Network layer - design Issues
- 2. Network Layer • The network layer is concerned with getting packets from the source all the way to the destination with minimal coast. • Unlike the DLL which has the more modest goal of just moving frames from one end of a wire to the other. • Network Layer is the lowest layer that deals with end-to-end transmission.
- 3. NETWORK LAYER DESIGN ISSUES • Store-and-Forward Packet Switching • Services Provided to the Transport Layer • Implementation of Connectionless Service • Implementation of Connection-Oriented Service • Comparison of Virtual-Circuit and Datagram Networks
- 4. Store-and-Forward Packet Switching • A host with a packet to send transmits it to the nearest router. • The packet is stored there until it has fully arrived. • the link has finished its processing by verifying the checksum. • Then it is forwarded to the next router along the path until it reaches the destination host. • This mechanism is store-and- forward packet switching.
- 5. Services Provided to the Transport Layer before providing these services to the transport layer following goals must be kept in mind: • 1-The services should be independent of the router technology. “why”?! • 2-The transport layer should be shielded from the number, type, and topology of the routers present. • 3-The network addresses made available to the transport layer should use a uniform numbering plan, even across LANs and WANs.
- 6. Services Provided to the Transport Layer - cont. • Definitions : • Connection-oriented service : is a network communication mode, where a communication session or a semi-permanent connection is established before any useful data can be transferred, and where a stream of data is delivered in the same order as it was sent. • Connectionless service : is a data transmission method used in packet switching networks by which each data unit is individually addressed and routed based on information carried in each unit, rather than in the setup information of a prearranged, fixed data channel as in connection-oriented communication. • Packet switching is a digital networking communications method that groups all transmitted data into suitably sized blocks, called packets • A datagram is a basic transfer unit associated with a packet-switched network. The delivery, arrival time, and order of arrival need not be guaranteed by the network. • A virtual circuit : is a means of transporting data over a packet switched computer network in such a way that it appears as though there is a dedicated physical layer link between the source and destination end systems of this data.
- 7. Which service is the best ? • Arguments : • The discussion is about on whether the network layer should provide connection oriented service or connectionless service. • One camp (represented by the Internet community) argues that the routers’ job is moving packets around and nothing else /connectionless. • The other camp (represented by the telephone companies) argues that the network should provide a reliable, connection-oriented service. • connectionless network layers have grown tremendously in popularity. The IP protocol is now an ever-present symbol of success.
- 8. Implementation of Service • If connection-oriented service is used, a path from the source router all the way to the destination router must be established before any data packets can be sent. This connection is called a VC (virtual circuit), • If connectionless service is offered, packets are injected into the network individually and routed independently of each other. No advance setup is needed. In this context, the packets are frequently called datagrams.
- 9. Implementation of Connectionless Service • Suppose that the process P1 in Fig. has a long message for P2It hands the message to the transport layer, • with instructions to deliver it to process P2 on host H2. The transport layer code runs on H1, typically within the operating system. It prepends a transport header to the front of the message and hands the result to the network layer, probably just another procedure within the operating system
- 10. Implementation of Connection-Oriented Service • For connection-oriented service, we need a virtual-circuit network. The idea behind virtual circuits is to avoid having to choose a new route for every packet sent. • With connection-oriented service, each packet carries an identifier telling which virtual circuit it belongs to. • Assigns a different connection identifier to the outgoing traffic for the second connection. Avoiding conflicts of this kind is why routers need the ability to replace connection identifiers in outgoing packets. In some contexts, this process is called label switching
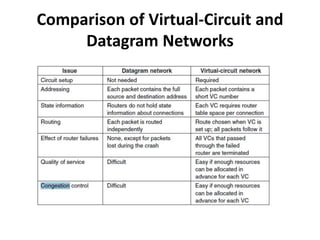
- 11. Comparison of Virtual-Circuit and Datagram Networks
- 12. references • https://en.wikipedia.org • COMPUTER NETWORKS ,FIFTH EDITION,ANDREW S. TANENBAUM. • Plotkin, Serge. "Competitive routing of virtual circuits in ATM networks."Selected Areas in Communications, IEEE Journal on 13.6 (1995): 1128-1136. • Protocol, User Datagram. "RFC 768 J. Postel ISI 28 August 1980." Isi (1980). • Bjerregaard, Tobias, and Jens Sparso. "A router architecture for connection-oriented service guarantees in the MANGO clockless network-on-chip." Design, Automation and Test in Europe, 2005. Proceedings. IEEE, 2005.