November 2009 - JSR-299 Context & Dependency Injection
- 1. J SR-2 9 9 Co n t e x t & De p e n d e n c y Injec t ion Max Rydahl Andersen JBossian, Red Hat 27th. November 1
- 2. Ro a d M a p Background Concepts Status 2 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 3. J av a EE 6 • The EE 6 web profile removes most of the “cruft” that has developed over the years • mainly totally useless stuff like web services, EJB 2 entity beans etc. • some useful stuff (e.g. JMS) is missing, but vendors can include it 3 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 4. J av a EE 6 • EJB 3.1 - asynch, no-interface views, embeddable • JPA 2.0 - typesafe criteria API, many more O/R mapping options • JSF 2.0 - Ajax, easy component creation, bookmarkable URLs • Bean Validation 1.0 - annotation-based validation API • Servlet 3.0 - async support, better support for frameworks • Standard global JNDI names • Managed Beans 4 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 5. Managed Beans • Container-managed POJOs with minimal requirements • support a set of basic services • resource injection • lifecycle callbacks • interceptors 5 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 6. Managed Beans • the foundation for all other component types in the platform • core services centralized under Managed Beans • Other specifications will add support for additional services • remoting • instance pooling • web services 6 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 7. Go a l s • JSR-299 defines a unifying dependency injection and contextual lifecycle model for Java EE 6 • a completely new, richer dependency management model • designed for use with stateful objects • integrates the “web” and “transactional” tiers • makes it much easier to build applications using JSF and EJB together • includes a complete SPI allowing third-party frameworks to integrate cleanly in the EE 6 environment 7 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 8. Loose c oupling • Events, interceptors and decorators enhance the loose- coupling that is inherent in this model: • event notifications decouple event producers from event consumers • interceptors decouple technical concerns from business logic • decorators allow business concerns to be compartmentalized 8 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 9. Go i n g b e yo n d t h e s p e c • Weld provides extra integrations • Tomcat/Jetty/Google App Engine support • Java SE support • OSGi containers • ??? 9 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 10. Go i n g b e yo n d t h e s p e c • and features which can be used in any CDI environment • Seam2 bridge • Spring bridge • Wicket support • Logger • Prototype new ideas for the next version of the spec 10 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 11. Se a m 3 • Use the CDI core • Provide a development environment • JBoss Tools • Seam-gen (command line tool) 11 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 12. Se a m 3 • include a set of modules for any container which includes CDI • jBPM integration • Seam Security • Reporting (Excel/PDF) • Mail • etc. 12 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 13. Ro a d M a p Background Concepts Status 13 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 14. Es s e n t i a l i n g r e d i e n t s • API types • Qualifier annotations • Scope • Alternatives • A name (optional) • Interceptors and Decorators • The implementation 14 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 15. Si m p l e Ex a m p l e public class Hello { Any Managed Bean public String sayHello(String name) { return "hello" + name; can use these } services } @Stateless So can EJBs public class Hello { public String sayHello(String name) { return "hello" + name; } } 15 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 16. Si m p l e Ex a m p l e public class Printer { @Inject defines an injection point. @Default @Inject Hello hello; qualifier is assumed public void printHello() { System.out.println( hello.sayHello("world") ); } } 16 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 17. Co n s t r u c t o r i n j e c t i o n Mark the constructor to be public class Printer { called by the container private Hello hello; @Inject @Inject public Printer(Hello hello) { this.hello=hello; } public void printHello() { System.out.println( hello.sayHello("world") ); } } Constructors are injected by default; @Default is the default qualifier 17 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 18. We b B e a n N a m e s @Named("hello") public class Hello { By default not public String sayHello(String name) { available through EL. return "hello" + name; } } If no name is specified, then a default name is used. Both these Managed Beans have @Named the same name public class Hello { public String sayHello(String name) { return "hello" + name; } } 18 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 19. J SF Pa g e <h:commandButton value=“Say Hello” action=“#{hello.sayHello}”/> Calling an action on a bean through EL 19 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 20. Qu a l i f i e r A qualifier is an annotation that lets a client choose between multiple implementations of an API at runtime 20 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 21. De f i n e a q u a l i f i e r @Retention(RUNTIME) @Target({TYPE, METHOD, FIELD, PARAMETER}) @Qualifier public @interface Casual {} Creating a qualifer is really easy! 21 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 22. Using a qualifier @Casual We also specify the public class Hi extends Hello { public String sayHello(String name) { @Casual qualifier. If return "hi" + name; no qualifer is specified } on a bean, @Default } is assumed 22 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 23. Using a qualifier Here we inject the Hello bean, and require an public class Printer { implementation which is @Inject @Casual Hello hello; qualified by @Casual public void printHello() { System.out.println( hello.sayHello("JBoss") ); } } 23 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 24. A l t e r n at i ve s • An alternative bean is one which must be specifically enabled for a particular deployment • It replaces the managed or session bean for which it is an alternative • May also completely replace it • all producers and observers defined on original bean are disabled for this deployment) • Alternatives enabled in XML deployment descriptor 24 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 25. De f i n i n g a n a l t e r n at i ve @Alternative Same API, different public class Hola extends Hello { implementation public String sayHello(String name) { return "hola " + name; } } 25 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 26. En a b l i n g a n a l t e r n at i ve <beans> <alternatives> <class>com.acme.Hola</class> <sterotype>com.acme.SouthernEuropean</stereotype> </alternatives> </beans> Can also define a sterotype as an alternatives. Any stereotyped beans will be an alternative 26 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 27. St e r e o t y p e s • We have common architectural “patterns” in our application, with recurring roles • Capture the roles using stereotypes 27 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
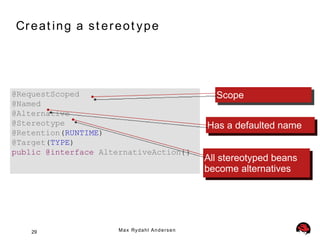
- 28. St e r e o t y p e s • A stereotype encapsulates any combination of: • a default scope, and • a set of interceptor bindings. • A stereotype may also specify that: • all beans with the stereotype have defaulted bean EL names • all beans with the stereotype are alternatives 28 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 29. Cr e at i n g a s t e r e o t y p e @RequestScoped Scope @Named @Alternative @Stereotype Has a defaulted name @Retention(RUNTIME) @Target(TYPE) public @interface AlternativeAction{} All stereotyped beans become alternatives 29 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 30. Using a st ereot ype @AlternativeAction public class Hello { public String sayHello(String name) { return "hi " + name; } } 30 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 31. Sc o p e s a n d Co n t ex t s • Built-in scopes: • Any servlet - @ApplicationScoped, @RequestScoped, @SessionScoped • JSF requests - @ConversationScoped • Dependent scope (De fa u l t ): @Dependent • Custom scopes • A scope type is an annotation, can write your own context implementation and scope type annotation 31 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 32. Sc o p e s @SessionScoped public class Login { Session scoped private User user; public void login() { user = ...; } public User getUser() { return user; } } 32 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 33. Sc o p e s public class Printer { No coupling between @Inject Hello hello; scope and use of @Inject Login login; implementation public void printHello() { System.out.println( hello.sayHello( login.getUser().getName() ) ); } } 33 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 34. Pr o d u c e r m e t h o d s • Producer methods allow control over the production of a bean where: • the objects to be injected are not managed instances • the concrete type of the objects to be injected may vary at runtime • the objects require some custom initialization that is not performed by the bean constructor 34 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 35. Pr o d u c e r m e t h o d s @SessionScoped public class Login { private User user; public void login() { user = ...; } @Produces User getUser() { return user; } } 35 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 36. Pr o d u c e r m e t h o d s public class Printer { @Inject Hello hello; @Inject User user; Much better, no public void hello() { dependency on System.out.println( Login! hello.sayHello( user.getName() ) ); } } 36 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 37. Pr o d u c e r Fi e l d s • Simpler alternative to Producer methods Similar to @SessionScoped outjection in public class Login { Seam @Produces @LoggedIn @RequestScoped private User user; public void login() { user = ...; } } 37 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 38. J av a EE Re s o u r c e s public class PricesTopic { @Produces @Prices @Resource(name="java:global/env/jms/Prices") Topic pricesTopic; } public class UserDatabasePersistenceContext { @Produces @UserDatabase @PersistenceContext EntityManager userDatabase; } 38 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 39. Eve n t s • Event producers raise events that are then delivered to event observers by the Web Bean manager. • not only are event producers decoupled from observers; observers are completely decoupled from producers • observers can specify a combination of "selectors" to narrow the set of event notifications they will receive • observers can be notified immediately, or can specify that delivery of the event should be delayed until the end of the current transaction 39 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 40. Ev e n t s Inject an instance of Event. Additional qualifiers can be specified to narrow the event consumers called. API type specified as a parameter on Event public class Hello { @Inject @Any Event<Greeting> greeting; public void sayHello(String name) { greeting.fire( new Greeting("hello " + name) ); } } “Fire” an event, the producer will be notified 40 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 41. Ev e n t s Observer methods, take the API public class Printer { type and additional qualifiers void onGreeting(@Observes Greeting greeting, @Default User user) { System.out.println(user + “ says “ + greeting); } } Additional parameters can be specified and will be injected by the container 41 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 42. Ro a d M a p Background Concepts Status 42 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 43. J SR-2 9 9 : Co n t ex t s a n d De p e n d e n c y I n j e c t i o n fo r J av a EE • Proposed Final Draft 2 published • Reference Manual being written now • http://www.seamframework.org/Weld • look for an update soon! • Send feedback to [email protected] 43 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 44. We l d • The Reference implementation • Feature complete preview of PFD2. Download it, try it out, give feedback! • http://seamframework.org/Download • Working on second release candidate 44 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 45. We l d • Integrated into: • JBoss 5.1.0.GA and above (6.0.0.Beta1 coming soon) • GlassFish V3 (get a recent build) • Available as an addon for: • Tomcat 6.0.x • Jetty 6.1.x • Java SE • Google App Engine 45 M a x Ry d a h l A n d e r s e n
- 46. J B o s s CDI To o l s (Wo r k i n p r o g r e s s ) • Code completion for @Named components • Validation of CDI constructs (”red squigly lines”) • Ambigious injection points • Non-matching injection •… • CDI component explorer • Show possible injection points for a given line • Show matching event types • Refactoring of EL result in updates to @Named • ... 46