategy.
- 48. Study of the way words are built up from smaller meaning-bearing units morphemes. Example: cats - consisting of two morpheme cat and –s. fox -consists of only one morpheme fox. Two broad classes of morphemes Stems-main morpheme of the word, which supplies the main meaning. Affixes- add additional meanings of various kinds.
- 49. Prefixes-precede the stem. Eg:unhappy –composed of stem happy and the prefix un- Suffixes- follow the stem Eg: eats-composed of stem eat and suffix –s. Infixes-inserted inside the stem Eg: fanbloomingtastic-word blooming in middle of fantastic. Circumfixes- do both including precede or follow. English and Malayalam doesn’t really have circumfixes, but many other languages like German do. Eg:segan(say)-gesagt(said)
- 50. A word can have more than one affix. ◦ Eg: rewrites : stem - write prefix - re- suffix - –s. ◦ Eg:unbelievably: stem - believe Prefix - un- Suffix - -able, -ly
- 51. English doesn’t support more than four or five affixes. But some languages like Turkish can support words with nine or ten affixes, called agglutinative languages.
- 52. Inflection-combination of a word stem with a grammatical morpheme resulting in a word of the same class as the original stem. Eg:-s for marking the plural on nouns and –ed for marking the past tense on verbs. Derivation-combination of a word stem with a grammatical morpheme resulting in a word of the a different class as the original stem. Eg:computerize by adding derivational suffix –ation can make computerization.
- 53. Compounding-combination of multiple word stems together. Eg:doghouse-concatenation of morphemes dog and house. Cliticization-combination of a word stem with clitic. Acts syntactically like a word,but is reduced in form and attached to anoth er word. Example:I ‘ve
- 54. English has relatively simple inflectional system. Only nouns, verbs and some adjectives can be inflected. Nouns can have two kinds of inflection-an affix that marks plural and an affix that marks possessive.
- 55. English nouns may appear in two forms: Regular Nouns Plural is formed with –s after most nouns Eg:catcats But for words ending in –s,-z,- sh,-ch and sometimes –x plural is formed with –es. Eg: ibisibises waltzwaltzes thrushthrushes finchfinches boxboxes Irregular nouns Eg: Mousemice oxoxen
- 56. Possessive suffix is realized by apostrophe + -s for regular singular nouns(eg: llama’s) and plural nouns not ending in –s eg:children’s. For regular plural nouns and for ends in –s, possessive suffix will be realized by lone apostrophe after nouns. Eg:Euripides’
- 57. English verbal inflection is more complicated than nominal inflection. First, English has three kinds of verbs; main verbs, (eat, sleep, impeach), modal verbs (can, will, should), and primary verbs (be, have, do) . we will mostly be concerned with the main and primary verbs, because it is these that have inflectional endings. Of these verbs a large class REGULAR are regular, that is to say all verbs of this class have the same endings marking the same functions. These regular verbs (e.g. walk, or inspect) have four morphological forms, as follow:
- 59. These verbs are called regular because just by knowing the stem we can predict the other forms by adding one of three predictable endings and making some regular spelling changes. Irregular verbs are those that have some more or less idiosyncratic forms of inflection. Irregular verbs in English often have five different forms, but can have as many as eight (e.g., the verb be) or as few as three (e.g. cut or hit).
- 60. Note that PRETERITE an irregular verb can inflect in the past form (also called the preterite) by changing its vowel (eat/ate), or its vowel and some consonants (catch/caught), or with no change at all (cut/cut).
- 62. Derivation in English is quite complex. Common kind of derivation in English is the formation of new nouns from verbs or adjectives. The process is known as nominalization. Verbs ending in suffix –ize can be converted to nouns by adding the suffix –ation. Eg: computerizecomputerization. Killkiller Fuzzyfuzziness
- 63. Adjectives can also be derived from verbs and nouns. Computation(Noun) + -al computational Embrace(verb) + -ableembraceable Clue(Noun) + -lessclueless
- 64. Less productive. Subtle and complex meaning differences among nominalising suffixes.
- 65. Clitic can be two types: Proclitics:clitics preceding a word Enclitics: clitics following a word Full form Clitic Full form clitic am ‘m have ‘ve are ‘re has ‘s is ‘s had ‘d will ‘ll would ‘d
- 66. Clitics in English are ambiguous. eg: she ‘s it can be she is or she has. Except for few such ambiguities, correctly segmenting clitics in English is simplified by the presence of an apostrophe. Clitics can be harder to parse in other languages.
- 67. Morphological parsing results stem+assorted morphological features. Example: Cats cat+N+PL Cat cat+N+SG Caught catch+V+Past
- 68. Lexicon: the list of stems and affixes,together with basic information about them(like whether the stem is verb or noun). Morphotactics: model of morpheme ordering that explains which classes of morphemes can follow other classes of morphemes inside a word. Orthographic rules: spelling rules used to model the changes that occur in a word, usually when two morphemes combine. Example:city+-scities(y ie)
- 69. A lexicon is a repository for words. The simplest possible lexicon would consist of an explicit list of every word of the language.
- 70. In finite state morphology a word can be represented as a correspondence between two levels. Lexical Level Surface Level represents a concatenation of morphemes making up a word. represents the concatenation of letters which make up the actual spelling of the word.
- 73. Irregular plurals like geese will parse into the correct stem goose +N +Pl. We do this by allowing the lexicon to also have two levels. Since surface geese maps to lexical goose, the new lexical entry will be “g:g o:e o:e s:s e:e”. Regular forms are simpler; the two-level entry for fox will now be “f:f o:o x:x”, but by relying on the orthographic convention that f stands for f:f and so on, we can simply refer to it as fox and the form for geese as “g o:e o:e s e”.
- 75. Since the output symbols include the morpheme and word boundary markers ˆ and #, the lower labels of above Figure do not correspond exactly to the surface level. Hence we refer to tapes with these morpheme boundary markers as intermediate tapes.
- 77. English often requires spelling changes at morpheme boundaries by introducing spelling rules (or orthographic rules). the ability to implement rules as a transducer turns out to be useful throughout speech and language processing.
- 80. FST Lexicons can be combined with orthographic rules for parsing and generating. Lexical transducer maps between the lexical level and an intermediate level. A host of transducers each representing a single spelling rule constraint, all run in parallel to map between this intermediate level to surface level.
- 82. The above architecture is a two level cascade of transducers. Cascading two automata means running them in series with the output of the first feeding the input to the second. Cascades can be of arbitrary depth. Each level might be built out of many transducers. Cascade can be run top-down to generate a string. Cascade can be run bottom up to parse it.
- 83. Parsing may be slightly complicated than generation. Ambiguity may arise in parsing. Example:Foxes can also be a verb rather than noun. So, after parsing two possibilities: Fox+N+PL Fox+V+3Sg Transducer will enumerate the possible choices and transduces both.
- 84. Local ambiguity may also arise during parsing. To handle this type of non determinism ,FST parsing algorithms need to incorporate some sort of search algorithm.
- 85. Running a cascade can be made more efficient by composing and intersecting the transducers. Transducers in general are not not closed under intersection. Transducers between strings of equal length are closed under intersection.
- 86. The intersection of two transducers F and G defines a relation R such that R(x,y) if and only if F(x,y) and G(x,y). intersection algorithm just takes the INTERSECTION Cartesian product of the states, i.e., for each state qi in machine 1 and state qj in machine 2, we create a new state qi j . Then for any input symbol a, if machine 1 would transition to state qn and machine 2 would transition to state qm, we transition to state qnm.
- 88. One of the most widely used such stemming algorithms is the simple and efficient Porter (1980) algorithm, which is based on a series of simple cascaded rewrite rules. Since cascaded rewrite rules are just the sort of thing that could be easily implemented as an FST, we think of the Porter algorithm as a lexicon-free FST stemmer.
- 89. Example Rules: ATIONAL→ ATE (e.g., relational→ relate) ING→ € if stem contains vowel (e.g., motoring→ motor) SSES-> SS(eg: grasses grass) stemming tends to somewhat improve the performance of information retrieval, especially with smaller documents (the larger the document, the higher the chance the keyword will occur in the exact form used in the query).
- 90. Nonetheless, not all IR engines use stemming, partly because of stemmer errors such as shown in the following.
- 92. psycholinguistic studies on how multi- morphemic words are represented in the minds of speakers of English. Example: walk walked,walks All the three words are listed in the human lexicon? or walk along with –ed and –s? Two hypothesis are proposed by scientists based on human’s lexicon representation in mind.
- 93. Full Listing Hypothesis: all words of a language are listed in the mental lexicon without any internal morphological structure. Minimum redundancy Hypothesis: suggests that only the constituent morphemes are represented in the lexicon, and when processing walks, we must access both morphemes (walk and -s) and combine them.
- 94. Some of the earliest evidence that the human lexicon represents at least some morphological structure comes from speech errors, also called slips of the tongue. inflectional and derivational affixes can appear separately from their stems. The ability of these affixes to be produced separately from their stem suggests that the mental lexicon contains some representation of morphological structure. Example: ◦ it’s not only us who have screw looses (for “screws loose”) ◦ words of rule formation (for “rules of word formation”) ◦ easy enoughly (for “easily enough”)
- 95. More recent experimental evidence suggests that neither the full listing nor the minimum redundancy hypotheses may be completely true. Instead, it’s possible that some but not all morphological relationships are mentally represented. Done using repetitive prime experiment. Findings Word is recognized faster if it has been seen before(if it is primed). spoken derived words can prime their stems, but only if the meaning of the derived form is closely related to the stem. Example: Government primesgovern but Department doesn’t prime depart
- 96. Early results suggest that (at least) productive morphology like inflection does play an online role in the human lexicon. Studies have also shows that words with a larger morphological family size are recognized faster. number of other multi morphemic words and compounds in which it appears Example: family for fear, for example, includes fearful, fearfully, fearfulness, fearless, fearlessly, fearlessness, fearsome, and god fearing for a total size of 9.
- 97. Studies shown that words with a larger morphological family size are recognized faster. Recent work has further shown that word recognition speed is effected by the total amount of information (or entropy) contained by the morphological paradigm. It is a measure of information. It can be used as a metric for how much information there is in a particular grammar, for how well a given grammar matches a given language etc.
- 98. End of Module I
- 99. WORD CLASSES & PART OF SPEECH TAGGING (Module II)
- 100. Parts of speech can be divided into two broad categories: those that have not fixed membership ◦ Open Classes ◦ Closed classes those that have relatively fixed membership
- 101. prepositions are a closed class because there is a fixed set of them in English; new prepositions are rarely coined. nouns and verbs are open classes because new nouns and verbs are continually coined or borrowed from other languages.
- 102. Closed class words are also generally function words like of, it, and, or you, which tend to be very short, occur frequently, and often have structuring uses in grammar. There are four major open classes that occur in the languages of the world; nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs. It turns out that English has all four of these, although not every language does.
- 103. Divided into two types: Proper nouns(names of specific people or entities) In written English, proper nouns are capitalized. Example: John, IBM Common nouns Divided into : count nouns mass nouns
- 104. Count nouns are those that allow grammatical enumeration; that is, they can occur in both the singular and plural (goat/goats, relationship/relationships) and they can be counted (one goat, two goats). Mass nouns are used when something is conceptualized as a homogeneous group. So words like snow, salt, and communism are not counted.
- 105. The verb class includes most of the words referring to actions VERB and processes, including main verbs like draw, provide, differ, and go. Verbs have a number of morphological classes, including progressive(eg:eating),past participle(eaten) etc.
- 106. semantically this class includes many terms that describe properties or qualities. Most languages have adjectives for the concepts of color (white, black), age (old, young), and value (good, bad), but there are languages without adjectives. eg: Korean
- 107. rather a hodge-podge (heterogeneous mixture), both semantically and formally. An adverb is a word that describes-modifies as grammarians put it-a verb, an adjective or another adverb. They simply explain most about the action. Example: He quickly runs She slowly walks
- 108. Directional adverbs or locative adverbs (home, here, downhill) specify the direction or location of some action; degree adverbs (extremely, very, somewhat) specify the extent of some action, process, or property. manner adverbs (slowly, delicately) describe the manner of some action or process temporal adverb describe the time that some action or event took place (yesterday, Monday).
- 109. Differ from language to language than do open classes. important closed classes in English, with a few examples of each: • prepositions: on, under, over, near, by, at, from, to, with • determiners: a, an, the • pronouns: she, who, I, others • conjunctions: and, but, or, as, if, when • auxiliary verbs: can, may, should, are • particles: up, down, on, off, in, out, at, by, • numerals: one, two, three, first, second, third
- 110. Tagsets for English, many of which evolved from the 87-tag tagset used for the Brown corpus . The Brown corpus is a 1 million word collection of samples from 500 written texts from different genres (newspaper, novels, non-fiction, academic, etc.) This corpus was tagged with parts-of-speech by first applying the TAGGIT program and then hand- correcting the tags.
- 111. Brown tagset Small 45 tag penn Treebank Test Medium size 61 tag C5 tagset
- 112. Penn Treebank is one of the most widely one used. Used to tag brown corpus, Wall street Journal corpus, Switchboard corpus and many others. The following will show the complete tagset for Penn Treebank.
- 115. Tag Indeterminacy and tokenization Unknown Words Part of Speech Tagging for other Languages Combining taggers
- 116. Tag indeterminacy arises when a word is ambiguous between multiple tags and it is very impossible or difficult to disambiguate. Some taggers allow the use of multiple tags. Example: Penn treebank, BNC Common tag indeterminacies include adjective versus preterite vs past participle(JJ/VBD/VBN)
- 117. There are 3 ways to deal with tag indeterminacy: Somehow replace the indeterminate tags with only one tag. In testing, count a tagger as having correctly tagged an indeterminate token if it gives either of the correct tags. In training, somehow choose only one of the tags for the word. Treat the indeterminate tag as a single complex tag.
- 118. Second approach is the most sensible. Third approach is widely used, but it requires more tags so that it will increase the size of tagset for penn treebank,BNC etc.
- 119. Issue coming in the differentiation of periods(.) which is using in sentence final markers and also as the word internal period(eg:etc.,B.Tech) Second issue is in word splitting. (example:children’s,wouldn’t) the special Treebank tag POS is used only for the morpheme ’s which must be segmented off during tokenization.
- 120. Another tokenization issue concerns multi-part words. The Treebank tagset assumes that tokenization of words like New York is done at whitespace. The phrase a New York City firm is tagged in Treebank notation as five separate words: a/DT New/NNP York/NNP City/NNP firm/NN. The C5 tagset, by contrast, allow prepositions like “in terms of” to be treated as a single word by adding numbers to each tag, as in in/II31 terms/II32 of/II33.
- 121. All the tagging algorithms we have discussed require a dictionary that lists the possible parts-of-speech of every word. But the largest dictionary will still not contain every possible word. Proper names and acronyms are created very often, and even new common nouns and verbs enter the language at a surprising rate. Therefore in order to build a complete tagger we cannot always use a dictionary to giveus p(wi|ti). We need some method for guessing the tag of an unknown word.
- 122. The simplest possible unknown-word algorithm is to pretend that each unknown word is ambiguous among all possible tags, with equal probability. A slightly more complex algorithm is based on the idea that the probability distribution of tags over unknown words is very similar to the distribution of tags over words that occurred only once in the training set. These words that only occur once are known as hapax legomena (singular hapax legomenon).
- 123. Most unknown word algorithms, however, make use of a much more powerful source of information: the morphology of the words. For example, words that end in -s are likely to be plural nouns (NNS), words ending with -ed tend to be past participles (VBN), words ending with able tend to be adjectives (JJ), and so on. Even if we’ve never seen a word, we can use facts about its morphological form to guess its part-of- speech.
- 124. Besides morphological knowledge, orthographic information can be very helpful. For example words starting with capital letters are likely to be proper nouns (NP). The presence of a hyphen is also a useful feature; hyphenated words in the Treebank version of Brown are most likely to be adjectives (JJ).
- 125. Part of speech tagging algorithms can also be applied to other languages without larger modifications. But a number of augmentations and changes become necessary when dealing with highly inflected or agglutinative languages. One problem with these languages is simply the large number of words, when compared to English.
- 126. Agglutinative languages like Malayalam are those in which words contain long strings of morphemes. where each morpheme has relatively few surface forms, and so it is often possible to clearly see the morphemes in the surface text. For these type of Languages, corpus may contain large no of similar words from one particular root.
- 127. The large vocabulary size seems to cause a significant degradation in tagging performance when the HMM algorithm is applied directly to agglutinative languages. one difficulty in tagging highly inflected and agglutinative languages is tagging of unknown words.
- 128. A second issue with such language is vast amount of information that is coded in the morphology of the word. For this reason, tagsets for agglutinative and highly inflectional languages are usually much larger than the 50-100 tags we have seen for English.
- 129. Various part of speech tagging algorithms can be combined. The most common approach to tagger combination is to run multiple taggers in parallel on the same sentence, and then combine their output, either by voting or by training another classifier to choose which tagger to trust in a given context.
- 130. Another option is to combine taggers in series. This is using the rule-based approach to remove some of the impossible tag possibilities for each word, and then an HMM tagger to choose the best sequence from the remaining tags.
- 132. The fundamental idea of constituency is that groups of words may behave as a single unit or phrase, called a constituent. For example we will see that a group of words called a noun phrase often acts as a unit; noun phrases include single words like she or Michael and phrases like the house, Russian Hill, and a well-weathered three-story structure.
- 133. Noun phrases can occur before verbs. Other kinds of evidence for constituency come from what are called preposed or postposed constructions. For example, the prepositional phrase on September seventeenth can be placed in a number of different locations in the following examples, including preposed at the beginning, and postposed at the end.
- 134. On September seventeenth, I’d like to fly from Atlanta to Denver I’d like to fly on September seventeenth from Atlanta to Denver I’d like to fly from Atlanta to Denver on September seventeenth
- 135. But again, while the entire phrase can be placed differently, the individual words making up the phrase cannot be: *On September, I’d like to fly seventeenth from Atlanta to Denver *On I’d like to fly September seventeenth from Atlanta to Denver *I’d like to fly on September from Atlanta to Denver seventeenth
- 136. The most commonly used mathematical system for modelling constituent structure in CFG English and other natural languages is the Context-Free Grammar, or CFG. Context free grammars are also called Phrase-Structure Grammars, and the formalism is equivalent to what is also called Backus-Naur Form or BNF.
- 137. A context-free grammar consists of a set of rules or productions, each of which expresses the ways that symbols of the language can be grouped and ordered together, and a lexicon of words and symbols. Example: NP → Det Nominal NP → ProperNoun Nominal → Noun | Nominal Noun
- 138. Context-free rules can be hierarchically embedded, so we can combine the previous rules with others like the following which express facts about the lexicon: Det → a Det → the Noun → flight
- 139. Two classes: Terminals: The symbols that correspond to words in the language (“the”, “nightclub”) are called terminal symbols; the lexicon is the set of rules that introduce these terminal symbols. Nonterminals: The symbols that express clusters or generalizations of these are called non-terminals.
- 140. In each context free rule, the item to the right of the arrow (→) is an ordered list of one or more terminals and non-terminals, while to the left of the arrow is a single non-terminal symbol expressing some cluster or generalization. A CFG can be thought of in two ways: as a device for generating sentences, and as a device for assigning a structure to a given sentence.
- 141. sequence of rule expansions is called a derivation of the string of words. Example: EE+T/F TT*F/F Fid For the string a+b*c, EE+TE+T*FE+T*idE+F+idE+id*id F+id*idid+id*ida+b*c It is common to represent a derivation by a parse tree.
- 142. a flight Starting from NP, NPDet NominalDet Nouna flight Parse tree can be represented as follows:
- 144. S → NP VP VP → Verb NP VP → Verb NP PP VP → Verb PP PP → Preposition NP
- 148. Parsing with CFG 14 8 Syntactic parsing ◦ The task of recognizing a sentence and assigning a syntactic structure to it Since CFGs are a declarative formalism, they do not specify how the parse tree for a given sentence should be computed. Parse trees are useful in applications such as ◦ Grammar checking ◦ Semantic analysis ◦ Machine translation ◦ Question answering ◦ Information extraction
- 149. Parsing with CFG 149 The parser can be viewed as searching through the space of all possible parse trees to find the correct parse tree for the sentence. How can we use the grammar to produce the parse tree?
- 150. Parsing with CFG 150 Top-down parsing
- 151. Parsing with CFG 151 Bottom-up parsing
- 152. Parsing with CFG 15 2 Comparisons ◦ The top-down strategy never wastes time exploring trees that cannot result in an S. ◦ The bottom-up strategy, by contrast, trees that have no hope to leading to an S, or fitting in with any of their neighbors, are generated with wild abandon. The left branch of Fig. 10.4 is completely wasted effort. ◦ Spend considerable effort on S trees that are not consistent with the input. The first four of the six trees in Fig. 10.3 cannot match the word book.
- 153. Parsing with CFG 153 Use depth-first strategy
- 155. Parsing with CFG 155 A top-down, depth-first, left- to-right derivation
- 157. Parsing with CFG 157 Adding bottom-up filtering Left-corner notion ◦ For nonterminals A and B, B is a left-corner of A if the following relation holds: A B Using the left-corner notion, it is easy to see that only the S Aux NP VP rule is a viable candidate Since the word Does can not server as the left-corner of other two S-rules. * S NP VP A Aux NP VP S VP
- 158. Parsing with CFG 15 8 Category Left Corners S Det, Proper-Noun, Aux, Verb NP Det, Proper-Noun Nominal Noun VP Verb
- 159. Parsing with CFG 15 9 Problems with the top-down parser ◦ Left-recursion ◦ Ambiguity ◦ Inefficiency reparsing of subtrees Then, introducing the Earley algorithm
- 160. Parsing with CFG 160 Exploring infinite search space, when left-recursive grammars are used A grammar is left-recursive if it contains at least one NT A, such that A A, for some and and ε. * * NP Det Nominal Det NP ‘s NP NP PP VP VP PP S S and S Left-recursive rules
- 161. Parsing with CFG 16 1 Two reasonable methods for dealing with left- recursion in a backtracking top-down parser: ◦ Rewriting the grammar ◦ Explicitly managing the depth of the search during parsing Rewrite each rule of left-recursion A A | A A’ A’ A | ε
- 162. Parsing with CFG 16 2 Common structural ambiguity ◦ Attachment ambiguity ◦ Coordination ambiguity ◦ NP bracketing ambiguity
- 163. Parsing with CFG 163 Example of PP attachment
- 164. Parsing with CFG 16 4 The gerundive-VP flying to Paris can be ◦ part of a gerundive sentence, or ◦ an adjunct modifying the VP We saw the Eiffel Tower flying to Paris.
- 165. Parsing with CFG 165 The sentence “Can you book TWA flights” is ambiguous ◦ “Can you book flights on behalf of TWA” ◦ “Can you book flights run by TWA”
- 166. Parsing with CFG 16 6 Coordination ambiguity ◦ Different set of phrases that can be conjoined by a conjunction like and. ◦ For example old men and women can be [old [men and women]] or [old men] and [women] Parsing sentence thus requires disambiguation: ◦ Choosing the correct parse from a multitude of possible parser ◦ Requiring both statistical (Ch 12) and semantic knowledge (Ch 17)
- 167. Parsing with CFG 16 7 Parsers which do not incorporate disambiguators may simply return all the possible parse trees for a given input. We do not want all possible parses from the robust, highly ambiguous, wide-coverage grammars used in practical applications. Reason: ◦ Potentially exponential number of parses that are possible for certain inputs ◦ Given the ATIS example: Show me the meal on Flight UA 386 from San Francisco to Denver. ◦ The three PP’s at the end of this sentence yield a total of 14 parse trees for this sentence.
- 168. Parsing with CFG 168 The parser often builds valid parse trees for portion of the input, then discards them during backtracking, only to find that it has to rebuild them again. a flight From Indianapolis To Houston On TWA A flight from Indianapolis A flight from Indianapolis to Houston A flight from Indianapolis to Houston on TWA 4 3 2 1 3 2 1
- 169. Parsing with CFG 16 9 Solving three kinds of problems afflicting standard bottom-up or top-down parsers Dynamic programming providing a framework for solving this problem ◦ Systematically fill in tables of solutions to sub-problems. ◦ When complete, the tables contain solution to all sub- problems needed to solve the problem as a whole. ◦ Reducing an exponential-time problem to a polynomial- time one by eliminating the repetitive solution of sub- problems inherently iin backtracking approaches ◦ O(N3), where N is the number of words in the input
- 170. Parsing with CFG 170 (10.7) Book that flight S VP, [0,0] NP Det Nominal, [1,2] VP V NP, [0,3]
- 173. Parsing with CFG 17 3 Sequence of state created in Chart while parsing Book that flight including Structural information
- 174. Parsing with CFG 17 4 Partial parsing or shallow parsing ◦ Some language processing tasks do not require complete parses. ◦ E.g., information extraction algorithms generally do not extract all the possible information in a text; they simply extract enough to fill out some sort of template of required data. Many partial parsing systems use cascade of finite-state automata instead of CFGs. ◦ Use FSA to recognize basic phrases, such as noun groups, verb groups, locations, etc. ◦ FASTUS of SRI Company Name: Verb Group: Noun Group: Noun Group: Verb Group Noun Group: Preposition Location: Preposition: Noun Group: Conjunction: Noun Group: Verb Group Noun Group: Verb Group: Preposition Location: Bridgestone Sports Co. said Friday it had set up a joint venture in Taiwan with a local concern and a Japanese trading hounse to produce golf clubs to be shipped to Japan
- 175. Parsing with CFG 17 5 Detection of noun group NG Pronoun | Time-NP | Date-NP she, him, them, yesterday NG (DETP) (Adjs) HdNns | DETP Ving HdNns the quick and dirty solution, the frustrating mathematics problem, the rising index DETP DETP-CP | DET-INCP DETP-CP … DETP-INCP … Adjs AdjP … AdjP … HdNns HdNn … HdNn PropN |PreNs … PreNs PreN … PreN ..
- 179. Feature Structures and Unification Unification-Based Grammars Chart Parsing with Unification- Based Grammars Type Hierarchies
- 180. We had a problem adding agreement to CFGs. What we needed were features, e.g., a way to say: ◦ [number sg person 3 ] A structure like this allows us to state properties, e.g., about a noun phrase ◦ [cat NP number sg person 3 ] Each feature (e.g., ‘number’) is paired with a value (e.g., ‘sg’) ◦ A bundle of feature-value pairs can be put into an attribute-value matrix (AVM)
- 181. Values can be atomic (e.g. ‘sg’ or ‘NP’ or ‘3’), or can be complex, and thus we can define feature paths [cat NP agreement [number sg person 3]] The value of the path [agreement number] is ‘sg’ A grammar with only atomic feature values can be converted to a CFG. ◦ e.g. AVM on previous page NP3,sg ◦ However, when the values are complex, it is more expressive than a CFG can represent more linguistic phenomena
- 182. Feature structures embedded in feature structures can share the same values That is, two features have the exact same value— they share precisely the same object as their value ◦ we’ll indicate this with a tag like *1 [cat S head [agr *1[num sg per 3] subj [agr *1 ]]] In this example, the agreement features of both the matrix sentence and the embedded subject are identical This is referred to as reentrancy
- 183. Technically, feature structures are directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) So, the feature structure represented by the attribute-value matrix (AVM): [cat NP agreement [number sg person 3]] is really the graph: CAT AGR NUM PER sg 3 np
- 184. Unification (U) = a basic operation to merge two feature structures into a resultant feature structure (FS) The two feature structures must be compatible, i.e., have no values that conflict Identical FSs: ◦ [number sg] U [number sg] = [number sg] Conflicting FSs: ◦ [number sg] U [number pl] = Fail Merging with an unspecified FS: ◦ [number sg] U [number []] = [number sg]
- 185. Merging FSs with different features specified: ◦ [number sg] U [person 3] = [number sg person 3] More examples: ◦ [cat NP] U [agreement [number sg]] = [cat NP agreement [number sg]] ◦ [agr [num sg] subj [agr [num sg]]] U [subj [agr [num sg]]]= [agr [num sg] subj [agr [num sg]]]
- 186. Remember that structure-sharing means they are the same object: [agr *1[num sg U [subj [agr [per 3 per 3] num sg]]] subj [agr *1]] = [agr *1[num sg per 3] subj [agr *1]] When unification takes place, shared values are copied over: [agr *1 U [sub [agr [per 3 subj [agr *1]] num sg]]] =[agr *1 subj [agr *1[per 3 num sg]]]
- 187. And remember that having similar values is not the same as structure-sharing: [agr [num sg] U [sub [agr [per 3 subj [agr [num sg]]] num sg]]] = [agr [num sg] subj [agr [per 3 num sg]]] With structure-sharing, you have to make sure the values are compatible everywhere that structure-sharing is specified [agr *1[num sg U [agr [num sg per 3] per 3] = Fail subj [agr *1]] subj [agr [num pl per 3]]]
- 188. We can see that a more general feature structure (less values specified) subsumes a more specific feature structure (1) [num sg] (2) [per 3] (3) [num sg per 3] So, we have the following subsumption relations, where ◦ (1) subsumes (3) ◦ (2) subsumes (3) ◦ (1) does not subsume (2), and (2) does not subsume (1)
- 189. Syntactic constraints are difficult to express using context free grammars alone. Feature structures and unification are the way to elegantly express the syntactic constraints. The better way is to integrate feature structures and unification operations into the specification of a grammar.
- 190. This can be accomplished by augmenting the rules of ordinary context-free grammars with attachments that specify feature structures for the constituents of the rules, along with appropriate unification operations that express constraints on those constituents.
- 191. to associate complex feature structures with both lexical items and instances of grammatical categories. to guide the composition of feature structures for larger grammatical constituents based on the feature structures of their component parts. to enforce compatibility constraints between specified parts of grammatical constructions.
- 192. β0 → β1 ・ ・ ・βn {set of constraints} The specified constraints have one of the following forms. βi feature path = Atomic value βi feature path = βj feature path
- 193. The notation βi feature path denotes a feature path through the feature structure associated with the βi component of the context-free part of the rule. The first style of constraint specifies that the value found at the end of the given path must unify with the specified atomic value. The second form specifies that the values found at the end of the two given paths must be unifiable.
- 194. For example, the rule S NP VP can be augmented with attachment of the feature structure for number agreement as follows: S NP VP <NP number> = <VP number>
- 195. If there are two or more constituents of the same syntactic category in a rule, we will subscript the constituents to keep them straight, as in VP→V NP1 NP2. in this approach the simple generative nature of context-free rules has been fundamentally changed by this augmentation.
- 196. Agreement Grammatical Heads Sub categorization Long distance dependencies
- 197. Discussing how unification can be used to capture two types of English agreement phenomena: Subject-Verb agreement Determiner-Nominal agreement
- 198. Look at the following sentences: Does this flight serves breakfast? Do these flights serve breakfast? In these Qns, the subject NP must agree with the Auxiliary verb rather than the main verb of the sentence. This agreement constraint can be handled by the following rule: SAux NP VP <Aux agreement>=<NP agreement>
- 199. Handled in a similar fashion. Constraints can be enforced with grammar rules as follows: NPDet Nominal <Det Agreement>=<Nominal Agreement> <NP Agreement>=<Nominal Agreement>
- 200. This rule states that the AGREEMENT feature of the Det must unify with the AGREEMENT feature of the Nominal, and moreover, that the AGREEMENT feature of the NP must also unify with the Nominal. The simpler lexical constituents, Aux and Det, receive values for their respective agreement features directly from the lexicon as in the following rules.
- 202. Returning to first S rule, let us first consider the AGREEMENT feature for the VP constituent. The constituent structure for this VP is specified by the following rule. VP → Verb NP It seems clear that the agreement constraint for this constituent must be based on its constituent verb. This verb, as with the previous lexical entries, can acquire its agreement feature values directly from lexicon as in the following rules.
- 205. The features for most grammatical categories are copied from one of the children to the parent. The child that provides the features is called the head of the phrase. features copied are referred to as head features.
- 206. VP Verb NP <VP Agreement>=<Verb Agreement> verb is the head of the verb phrase. The constituent providing the agreement feature structure to its parent is the head of the phrase. So, we can say ,agreement feature structure is a head feature.
- 207. We can rewrite our rules to reflect these generalizations by placing the agreement feature structure under a HEAD feature. VP Verb NP <VP Agreement>=<Verb Agreement> It becomes, VP Verb NP <VP HEAD>=<Verb HEAD>
- 208. Traditional grammar distinguishes between transitive ( take a direct object NP) and intransitive verbs( don’t). Traditional Grammars subcategorize verbs into these two categories. Modern Grammars distinguishes as many as 100 subcategories.
- 209. Feature structures are introduced to distinguish among various members of the verb category. Can accomplish this goal by associating with each of the verbs in the lexicon an atomic feature called SUBCAT, with an appropriate value.
- 210. Transitive version of serves could be assigned the following feature structure in the lexicon: Verbserves <Verb HEAD AGREEMENT NUMBER>=sg <Verb HEAD SUBCAT>=trans SUBCAT feature signals to the rest of the grammar that this verb should only appear in verb phrases with a single noun phrase argument.
- 213. The model of sub categorization has two components. Each head word has a SUBCAT feature which contains a list of the complements it expects. Then phrasal rules like the VP rule match up each expected complement in the SUBCAT list with an actual constituent. This mechanism works fine when the complements of a verb are in fact to be found in the verb phrase.
- 214. Sometimes, however, a constituent subcategorized for by the verb is not locally instantiated, but stands in a long-distance relationship with its predicate. Example sentences: What cities does Continental service? What flights do you have from Boston to Baltimore? What time does that flight leave Atlanta?
- 215. First example, the constituent what cities is subcategorized for by the verb service, but because the sentence is an example of a wh- non-subject question, the object is located at the front of the sentence. phrase-structure rule for a wh-non-subject- question is something like the following S → Wh-NP Aux NP VP
- 216. we can augment this phrase-structure rule to require the Aux and the NP to agree (since the NP is the subject). But we also need some way to augment the rule to tell it that the Wh-NP should fill some sub categorization slot in the VP. The representation of such long-distance dependencies is a quite difficult problem, because the verb whose sub categorization requirement is being filled can be quite distant from the filler
- 217. One of the solution to long distant dependencies. implemented as a feature GAP, which is passed up from phrase to phrase in the parse tree. The filler (for example, which flight above) is put on the gap list, and must eventually be unified with the sub categorization frame of some verb.
- 218. The unification operator takes two feature structures as input and returns a single merged feature structure if successful, or a failure signal if the two inputs are not compatible. The input feature structures are represented as directed acyclic graphs (DAGs), where features are depicted as labels on directed edges, and feature values are either atomic symbols or DAGs.
- 219. A notable aspect of this algorithm is that rather than constructing a new feature structure with the unified information from the two arguments, it destructively alters the arguments so that in the end they point to exactly the same information. destructive nature of this algorithm necessitates certain minor extensions to the simple graph version of feature structures as DAGs.
- 220. each feature structure consists of two fields: 1.Content Field. 2. Pointer Field The content field may be null or contain an ordinary feature structure. Pointer field may be null or contain a pointer to another feature structure.
- 221. If the pointer field of the DAG is null, then the content field of the DAG contains the actual feature structure to be processed. If the pointer field is non-null, then the destination of the pointer represents the actual feature structure to be processed. The merger aspects of unification will be achieved by altering the pointer fields of DAGs during processing.
- 225. From figure, it can seen that first argument now contains all the correct information, the second one does not; it lacks a NUMBER feature. We could, of course, add a NUMBER feature to this argument with a pointer to the appropriate place in the first one. This change would result in the two arguments having all the correct information from this unification. Unfortunately, this solution is inadequate since it does not meet our requirement that the two arguments be truly unified.
- 226. The solution to this problem is to simply set the POINTER field of the second argument to point at the first one. When this is done any future change to either argument will be immediately reflected in both. The following DAG will result after unification.
- 228. The first step in this algorithm is to acquire the true contents of both of the arguments. Recall that if the pointer field of an extended feature structure is non null, then the real content of that structure is found by following the pointer found in pointer field. The variables f1 and f2 are the result of this pointer following process, often referred to as dereferencing.
- 230. The basic feature structures have two problems. The first problem is that there is no way to place a constraint on what can be the value of a feature.(eg:value of number can be sg or pl) The second problem with simple feature structures is that there is no way to capture generalizations across them. A general solution to both of these problems is the use of types.
- 232. Simple: Complex An atomic symbol like sg or pl. All types are organized into a multiple-inheritance type hierarchy (a kind of partial order called a lattice).
- 236. Complex types are also part of the type hierarchy. Subtypes of complex types inherit all the features of their parents, together with the constraints on their values.
- 237. The simplest augmentation of the context-free grammar. Also known as stochastic Context Free Grammar(SCFG). a context-free grammar G is defined by four parameters (N, S, P, S). a probabilistic context-free grammar augments each rule in P with a conditional probability.
- 239. PCFG differs from standard CFG by augmenting each rule in R with a conditional probability: Aβ [p] Here p expresses the probability that the given non-terminal A will be expanded to the sequence b. That is, p is the conditional probability of a given expansion b given the left-hand-side (LHS) non-terminal A. i.e. P(Aβ)
- 241. The sum of probabilities of all possible expansion of a non terminal must be one. In the above example, we can see that all the probabilities of expansions of S will results the probability as 1.(.80+.15+.05) A PCFG is said to be consistent if the sum of the probabilities of all sentences in the language equals 1.
- 242. poor independence assumptions: CFG rules impose an independence assumption on probabilities, resulting in poor modelling of structural dependencies across the parse tree. lack of lexical conditioning: CFG rules don’t model syntactic facts about specific words, leading to problems with sub categorization ambiguities, preposition attachment, and coordinate structure ambiguities
- 243. In a CFG the expansion of a non-terminal is independent of the context, i.e., of the other nearby non-terminals in the parse tree. Similarly, in a PCFG, the probability of a particular rule like NPDet N is also independent of the rest of the tree. the probability of a group of independent events is the product of their probabilities.
- 244. PCFGs can achieve extremely high parsing accuracy if the grammar rule symbols are redesigned via automatic splits and merges. An alternative model is , instead of modifying grammar rules we can go for modification of the probabilistic model of the parser to allow for lexicalized rules. Examples are:Collins ,Charniak parsers.
- 245. Each non terminal in the tree is annotated with its lexical head. Example: VPVBD NP PP Can be extended as VP(dumped)VBD(dumped) NP(sacks) PP(into)
- 246. In some cases, it can be extended with the head tag (part of speech tag of the head words). VP(dumped,VBD) VBD(dumped,VBD) NP(sacks,NNS) PP(into,IN) Then,a lexicalized parse tree can be shown as follws:
- 248. Lexicalized grammar consists of two rules: Lexical Rules Internal Rules Express the expansion of a pre terminal to a word NNS(workers,NNS)- workers express the other rule expansions. NP(workers,NNS)NNS(workers,NNS)
- 249. Rules in lexicalized grammar associate with different probabilities. Lexical rules always have the probability 1.(eg:NN(bin,NN)can only expand to the word bin.) But for internal Rules we need to estimate probabilities.
- 250. Given a treebank , we can compute the probability of each expansion of a non terminal by counting the number of times that expansion occurs and then normalizing.
- 253. Constituent and phrase structure rules do not play any fundamental role. Instead, syntactic structures of a sentence is described in terms of word and syntactic relations between these words. Quite important in speech and language processing.
- 257. Strong predictive parsing power that words have for their dependence. Knowing the identity of the verb can help in deciding which noun is the subject or the object. Ability to handle languages with relatively free word order.
- 258. A phrase structure grammar would need a separate rule for each possible place in the parse tree. Dependency grammar abstracts from word order variation ,representing only the information that is necessary for the parse. Example: stanford parser, Link grammar.
- 259. Early lexicalized grammar model Two components: Categorial lexicons-associate each word with a syntactic and semantic category. Combinatory rules- allow functions and arguments to be combined.
- 260. Categories are of two types: Functors and Arguments Arguments, like nouns, have simple categories like N. Verbs or determiners act as functors. For example, a determiner can be thought of as a function that applies to an N on its right to produce an NP. Such complex categories can be built using the X/Y and XY operators
- 261. X/Y means a function from Y to X, that is, something which combines with a Y on its right to produce an X. Determiners thus receive the category NP/N: something that combines with an N on its right to produce an NP. The simplest combination rules just combine an X/Y with a Y on its right to produce an X or a XY with a Y on its left to produce an X.
- 262. Human sentence processing may use in different probabilistic parsing methods? Recent studies shows that there are at least two ways in which humans apply probabilistic parsing algorithms. Still there are some disagreement on the details.
- 263. One family of studies has shown that when humans read, the predictability of a word seems to influence the reading time; more predictable words are read more quickly. One way of defining predictability is from simple bigram measures. It is found that the higher the bigram predictability of a word, the shorter the time that participants looked at the word (the initial- fixation duration).
- 264. The second family of studies has examined how humans disambiguate sentences which have multiple possible parses, suggesting that humans prefer whichever parse is more probable. Studies were done on garden path sentences. These are sentences which are cleverly constructed to have three properties that combine to make them very difficult for people to parse.
- 265. They are temporarily ambiguous: The sentence is unambiguous, but its initial portion is ambiguous. One of the two or more parses in the initial portion is somehow preferable to the human parsing mechanism. But the dispreferred parse is the correct one for the sentence. The result of these three properties is that people are “led down the garden path” toward the incorrect parse, and then are confused when they realize it’s the wrong one.
- 268. Besides grammatical knowledge some other factors are also there to influence human parsing.
- 270. Semantics is the study of the meaning of linguistic utterances. Study of formal representations(capture the meaning of linguistic utterances) Studying of Algorithms(Mapping from linguistic utterance to meaning representations)
- 271. Meaning of linguistic utterance can be captured in formal structures , called meaning representations. Frame works used to specify the syntax and semantics of this representation are called meaning representation languages.
- 272. In the representational approach, we take linguistic inputs and construct meaning representations that are made up of the same kind of stuff that is used to represent this kind of everyday commonsense knowledge of the world. The process whereby such representations are created and assigned to linguistic inputs is called semantic analysis.
- 273. Reading a menu and deciding what to order, giving advice about where to go to dinner, following a recipe, and generating new recipes all require deep knowledge about food, its preparation, what people like to eat and what restaurants are like.
- 274. First order Logic Semantic Network Conceptual Dependency Frame based Representation
- 275. Meaning Representation will be helpful for the systems to give appropriate responses by using a knowledge base of relevant domain knowledge.
- 276. Representations can be used to determine the relationship between the meaning of a sentence and the world as we know it. That is , we need to able to be determine the truth of our representations. The system have the ability to compare the meaning of representations with representation in knowledge base. Knowledge base is nothing but it stores the information about its world.
- 277. Maharani serves vegetarian food. We can gloss this representation as: Serves(Maharani, VegetarianFood) Representation will be matched against the knowledge base of set of restaurants. If the system finds matching , it can return an affirmative answer.
- 278. Other wise, it must either say NO if its knowledge of local restaurants is complete or say that it doesn’t know if there is reason to believe that its knowledge is incomplete. This notion is known by the name verifiability.
- 279. System’s ability to compare the state of affairs described by a representation to the states of affairs in some world as modelled in a knowledge base.
- 280. Domain of semantics also subject to ambiguity. The answer generated by the system for this request will depend on which interpretation is chosen as the correct one. Ambiguities can be resolved by some means of determining that certain interpretations are preferable (alternatively not preferable) to others is needed.
- 281. A concept closely related to ambiguity is vagueness. It will be difficult to determine what to do with a particular input on the basis of its meaning representation. But it doesn’t give rise to multiple presentations.
- 282. I want to eat Italian food. It provide enough information to a restaurant advisor to provide reasonable recommendations, but quite vague in terms of what item the user wants to eat. The representation is useful in some situations.
- 283. There is possibility that distinct inputs may lead to the same meaning representations. Examples: Does Maharani have vegetarian Dishes? Do they have vegetarian dishes at Maharani? Are vegetarian dishes serves at maharani? Does Maharani serve vegetarian fare?
- 284. These alternatives using different words and syntactic structures. Unfair to expect different meaning representations. If KB contains only one meaning representation, there is a chance to fail any one of the above alternatives. If we have stored all alternative representations, it will lead to some other problems like keeping such a KB consistent.
- 285. The notion that the input s that mean the same thing should have the same meaning representation is known as canonical form. This will simplifies various reasoning tasks since systems need to deal with single meaning representation. Canonical forms will complicate the task of semantic analysis.
- 286. Inference is the system’s ability to draw valid conclusions based on the meaning representation of inputs and its store of background knowledge. To answer some type of request, it requires complex kind of magic that involves the use of variables.
- 287. I’d like to find a restaurant where I can get vegetarian food. Representation can be expressed with the use of variables as follows: Serves(x, VegetarianFood) Matching will be succeed only if the variables can be replaced by some known object in the KB.
- 288. A meaning representation must be expressive enough to handle an extremely wide range of subject matter. A single meaning representation language that could adequately represent the meaning of any sensible natural language utterance. First Order Logic is expressive enough to handle quite a lot of what needs to be represented.
- 289. Words and sentences have parts that combine in patterns, exhibiting the grammar of the language. Syntax and semantics involve studying patterns in sentence structure from the vantages of form and meaning respectively.
- 290. Various methods by which human languages convey meaning is: Conventional form meaning associations Word order regularities Tense systems Conjunctions and quantifiers Predicate argument structure. Among this predicate argument structure have greatest practical influence in the meaning structure of language.
- 291. All human languages have a form of predicate argument arrangement at the core of their semantic structure. One of the most important jobs of a grammar is to help organize this predicate argument structure.
- 292. I want Italian food. This can be classified as the following syntactic argument frame. NP want NP The syntactic frames specify the number, position and syntactic category of the arguments that are expected to accompany a verb.
- 293. For example, the frame in the above example specifies the following facts: There are two arguments to this predicate. Both arguments must be NPs. The first argument is pre-verbal and plays the role of the subject. The second argument is post verbal and plays the role of the direct object.
- 294. These types of facts may lead valuable information in syntax and meaning representations. The notion of semantic roles can be understood by looking the similarities among the arguments. The study of roles associated with specific verbs and across classes of verbs is referred as thematic role or case role analysis.
- 295. The notion of semantic restrictions arises directly from these semantic roles. Selection restriction is one among these whereby verbs can specify semantic restrictions on their arguments. The predicate argument structure is not only based on verbs rather nouns, prepositions etc. Following example will illustrate the concept in more detail.
- 296. An Italian restaurant under fifteen dollars. Meaning representation associated with the preposition ‘under’ can have the following structure. Under(ItaliaRestaurant,$15) Make a reservation for this evening for a table for two persons at 8. Meaning representation will be: Reservation(hearer,today,8 PM,2) Here the predicate argument structure is based on the noun Reservation, rather than ‘make’ the main verb in the phrase.
- 297. The following are the different semantic information that languages have: Variable arity predicate argument structures. The semantic labelling of arguments to predicates. The statement of semantic constraints on the fillers of argument roles.
- 298. Flexible, well understood and computationally tractable approach to the representation of knowledge. Satisfies many of the requirements for a meaning representation language. It makes very few specific commitments as to how things ought to be represented.
- 299. Term Predicates Logical connectives
- 300. FOPC Device for representing objects. FOPC provides 3 ways to represent these basic building blocks. Constants Functions Variables
- 301. Refer to specific objects in the world being described. Constants are conventionally depicted as either single capitalized letters or single capitalized words that are often reminiscent of proper nouns such as Maharani or Harry. Constants refer to exactly one object. Objects can have multiple constants that refer to them.
- 302. FOPC functions are syntactically same as single argument predicates. Example: LocationOf (Maharani) Functions provide a way to refer to specific objects without having to associate a named constant with them.
- 303. Gives us the ability to make assertions and draw inferences about objects without having to make reference to any particular named object. Normally depicted as single lower case letters.
- 304. One of the FOPC mechanism used to state relations that hold among objects. Eg:Maharani serves vegetarian food. Reasonable FOPC representation might look like the following formula: Serves(Maharani, VegetarianFood) Here Serves is a two place predicate holds between the objects denoted by constants Maharani and Vegetarian Food.
- 305. Maharani is a restaurant. FOPC Representation Restaurant(Maharani) This is an example of one place predicate that is used not to relate multiple objects,rather to assert a property of a single object.
- 306. Larger composite representations can be put together through the use of logical connectives. It gives the ability to create larger representations by conjoining logical formulas using one of three operators.
- 307. I only have five dollars and I don’t have a lot of time. Have (Speaker,FiveDollars) ∧ ┒Have(Speaker,LotOfTime)
- 308. FOPC sentence can be assigned a value true or false based on the propositions they encode are in accord with the world or not. FOPC will identify the terms and predicates that corresponds to the various grammatical elements of the sentence, and creating logical formulas that capture the relations implied by the words and syntax of the sentence.
- 309. Ilahia is near Mulavoor. It will yield the following representation. Near(LocationOf(Ilahia),LocationOf(Mulavoor)) This sentence can be assigned a value true or false based on whether or not the real Ilahia is actually close to the Mulavoor or not.
- 310. For determining the truth of our logical formulas ,a database semantics may used. Atomic formula are taken to be true if they are literally present in the KB or if they can be inferred from other formula that are in knowledge base.
- 312. Variables are used in two ways in FOPC. To refer to particular anonymous objects To refer generically to all objects in a collection. These two uses are made possible through two operators known as quantifiers.
- 313. They are two types: Universal quantifier denoted ∀, and is pronounced as “for all”. Existential quantifier denoted by ∃, and is pronounced as “there exists”
- 314. A restaurant that serves Chinese food near Cochin. Here reference is made to an anonymous object. So the reasonable representation of the meaning is: ∃xRestaurant(x) ∧Serves(x,ChineseFood) ∧Near((LocationO f (x),LocationO f (Cochin)
- 315. The sentence to be true if there must be at least one object such that if we were to substitute it for the variable x. ∧ indicate that the sentence will be true if all atomic formulas are true.
- 316. All vegetarian restaurants serve vegetarian Food. Reasonable representation for this sentence will be: ∀xVegetarianRestaurant(x)⇒ Serves(x,VegetarianFood) For this sentence to be true, it must be the case that every substitution of a known object for x must result in a sentence that is true.
- 317. The ability to add valid new propositions to a KB. The most important inference method provided by FOPC is modus ponens(informally known as if then reasoning). We can abstractly define modus ponens as follows, where α and β should be taken as FOPC formulas.
- 318. α α ⇒ β β In general, schemas like this indicate that the formula below the line can be inferred from the formulas above the line by some form of inference. Modus ponens simply states that if the left-hand side of an implication rule is present in the knowledge base, then the right-hand side of the rule can be inferred.
- 320. Modus ponens is typically put to practical use in one of two ways: Forward chaining Backward chaining
- 321. As soon as a new fact is added to the knowledge base, all applicable implication rules are found and applied, each resulting in the addition new facts to the knowledge base. These new propositions in turn can be used to fire implication rules applicable to them. The process continues until no further facts can be deduced.
- 322. Modus ponens is run in reverse to prove specific propositions, called queries. The first step is to see if the query formula is true by determining if it is present in the knowledge base. If it is not, then the next step is to search for applicable implication rules present in the knowledge base. An applicable rule is one where the consequent of the rule matches the query formula. If there are any such rules, then the query can be proved if the antecedent of any one them can be shown to be true. Not surprisingly, this can be performed recursively by backward chaining on the antecedent as a new query.
- 323. Both backward and forward chaining are sound, but neither of them is complete. Another inference technique named resolution is there, which is found to be sound and complete. But these are computationally more expensive. In practice, most of them uses any one of the chaining methods.
- 324. This sections will provide introductions to the meaning representations of Categories Events Time Beliefs.
- 325. Categories are represented in the following way: ◦ create a unary predicate for each category of interest. ◦ Such predicates are then asserted for each member of the category. Example:VegetarianRestaurant(Maharani) Unary Predicate Similar Logical formulas are included in our KB for each known vegetarian restaurant.
- 326. Here categories are relations, rather than full fledged objects. There for difficult to make assertions about categories themselves, rather than about their individual members. Example: MostPopular(Maharani,VegetarianRestaurant) This is not legal FOPC formula.(Because arguments must be terms, not other predicates)
- 327. One way to solve this problem is to represent all the concepts that we want to make statements about as full-fledged objects via a technique called reification. In this case, we can represent the category of VegetarianRestaurant as an object just as Maharani is. The notion of membership in such a category is then denoted via a membership relation as in the following: ISA(Maharani,VegetarianRestaurant) Relation denoted by ISA(is a) holds between object and the categories in which they are members.
- 328. This technique can be extended to create hierarchies of categories through the use of other similar relations, as in the following: AKO(VegetarianRestaurant,Restaurant) Here, the relation AKO (a kind of) holds between categories and denotes a category inclusion relationship.
- 329. The representation of events consisted of single predicates with as many arguments as are needed to incorporate all the roles associated with a given example. Example: Reservation(hearer,Maharani,Today,8 PM,2)
- 330. In the case of verbs, this approach simply assumes that the predicate representing the meaning of a verb has the same number of arguments as are present in the verb’s syntactic sub categorization frame. The following problems will occur due to this approach:
- 331. Determining the correct number of roles for any given event. Representing facts about the roles associated with an event. Ensuring that all the correct inferences can be derived directly from the representation of an event. Ensuring that no incorrect inferences can be derived from the representation of an event.
- 332. The following example will illustrate a series of representation for events, based on the verb eat. I ate. I ate a vegetable sandwich. I ate a vegetable sandwich at my desk. I ate at my desk. I ate lunch. I ate a vegetable sandwich for lunch. I ate a vegetable sandwich for lunch at my desk.
- 333. The variable number of arguments for a predicate bearing verb like eat poses a tricky problem. If we think that all of these examples represents same FOPC have fixed arity-they take a fixed number of arguments. One possible solution is to create a sub categorization frame for each of the configurations of arguments that a verb follows.
- 334. The semantic analog to this approach is to create as many different eating predicates as are needed to handle all of the ways that eat behaves. Such an approach would yield the following kinds of representations:
- 335. Eating₁(Speaker) Eating₂(Speaker, VegetableSandwich) Eating₃(Speaker, VegetableSandwich, Desk) Eating₄(Speaker,Desk) Eating₅(Speaker,Lunch) Eating₆(Speaker,VegetableSandwich,Lunch) Eating₇(Speaker,VegetableSandwich,Lunch,Desk)
- 336. Distinct predicates are created for each sub categorization frame. This will solves the problem of how many arguments to eat predicate. But it will results in high cost. Other than the suggestive names of the predicates, there is nothing to tie these events to one another even though there are obvious logical relations among them.
- 337. One method to solve this problem is meaning postulates. This postulates explicitly ties together the semantics of two of our predicates. ∀ w,x,y,z Eating₇(w,x,y,z) Eating ₆(w,x,y)
- 338. In the previous discussions,reperesentations are done in terms of events. Time can also be incorporated along with. The concerned domain is known as temporal logic. Here it deals with how human languages convey temporal information along with tense logic, the ways that verb tenses convey temporal information.
- 339. Time always flows forward and that events associated with either points or interval in time. an ordering can be imposed on distinct events by situating them on the timeline. More specifically, we can say that one event precedes another, if the flow of time leads from the first event to the second. There are no of schemes for representing temporal information. Here we are discussing one simple one that stays within FOPC framework.
- 340. I arrived in New York. I am arriving in New York. I will arrive in New York. These sentences will refer to the same kind of events and differ only in the tense of verb. In the scheme representing events,all three would share the following kind of information,which lacks temporal information.
- 342. Here w is an event variable. Similarly we can also put temporal variable. Such an approach will yield to the following representation:
- 345. Unfortunately, the relation between simple verb tenses and points in time is by no means straightforward. Consider the following examples. Ok, we fly from San Francisco to Boston at 10. Flight 1390 will be at the gate an hour now. In the first example, the present tense of the verb fly is used to refer to a future event, while in the second the future tense is used to refer to a past event.
- 346. More complications occur when we consider some of the other verb tenses. Consider the following examples. Flight 1902 arrived late. Flight 1902 had arrived late. Although both refer to events in the past, representing them in the same way seems wrong. The second example seems to have another unnamed event lurking in the background (eg. Flight 1902 had already arrived late when something else happened).
- 347. To account for this phenomena, reichenbach(1947) introduced the notion of a reference point. In our simple temporal reference scheme, the current moment in time is equated with the time of the utterance, and is used as a reference point for when the event occurred (before, at, Or after). In Reichenbach’s approach, the notion of the reference point is separated out from the utterance time and the event time.
- 348. The following examples illustrate the basics of this approach. When Mary’s flight departed, I ate lunch. When Mary’s flight departed, I had eaten lunch. In both of these examples, the eating event has happened in the past, ie. prior to the utterance. However, the verb tense in the first example indicates that the eating event began when the flight departed, while the second example indicates that the eating was accomplished prior to the flight’s departure.
- 349. Therefore, in Reichenbach’s terms the departure event specifies the reference point. These facts can be accommodated by asserting additional constraints relating the eating and departure events. In the first example, the reference point precedes the eating event, and in the second example, the eating precedes the reference point.
- 350. Therefore, in Reichenbach’s terms the departure event specifies the reference point. These facts can be accommodated by asserting additional constraints relating the eating and departure events. In the first example, the reference point precedes the eating event, and in the second example, the eating precedes the reference point.
- 351. Concerns a cluster of related topics, including whether an event has ended or is ongoing, whether it is conceptualized as happening at a point in time or over some interval, and whether or not any particular state in the world comes about because of it. Based on these and related notions, event expressions have traditionally been divided into four general classes:
- 352. Statives Activities Accomplishments Achievements.
- 353. Stative expressions represent the notion of an event participant having a particular property, or being in a state, at a given point in time. As such, they can be thought of as capturing an aspect of a world at a single point in time. Example: I know my departure gate.
- 354. Stative verbs are distinctly odd when used in the progressive form. Statives are also odd when used as imperatives. Statives are not easily modified by adverbs like deliberately and carefully.
- 355. Activity expressions describe events undertaken by a participant that have no particular end-point. Unlike statives, activities are seen as occurring over some span of time, and are therefore not associated with single points in time. Example: John is flying.
- 356. Unlike statives, activity expressions are fine in both the progressive and imperative forms. Examples: She is living in Brooklyn. Drive a Mazda! However, like statives, activity expressions are odd when temporally modified with temporal expressions using in. Examples: I live in Brooklyn in a month. She drove a Mazda in an hour.
- 357. They can, however, successfully be used with for temporal adverbials. Example: I live in Brooklyn for a month. She drove a Mazda for an hour.
- 358. Unlike activities, accomplishment expressions describe events that have a natural end-point and result in a particular state. Consider the following examples. He booked me a reservation. United flew me to New York. In these examples, there is an event that is seen as occurring over some period of time that ends when the intended state is accomplished.
- 359. A number of diagnostics can be used to distinguish accomplishment events from activities. Consider the following examples, which make use of the word stop as a test. I stopped living in Brooklyn. She stopped booking my flight.
- 360. In the first example, which is an activity, one can safely conclude that the statement I lived in Brooklyn even though this activity came to an end. However, from the second example, one can not conclude the statement She booked her flight, since the activity was stopped before the intended state was accomplished. Therefore, although stopping an activity entails that the activity took place, stopping an accomplishment event indicates that the event did not succeed.





































































































































































![Parsing with CFG
16
6
Coordination ambiguity
◦ Different set of phrases that can be conjoined by a
conjunction like and.
◦ For example old men and women can be
[old [men and women]] or [old men] and [women]
Parsing sentence thus requires
disambiguation:
◦ Choosing the correct parse from a multitude of
possible parser
◦ Requiring both statistical (Ch 12) and semantic
knowledge (Ch 17)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nlpslides-240210134528-464e1189/85/Natural-Language-Processing-Topics-for-Engineering-students-166-320.jpg)



![Parsing with CFG 170
(10.7) Book that flight
S VP, [0,0]
NP Det Nominal, [1,2]
VP V NP, [0,3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nlpslides-240210134528-464e1189/85/Natural-Language-Processing-Topics-for-Engineering-students-170-320.jpg)









![ We had a problem adding agreement to CFGs.
What we needed were features, e.g., a way to say:
◦ [number sg
person 3 ]
A structure like this allows us to state properties,
e.g., about a noun phrase
◦ [cat NP
number sg
person 3 ]
Each feature (e.g., ‘number’) is paired with a
value (e.g., ‘sg’)
◦ A bundle of feature-value pairs can be put into an
attribute-value matrix (AVM)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nlpslides-240210134528-464e1189/85/Natural-Language-Processing-Topics-for-Engineering-students-180-320.jpg)
![ Values can be atomic (e.g. ‘sg’ or ‘NP’ or ‘3’), or
can be complex, and thus we can define feature
paths
[cat NP
agreement [number sg
person 3]]
The value of the path [agreement number] is ‘sg’
A grammar with only atomic feature values can
be converted to a CFG.
◦ e.g. AVM on previous page NP3,sg
◦ However, when the values are complex, it is more
expressive than a CFG can represent more linguistic
phenomena](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nlpslides-240210134528-464e1189/85/Natural-Language-Processing-Topics-for-Engineering-students-181-320.jpg)
![ Feature structures embedded in feature
structures can share the same values
That is, two features have the exact same value—
they share precisely the same object as their
value
◦ we’ll indicate this with a tag like *1
[cat S
head [agr *1[num sg
per 3]
subj [agr *1 ]]]
In this example, the agreement features of both
the matrix sentence and the embedded subject
are identical
This is referred to as reentrancy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nlpslides-240210134528-464e1189/85/Natural-Language-Processing-Topics-for-Engineering-students-182-320.jpg)
![ Technically, feature structures are directed
acyclic graphs (DAGs)
So, the feature structure represented by the
attribute-value matrix (AVM):
[cat NP
agreement [number sg
person 3]]
is really the graph:
CAT
AGR
NUM
PER
sg
3
np](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nlpslides-240210134528-464e1189/85/Natural-Language-Processing-Topics-for-Engineering-students-183-320.jpg)
![ Unification (U) = a basic operation to merge
two feature structures into a resultant feature
structure (FS)
The two feature structures must be
compatible, i.e., have no values that conflict
Identical FSs:
◦ [number sg] U [number sg] = [number sg]
Conflicting FSs:
◦ [number sg] U [number pl] = Fail
Merging with an unspecified FS:
◦ [number sg] U [number []] = [number sg]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nlpslides-240210134528-464e1189/85/Natural-Language-Processing-Topics-for-Engineering-students-184-320.jpg)
![ Merging FSs with different features specified:
◦ [number sg] U [person 3] = [number sg
person 3]
More examples:
◦ [cat NP] U [agreement [number sg]] =
[cat NP
agreement [number sg]]
◦ [agr [num sg]
subj [agr [num sg]]] U [subj [agr [num
sg]]]=
[agr [num sg]
subj [agr [num sg]]]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nlpslides-240210134528-464e1189/85/Natural-Language-Processing-Topics-for-Engineering-students-185-320.jpg)
![ Remember that structure-sharing means they are the
same object:
[agr *1[num sg U [subj [agr [per 3
per 3] num sg]]]
subj [agr *1]]
= [agr *1[num sg
per 3]
subj [agr *1]]
When unification takes place, shared values are copied
over:
[agr *1 U [sub [agr [per 3
subj [agr *1]] num sg]]]
=[agr *1
subj [agr *1[per 3
num sg]]]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nlpslides-240210134528-464e1189/85/Natural-Language-Processing-Topics-for-Engineering-students-186-320.jpg)
![ And remember that having similar values is not
the same as structure-sharing:
[agr [num sg] U [sub [agr [per 3
subj [agr [num sg]]] num sg]]]
= [agr [num sg]
subj [agr [per 3
num sg]]]
With structure-sharing, you have to make sure
the values are compatible everywhere that
structure-sharing is specified
[agr *1[num sg U [agr [num sg
per 3] per 3] = Fail
subj [agr *1]] subj [agr [num pl
per 3]]]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nlpslides-240210134528-464e1189/85/Natural-Language-Processing-Topics-for-Engineering-students-187-320.jpg)
![ We can see that a more general feature structure
(less values specified) subsumes a more specific
feature structure
(1) [num sg]
(2) [per 3]
(3) [num sg
per 3]
So, we have the following subsumption relations,
where
◦ (1) subsumes (3)
◦ (2) subsumes (3)
◦ (1) does not subsume (2), and (2) does not subsume (1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nlpslides-240210134528-464e1189/85/Natural-Language-Processing-Topics-for-Engineering-students-188-320.jpg)































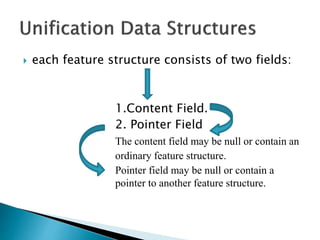


















![ PCFG differs from standard CFG by
augmenting each rule in R with a conditional
probability:
Aβ [p]
Here p expresses the probability that the given
non-terminal A will be expanded to the
sequence b. That is, p is the conditional
probability of a given expansion b given the
left-hand-side (LHS) non-terminal A.
i.e. P(Aβ)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nlpslides-240210134528-464e1189/85/Natural-Language-Processing-Topics-for-Engineering-students-239-320.jpg)
























































































































