OPTIMIZING SMART THINGS ADDRESSING THROUGH THE ZIGBEE-BASED INTERNET OF THINGS
- 1. International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) Vol.8, No.2, March 2016 DOI : 10.5121/ijcnc.2016.8210 113 OPTIMIZING SMART THINGS ADDRESSING THROUGH THE ZIGBEE-BASED INTERNET OF THINGS Tariq Lasloum and Ahmad S. Almogren Computer Science Department, College of Computer and Information Sciences, King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia ABSTRACT Devices are becoming increasingly interconnected; linked with each other and with humans. The internet of things(IoT) concept is currently used in machine to machine (M2M) applications like power, gas, and oil utilities transmission and transport. The most profound challenge that IoT faces is how to connect several very different devices into a network of things. In this regard, the standard for sending information between devices supporting IoT is called ZigBee, also known as the IEEE 802.15.4-2006 standard: ZigBee is indispensable to the functioning of the IoT. In this paper, OPNET has been used to simulate two quite differently scaled Wireless Sensor Network environments. The two environments had quite different ZigBee topologies; thus, an analysis of the performance in regard to each topology could be made. We propose,ZigBee as optional addressing method for smart-things making up the smart world which facilitates the transmission and analysis of data automatically. KEYWORDS IoT, Wireless Sensor Network, ZigBee & RFID. 1.INTRODUCTION The IoT concept was introduced in Chicago in 2003 during an EPC Symposium. It is a concept whereby the real world can be made to integrate with virtual technology. As a business tool, IoT is bound to make many tasks easier and their solution more convenient than previously believed possible. Also, increased scalability and pervasiveness will lead to further improvements in the technology [1]. The IoT is a combination of networking and computing technologies embedded in applications (applications which are often used in daily life). It is also worth noting that social interactions and relationships may well be affected as a consequence of increasing amounts and availability of data, as well as the spread of IoT in homes, offices, and other arenas of use. Further, It is important to note that several definitions of the IoT imply computation in a broad range of objects, resultant smart behaviour, and networking to share data as well as ideas [2]. The Internet, as such, can be referred to as the "Internet of People -" partly because of its accelerated success since the 1990's. Indeed, it is hard for many members of the current generation to conceptualize a life in which the Internet is absent [3]. The IoT is proposed as a method of implementing the vision of interconnecting all devices, globally, into a Smart Network using the existing IT infrastructure. It is worth noting that such infrastructural technology includes mobile telephony, wireless sensor networks, and RFID
- 2. International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) Vol.8, No.2, March 2016 114 (Radio-Frequency Identification) – the latter to be deployed cheaply on a widely massive scale. It can be seen that the impact on daily life, public services, and businesses will be incalculable once the IoT is properly incorporated into existing networks [4]. Thus, the IoT is a term that can refer to the next era of the Internet - which will then contain millions of nodes representing a variety of devices, including hand-helds, sensor appliances, supercomputer clusters, and large web servers. Such a technology may well be the next move for the Internet and for computing, integrating new technologies of communications and computing, including IPv6, ubiquitous computing, real-time localization, mobile communications technologies, the RFID technology, and sensor networks. For these reasons it is envisaged that the IoT will produce a very large amount of data. In order to handle this more appropriately, the data can be categorized into several types: sensor network, descriptive, positional, unique identifier, address identifier, and RFID stream data amongst others [5]. Here we have introduced the IoT. In section 2, we show related work. In section 3, we show the IoT architecture. Section 4 demonstrates the proposed simulation. Finally, our conclusions are discussed in section 5. 2.RELATED WORK The IoT concept recognizes three paradigms by which components are categorized: things- oriented (sensors), semantic-oriented (knowledge), and Internet-oriented (middleware). In addition, a smart environment is an agglomeration of objects running simultaneously. Trends manifested in relation to the IoT include the use of the terms Ubiquitous Computing, Wireless Sensor Networks, and of course the IoT itself over the past decade. General elements of the IoT include WSN, RFID technology, data storage and analytics, addressing schemes, and visualizations [6] as shown in Fig. 1. Figure 1. sensors and actuators linked directly to an Access Point (AP) Md. Mamunur Rashid and Rethwan Faiz compare three different frequency radio bands: 868 MHz, 915 MHz and 2.4 GHz on ZigBee Star and Mesh topology and conclude that the 204GHz gives better performance than the other two bands [7]. Chavan S.G., Shirsat S.A also compare mesh and star ZigBee performance based only on the packet received using the NS-2 and conclude that mesh topology outperformed the star as the number of nodes increases [8].
- 3. International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) Vol.8, No.2, March 2016 115 ELKISSANI Kaoutar, Pr.Moughit Mohammed, and Pr.NasserdineBouchaib use OPNET to compare the performance of the three ZigBee topologies. They conclude that Tree is less suitable for WSN due to the number of hops which means more energy consumption [9]. 3.IOT ARCHITECTURE The use of an architecture based on network embedded applications and the cloud is imperative in order to assess how devices function on the RESTful interface. This approach, also using Actinium, is bound to increase the scalability and flexibility of the technologies and applications it supports. It is worth noting that the use of this architecture increases the speed of uploading and downloading while customizing and signing applications. Scripting is not limited to JavaScript but is open to a broad range of scripting languages in which applications may be transferred and modified by developers. However, this latter does not apply to devices based on HTTP because of the issue of incompatibility with modular Actinium applications and the runtime environment developers must utilize. It is important to note that applications are bundled into one file in order to increase portability and ease of modification, and that they can be configured through PUT, HTTP method [10] as shown in Fig. 2. Figure 2. Typical Architecture of IoT 3.1 Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) RFID is used to identify devices, from a distance, running on a given network. A stationary can be deployed in such a scenario. It is worth noting that RFID has evolved from a solution to problems experienced in the course of technological advancement to one that is focused on standardization of interconnected devices and cost reduction. The EPC network improves the functionality of RFID and appliances: it can be used in identification of the network. This implies that the EPC network has a broad range of features that support devices on the IoT, and that developers might deploy when creating device - to ensure they lie within the given range and avoid incompatibility issues [11].
- 4. International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) Vol.8, No.2, March 2016 116 3.2 Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN) WSNs generally consist of a large number of sensor devices with limited power and processing capability. WSNs can be used for monitoring and tracking functions in very different arenas such as the military and healthcare, and especially in inaccessible environments. WSN is very attractive due to its low cost and easy deployment. 3.3 ZigBee The most profound challenge the IoT faces is how to connect very manydifferent devices onto a network of things. In this regard, the standard for sending information between devices supporting the IoT is called ZigBee, also known as the IEEE 802.15.4-2006 standard; ZigBee is indispensable to the functioning of the IoT. ZigBee is usually used to create personal area wireless networks because of its low power consumption. [11]. A ZigBee network consists of three items: coordinator, router, and end device. ZigBee Coordinator (ZC):The coordinator is the start device of the network. There is only one coordinator in every network; it allows any device to connect to its node and may bridge to other networks. The coordinator is responsible for the traffic routing in the network. ZigBee Router (ZR):The router is responsible for passing messages between two nodes; each of its child nodes may be either an end device or another router. ZigBee End Device (ZED):An end device only communicates to its parent and cannot have a child, or work as a router (this saves power consumption). End devices also sleep most of the time in order to be power efficient [12]. 3.3.1 Star Topology In star topology, the coordinator is centralized, and all router and end devices are connected to it as shown in Fig. 3. It is very straightforward, but if the coordinator stops working, the entire network will be down since all traffic goes through the coordinator. Figure 3.Star topology
- 5. International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) Vol.8, No.2, March 2016 117 3.3.2 Tree Topology In Tree topology the coordinator is considered the root of the tree. Router or end devices will be connected to the coordinator. A router may have a child: either another router or an end device; end devices never have child nodes. Every child node passes its message to its parent until this message reaches the destination node as shown in Fig. 4. The problem with this topology is the loss of a whole path in the case of one router being down; all its child nodes will be down. Figure 4. Tree topology 3.3.3 Mesh Topology Mesh topology is the most reliable since each node has a different path from source to destination as shown in Fig. 5. If one router fails, the node will have another path by which to send/receive messages. Figure 5. Mesh topology 4. THE PROPOSED SIMULATION OPNET is well known simulator for network research which can provide a graphical simulation for the network traffic for different protocols. Its user friendly interface makes it very popular among researchers, students, and network designers. OPNET offers more than 400 protocols and also various types of vendor devices. In this paper, we have used OPNET to compare the performance of the three types of ZigBee network topology, star, tree, and mesh in relation to two different size networks - The three scenarios were implemented on both networks. Each network consisted of three subnets: Saudi, India, and China as shown in Fig. 6. The Personal Area Network (PAN) ID for India, China, and Saudi were one, two, and three respectively. In each subnet, the PAN ID for the ZigBee
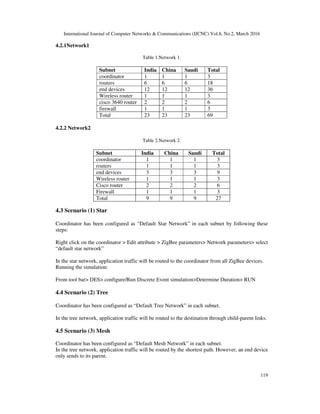
- 6. International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) Vol.8, No.2, March 2016 118 parameter was set to be the same for the whole subnet, coordinator, router, and end device. Each subnet was connected to the internet through an internet router. For security purpose a firewall was placed front of each subnet. In network1, each subnet contains one coordinator, plus six routers, and 12-end device as listed in table 1. However, each subnet in network2 contains only one router, three end devices, and one coordinator as listed in table 2. Figure 6. Saudi, India, and China subnets 4.1 Network Creation File>new> project>: • Write the project and scenario name • Create Empty scenario> world • Topology> Open object Palette: • Drag three fixed subnets • Change the subnet name to India, China, and Saudi • In each Subnet, drag o coordinator o routers o end devices o wireless router o cisco 3640 router o firewall • Select all device> edit attribute> ZigBee parameters> PAN ID= 1, 2, and 3 for India, China, and Saudi
- 7. International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) Vol.8, No.2, March 2016 119 4.2.1Network1 Table 1.Network 1. Subnet India China Saudi Total coordinator 1 1 1 3 routers 6 6 6 18 end devices 12 12 12 36 Wireless router 1 1 1 3 cisco 3640 router 2 2 2 6 firewall 1 1 1 3 Total 23 23 23 69 4.2.2 Network2 Table 2.Network 2. Subnet India China Saudi Total coordinator 1 1 1 3 routers 1 1 1 3 end devices 3 3 3 9 Wireless router 1 1 1 3 Cisco router 2 2 2 6 Firewall 1 1 1 3 Total 9 9 9 27 4.3 Scenario (1) Star Coordinator has been configured as “Default Star Network” in each subnet by following these steps: Right click on the coordinator > Edit attribute > ZigBee parameters> Network parameters> select “default star network” In the star network, application traffic will be routed to the coordinator from all ZigBee devices. Running the simulation: From tool bar> DES> configure/Run Discrete Event simulation>Determine Duration> RUN 4.4 Scenario (2) Tree Coordinator has been configured as “Default Tree Network” in each subnet. In the tree network, application traffic will be routed to the destination through child-parent links. 4.5 Scenario (3) Mesh Coordinator has been configured as “Default Mesh Network” in each subnet. In the tree network, application traffic will be routed by the shortest path. However, an end device only sends to its parent.
- 8. International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) Vol.8, No.2, March 2016 120 4.6 Result After running the three scenarios on both networks, the results were as follows: Network 1 Network2 Figure 7. Aaverage Delay in network The delay measures the time taken for one bit (binary digit) of data to travel from one device to another. In Fig. 7, the blue, red, and green lines indicate Mesh, Star, and Tree topologies respectively. In network1, Mesh has the least delay, then Tree, and finally Star. However, the delay results in network2 are different. Mesh and Star delay results are almost the same, while that for Tree is higher. Network 1 Network2 Figure 8. Average loads in network Fig. 8 shows the result of average load (bits/sec). In network1, the Tree has the highest load rate, then Star, and finally Mesh. In network2, the Mesh has the highest average load, then Star, and finally Tree.
- 9. International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) Vol.8, No.2, March 2016 121 Network1 Network2 Figure 9. Average Throughput in network Throughput is the rate of successfully delivered messages. Fig.9 shows the throughput results for both networks. In network1, the Tree has the highest throughput, then Star, and finally Mesh. In network2, the Mesh has the highest throughput, then Star, and finally Tree. Table 3. Compare between two networks. Ranking Network 1 Network2 Delay 1st Tree Mesh/Star 2nd Mesh Mesh/Star 3rd Star Tree Load 1st Tree Mesh 2nd Star Star 3rd Mesh Tree Throughput 1st Tree Mesh 2nd Star Star 3rd Mesh Tree From the result above, we can conduct that Tree topology is the best option for a small ZigBee network while Mesh is the best for a large network. 5. CONCLUSION The IoT is a promising development: It offers the possibility of a great many “things” interconnected through networks and communicating by using various network protocols. IoT is the concept of uniquely addressed ‘things’ which can be physical or human and which are able to gather and transmit information and data autonomously. IoT has been used in M2M applications such as power, gas, and oil utilities transmission and transport. In this paper, OPNET has been used to simulate two different size environments of Wireless Sensor Network for different ZigBee topologies in order to select the most appropriate topology for particular applications.
- 10. International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) Vol.8, No.2, March 2016 122 Based on the performance results, Tree topology outperforms others in a small ZigBee network while Mesh is the best for large network. IoT has a bright future and will revolutionize how people do business, communicate, and interact with “things.” It is a network of networks. REFERENCES [1] Dieter Uckelmann, Mark Harrison, Florian Michahelles, (2010) “An Architectural Approach towards the Future Internet of Things”. [2] PhD, Michele Royer, (2013)“the Internet of Things (IoT)”. [3] Cees Links, Founder and CEO,(2013) “Sentrollers and The Internet of Things ” GreenPeak Technologies . [4] FaycalBouhafs, and DavoodRajabi, (2013)“Open Sensing Platform for HomeEnergy Monitoring in the Internet of Things ”The International Journal of Engineering And Science (IJES). [5] Shen Bin, Liu Yuan and Wang Xiaoyi,(2010) “Research on Data Mining Models for the Internet of things”978-1-4244-5555 -3/10/$26.00 ©2010 IEEE. [6] JayavardhanaGubbi, SlavenMarusic, RajkumarBuyya and M.Palaniswami, (2013) “Future Generation Computer Systems “J.Gubbietal./FutureGenerationComputerSystems29,1645–1660. [7] Md. Mamunur Rashid and RethwanFaiz(2015) “ZigBee: Simulation and Investigation of Star and Mesh Topology by using different Transmission Bands” The AIUB Journal of Science and Engineering (AJSE), Vol. 14, No. 1. [8] Chavan S.G., Shirsat S.A.(2013) “Performance Comparison of Network Topologies in ZigBee Based WPAN ”International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 10. [9] ELKISSANI Kaoutar, Pr.Moughit Mohammed, and Pr.NasserdineBouchaib. (2014) “Zigbee Routing Opnet Simulation for a Wireless Sensors Network” nternational Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications,Vol. 5, No. [10] Matthias Kovatsch, Martin Lanter and Simon Duquennoy, (2012) “Actinium: A RESTful Runtime Container for Scriptable Internet of Things Applications ” Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on the Internet of Things (IoT 2012). Wuxi, China. [11] FriedemannMattern and Christian Floerkemeier, (2010)” From the Internet of Computers to the Internet of Things”. [12] Jun-Ho Huh, Seung-Mo Je and KyungryongSeo, (2015) “Design and Simulation of Foundation Technology for Zigbee-based Smart Grid Home Network System using OPNET Simulation” Asia- pacific Journal of Multimedia Services Convergent with Art, Humanities, and Sociology . AUTHORS Tariq Lasloumis computer engineer.Presently, he works as director of network and system at ministry of communications and information technology. Currently, he is studying master’s degree in computer science at KingSaudUniversity in SaudiArabia. Ahmad S. Almogren obtained his PhD degree in computer sciences and telecommunications from Southern Methodist University, Dallas, Texas, USA in 2002. Previously, he worked as assistant professor of computer science and the head of the Scientific Council at Riyadh College of Technology. He also served as the dean of Computer College and the head of the Council of Academic Accreditation at Al Yamamah University. Presently, he works as associate professor of computer science and the vice dean for Development and Quality at King Saud University in Saudi Arabia. His research areas of interest include computer networks,security, and data consistency.
![International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) Vol.8, No.2, March 2016
DOI : 10.5121/ijcnc.2016.8210 113
OPTIMIZING SMART THINGS ADDRESSING
THROUGH THE ZIGBEE-BASED INTERNET OF
THINGS
Tariq Lasloum and Ahmad S. Almogren
Computer Science Department, College of Computer and Information Sciences, King
Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
ABSTRACT
Devices are becoming increasingly interconnected; linked with each other and with humans. The internet
of things(IoT) concept is currently used in machine to machine (M2M) applications like power, gas, and oil
utilities transmission and transport. The most profound challenge that IoT faces is how to connect several
very different devices into a network of things. In this regard, the standard for sending information between
devices supporting IoT is called ZigBee, also known as the IEEE 802.15.4-2006 standard: ZigBee is
indispensable to the functioning of the IoT. In this paper, OPNET has been used to simulate two quite
differently scaled Wireless Sensor Network environments. The two environments had quite different ZigBee
topologies; thus, an analysis of the performance in regard to each topology could be made. We
propose,ZigBee as optional addressing method for smart-things making up the smart world which
facilitates the transmission and analysis of data automatically.
KEYWORDS
IoT, Wireless Sensor Network, ZigBee & RFID.
1.INTRODUCTION
The IoT concept was introduced in Chicago in 2003 during an EPC Symposium. It is a concept
whereby the real world can be made to integrate with virtual technology. As a business tool, IoT
is bound to make many tasks easier and their solution more convenient than previously believed
possible. Also, increased scalability and pervasiveness will lead to further improvements in the
technology [1].
The IoT is a combination of networking and computing technologies embedded in applications
(applications which are often used in daily life). It is also worth noting that social interactions and
relationships may well be affected as a consequence of increasing amounts and availability of
data, as well as the spread of IoT in homes, offices, and other arenas of use. Further, It is
important to note that several definitions of the IoT imply computation in a broad range of
objects, resultant smart behaviour, and networking to share data as well as ideas [2].
The Internet, as such, can be referred to as the "Internet of People -" partly because of its
accelerated success since the 1990's. Indeed, it is hard for many members of the current
generation to conceptualize a life in which the Internet is absent [3].
The IoT is proposed as a method of implementing the vision of interconnecting all devices,
globally, into a Smart Network using the existing IT infrastructure. It is worth noting that such
infrastructural technology includes mobile telephony, wireless sensor networks, and RFID](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10-160407102120/85/OPTIMIZING-SMART-THINGS-ADDRESSING-THROUGH-THE-ZIGBEE-BASED-INTERNET-OF-THINGS-1-320.jpg)
![International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) Vol.8, No.2, March 2016
114
(Radio-Frequency Identification) – the latter to be deployed cheaply on a widely massive scale. It
can be seen that the impact on daily life, public services, and businesses will be incalculable once
the IoT is properly incorporated into existing networks [4].
Thus, the IoT is a term that can refer to the next era of the Internet - which will then contain
millions of nodes representing a variety of devices, including hand-helds, sensor appliances,
supercomputer clusters, and large web servers. Such a technology may well be the next move for
the Internet and for computing, integrating new technologies of communications and computing,
including IPv6, ubiquitous computing, real-time localization, mobile communications
technologies, the RFID technology, and sensor networks. For these reasons it is envisaged that
the IoT will produce a very large amount of data. In order to handle this more appropriately, the
data can be categorized into several types: sensor network, descriptive, positional, unique
identifier, address identifier, and RFID stream data amongst others [5].
Here we have introduced the IoT. In section 2, we show related work. In section 3, we show the
IoT architecture. Section 4 demonstrates the proposed simulation. Finally, our conclusions are
discussed in section 5.
2.RELATED WORK
The IoT concept recognizes three paradigms by which components are categorized: things-
oriented (sensors), semantic-oriented (knowledge), and Internet-oriented (middleware). In
addition, a smart environment is an agglomeration of objects running simultaneously. Trends
manifested in relation to the IoT include the use of the terms Ubiquitous Computing, Wireless
Sensor Networks, and of course the IoT itself over the past decade. General elements of the IoT
include WSN, RFID technology, data storage and analytics, addressing schemes, and
visualizations [6] as shown in Fig. 1.
Figure 1. sensors and actuators linked directly to an Access Point (AP)
Md. Mamunur Rashid and Rethwan Faiz compare three different frequency radio bands: 868
MHz, 915 MHz and 2.4 GHz on ZigBee Star and Mesh topology and conclude that the 204GHz
gives better performance than the other two bands [7].
Chavan S.G., Shirsat S.A also compare mesh and star ZigBee performance based only on the
packet received using the NS-2 and conclude that mesh topology outperformed the star as the
number of nodes increases [8].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10-160407102120/85/OPTIMIZING-SMART-THINGS-ADDRESSING-THROUGH-THE-ZIGBEE-BASED-INTERNET-OF-THINGS-2-320.jpg)
![International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) Vol.8, No.2, March 2016
115
ELKISSANI Kaoutar, Pr.Moughit Mohammed, and Pr.NasserdineBouchaib use OPNET to
compare the performance of the three ZigBee topologies. They conclude that Tree is less suitable
for WSN due to the number of hops which means more energy consumption [9].
3.IOT ARCHITECTURE
The use of an architecture based on network embedded applications and the cloud is imperative in
order to assess how devices function on the RESTful interface. This approach, also using
Actinium, is bound to increase the scalability and flexibility of the technologies and applications
it supports. It is worth noting that the use of this architecture increases the speed of uploading and
downloading while customizing and signing applications. Scripting is not limited to JavaScript
but is open to a broad range of scripting languages in which applications may be transferred and
modified by developers. However, this latter does not apply to devices based on HTTP because of
the issue of incompatibility with modular Actinium applications and the runtime environment
developers must utilize. It is important to note that applications are bundled into one file in order
to increase portability and ease of modification, and that they can be configured through PUT,
HTTP method [10] as shown in Fig. 2.
Figure 2. Typical Architecture of IoT
3.1 Radio Frequency Identification (RFID)
RFID is used to identify devices, from a distance, running on a given network. A stationary can
be deployed in such a scenario. It is worth noting that RFID has evolved from a solution to
problems experienced in the course of technological advancement to one that is focused on
standardization of interconnected devices and cost reduction. The EPC network improves the
functionality of RFID and appliances: it can be used in identification of the network. This implies
that the EPC network has a broad range of features that support devices on the IoT, and that
developers might deploy when creating device - to ensure they lie within the given range and
avoid incompatibility issues [11].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10-160407102120/85/OPTIMIZING-SMART-THINGS-ADDRESSING-THROUGH-THE-ZIGBEE-BASED-INTERNET-OF-THINGS-3-320.jpg)
![International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) Vol.8, No.2, March 2016
116
3.2 Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN)
WSNs generally consist of a large number of sensor devices with limited power and processing
capability. WSNs can be used for monitoring and tracking functions in very different arenas such
as the military and healthcare, and especially in inaccessible environments. WSN is very
attractive due to its low cost and easy deployment.
3.3 ZigBee
The most profound challenge the IoT faces is how to connect very manydifferent devices onto a
network of things. In this regard, the standard for sending information between devices
supporting the IoT is called ZigBee, also known as the IEEE 802.15.4-2006 standard; ZigBee is
indispensable to the functioning of the IoT. ZigBee is usually used to create personal area
wireless networks because of its low power consumption. [11].
A ZigBee network consists of three items: coordinator, router, and end device.
ZigBee Coordinator (ZC):The coordinator is the start device of the network. There is only one
coordinator in every network; it allows any device to connect to its node and may bridge to other
networks. The coordinator is responsible for the traffic routing in the network.
ZigBee Router (ZR):The router is responsible for passing messages between two nodes; each of
its child nodes may be either an end device or another router.
ZigBee End Device (ZED):An end device only communicates to its parent and cannot have a
child, or work as a router (this saves power consumption). End devices also sleep most of the
time in order to be power efficient [12].
3.3.1 Star Topology
In star topology, the coordinator is centralized, and all router and end devices are connected to it
as shown in Fig. 3. It is very straightforward, but if the coordinator stops working, the entire
network will be down since all traffic goes through the coordinator.
Figure 3.Star topology](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10-160407102120/85/OPTIMIZING-SMART-THINGS-ADDRESSING-THROUGH-THE-ZIGBEE-BASED-INTERNET-OF-THINGS-4-320.jpg)




![International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) Vol.8, No.2, March 2016
122
Based on the performance results, Tree topology outperforms others in a small ZigBee network
while Mesh is the best for large network. IoT has a bright future and will revolutionize how
people do business, communicate, and interact with “things.” It is a network of networks.
REFERENCES
[1] Dieter Uckelmann, Mark Harrison, Florian Michahelles, (2010) “An Architectural Approach towards
the Future Internet of Things”.
[2] PhD, Michele Royer, (2013)“the Internet of Things (IoT)”.
[3] Cees Links, Founder and CEO,(2013) “Sentrollers and The Internet of Things ” GreenPeak
Technologies .
[4] FaycalBouhafs, and DavoodRajabi, (2013)“Open Sensing Platform for HomeEnergy Monitoring in
the Internet of Things ”The International Journal of Engineering And Science (IJES).
[5] Shen Bin, Liu Yuan and Wang Xiaoyi,(2010) “Research on Data Mining Models for the Internet of
things”978-1-4244-5555 -3/10/$26.00 ©2010 IEEE.
[6] JayavardhanaGubbi, SlavenMarusic, RajkumarBuyya and M.Palaniswami, (2013) “Future Generation
Computer Systems “J.Gubbietal./FutureGenerationComputerSystems29,1645–1660.
[7] Md. Mamunur Rashid and RethwanFaiz(2015) “ZigBee: Simulation and Investigation of Star and
Mesh Topology by using different Transmission Bands” The AIUB Journal of Science and
Engineering (AJSE), Vol. 14, No. 1.
[8] Chavan S.G., Shirsat S.A.(2013) “Performance Comparison of Network Topologies in ZigBee Based
WPAN ”International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 10.
[9] ELKISSANI Kaoutar, Pr.Moughit Mohammed, and Pr.NasserdineBouchaib. (2014) “Zigbee Routing
Opnet Simulation for a Wireless Sensors Network” nternational Journal of Advanced Computer
Science and Applications,Vol. 5, No.
[10] Matthias Kovatsch, Martin Lanter and Simon Duquennoy, (2012) “Actinium: A RESTful Runtime
Container for Scriptable Internet of Things Applications ” Proceedings of the 3rd International
Conference on the Internet of Things (IoT 2012). Wuxi, China.
[11] FriedemannMattern and Christian Floerkemeier, (2010)” From the Internet of Computers to the
Internet of Things”.
[12] Jun-Ho Huh, Seung-Mo Je and KyungryongSeo, (2015) “Design and Simulation of Foundation
Technology for Zigbee-based Smart Grid Home Network System using OPNET Simulation” Asia-
pacific Journal of Multimedia Services Convergent with Art, Humanities, and Sociology .
AUTHORS
Tariq Lasloumis computer engineer.Presently, he works as director of network and
system at ministry of communications and information technology. Currently, he is
studying master’s degree in computer science at KingSaudUniversity in SaudiArabia.
Ahmad S. Almogren obtained his PhD degree in computer sciences and
telecommunications from Southern Methodist University, Dallas, Texas, USA in 2002.
Previously, he worked as assistant professor of computer science and the head of the
Scientific Council at Riyadh College of Technology. He also served as the dean of
Computer College and the head of the Council of Academic Accreditation at Al Yamamah
University. Presently, he works as associate professor of computer science and the vice
dean for Development and Quality at King Saud University in Saudi Arabia. His research
areas of interest include computer networks,security, and data consistency.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10-160407102120/85/OPTIMIZING-SMART-THINGS-ADDRESSING-THROUGH-THE-ZIGBEE-BASED-INTERNET-OF-THINGS-10-320.jpg)