Oracle 12c New Features For Better Performance
- 1. Zohar Elkayam www.realdbamagic.com Twitter: @realmgic Oracle 12c New Features for Better Performance
- 2. Who am I? • Zohar Elkayam, CTO at Brillix • Programmer, DBA, team leader, database trainer, public speaker, and a senior consultant for over 19 years • Oracle ACE Associate • Member of ilOUG – Israel Oracle User Group • Blogger – www.realdbamagic.com and www.ilDBA.co.il 2 http://brillix.co.il
- 3. About Brillix • We offer complete, integrated end-to-end solutions based on best-of- breed innovations in database, security and big data technologies • We provide complete end-to-end 24x7 expert remote database services • We offer professional customized on-site trainings, delivered by our top-notch world recognized instructors 3
- 4. Some of Our Customers http://brillix.co.il4
- 5. Agenda •Database In Memory (column store) – 12.1.0.2 •Oracle Database Sharding – 12.2.0.1 •Optimizer and Statistics changes – 12c http://brillix.co.il5
- 6. Our Goal for Today •Getting to know some of Oracle 12cR1 and 12cR2 new features around performance •Not a lot of syntax today – mainly concepts •Way too many slides, let’s try to catch ‘em all… http://brillix.co.il6
- 7. Oracle Database In-Memory (Column Store) 12.1.0.2 http://brillix.co.il7
- 8. What is an In Memory Database? • In memory databases are management systems that keeps the data in a non-persistent storage (RAM) for faster access Examples: • AeroSpike • SQLite • MemcacheDB • Oracle TimesTen and Oracle Coherence http://brillix.co.il8
- 9. What is a Column Store Database? • Column Store databases are management systems that use data managed in a columnar structure format for better analysis of single column data (i.e. aggregation). Data is saved and handled as columns instead of rows. Examples: • Apache Cassandra • Apache HBase • Apache Parquet • Sybase IQ • HP Vertica http://brillix.co.il9
- 10. How Records are Organized? • This is a logical table in RDBMS • Its physical organization is just like the logical one: column by column, row by row http://brillix.co.il10 Row 1 Row 2 Row 3 Row 4 Col 1 Col 2 Col 3 Col 4
- 11. Query Data • When we query data, records are read at the order they are organized in the physical structure • Even when we query a single column, we still need to read the entire table and extract the column http://brillix.co.il11 Row 1 Row 2 Row 3 Row 4 Col 1 Col 2 Col 3 Col 4 Select Col2 From MyTable Select * From MyTable
- 12. How Does Column Stores Keep Data Organization in row store Organization in column store http://brillix.co.il12 Select Col2 From MyTable
- 13. Row Format vs. Column Format http://brillix.co.il13
- 14. In Memory Option Breakthrough • In memory option introduces a dual format database • Tables can be accessed as row format and column format at the same time – the Optimizer is aware to the new format so: • OLTP continue using the old row format • Analytic queries start using the column format http://brillix.co.il14
- 15. Oracle In Memory Option •Column data is pure in memory format: it’s non- persistent and require no logging, archiving or backup •Data changes are simultaneously changed in both formats so data is consistent and current •Application code requires no changes – just turn on and start using http://brillix.co.il15
- 16. In Memory Option – Good To Know • It is Not “In Memory Database” – it’s an accelerator to the regular database • It is Not “Column Store Database” – column organized data is non-persistent* • In Memory Option requires more memory than the data you plan to load to the memory: no LRU mechanism • Not related to Oracle Times-Ten or Oracle Coherence http://brillix.co.il16
- 17. Oracle Buffer Cache and Memory Management •Oracle buffer cache can keep data blocks in memory for optimization •Blocks are removed from memory based on their usability (LRU) •If data is smaller than available memory, we can use Oracle 12c new features: Full Database Caching http://brillix.co.il17
- 18. Full Database Caching • Full Database Caching: Implicit default and automatic mode in which an internal calculation determines if the database can be fully cached • Force Full Database Caching: This mode requires the DBA to execute the ALTER DATABASE FORCE FULL DATABASE CACHING command • Neither Full Database Caching nor Force Full Database Caching forces prefetch of data into the memory http://brillix.co.il18
- 19. What’s new In 12cR2? •In memory support for Active Data Guard configuration •In memory virtual columns and expressions •In memory FastStart •Automatic Data Optimization Support for In-Memory Column Store http://brillix.co.il19
- 20. Oracle Sharding 12.2.0.1 http://brillix.co.il20
- 21. Scaling Databases •Why would we want to scale our database • Performance • Elasticity • Global data distribution •Possible solutions: • Scaling up – adding more hardware • Scaling out – the Oracle way, using RAC • Scaling out using sharding http://brillix.co.il21
- 22. What Is Sharding? •Sharding is a way of horizontal scaling (horizontal partitioning) •Instead of scaling the database infrastructures, we scale out the data itself •Not a new concept: MongoDB, Cassandra, MySQL… •Starting with Oracle 12.2 we can use Sharded Database Architecture (SDA) as part of Oracle Global Data Services (GDS) architecture http://brillix.co.il22
- 23. Global Data Services (GDS) http://brillix.co.il23
- 24. Sharded Database Architecture (SDA) •Part of the Global Data Services (GDS) architecture •Databases in the logical database doesn’t share any physical resources or clusterware software •Databases can reside in different geo-locations •Application must be compatible with sharded behavior http://brillix.co.il24
- 25. Benefits of Sharding • Linear Scalability - eliminates performance bottlenecks and makes it possible to linearly scale performance by adding shards • Fault Containment - Sharding is a shared nothing hardware infrastructure that eliminates single points of failure • Geographical Distribution of Data - store data close to its users • Rolling Upgrades – changes to one shard at a time does not affect other shards • Simplicity of Cloud Deployment - supports on-premises, cloud, and hybrid deployment models http://brillix.co.il25
- 26. Why RDBMS Sharding? •Unlike NoSQL sharding, Oracle Shards still support • Relational schemas • ACID transactions properties and read consistency • SQL and other programmatic interfaces • Complex data types • Database partitioning • Advanced security • High Availability features • And more… http://brillix.co.il26
- 28. Server A – Non-Sharded Sharding Methods •We can use two methods of sharding data: • Sharded tables: data exist is one shared • Duplicated tables: data exist in all shareds http://brillix.co.il28 SDB – Sharded (Logical) Database Server B Server C Server D Shard 1 Shard 2 Shard 3
- 29. Example – Sharded Table Creation http://brillix.co.il29 CREATE SHARDED TABLE customers ( cust_id NUMBER NOT NULL , name VARCHAR2(50) , address VARCHAR2(250) , region VARCHAR2(20) , class VARCHAR2(3) , signup DATE CONSTRAINT cust_pk PRIMARY KEY(cust_id) ) PARTITION BY CONSISTENT HASH (cust_id) TABLESPACE SET ts1 PARTITIONS AUTO;
- 30. Example – Duplicated Table Creation http://brillix.co.il30 CREATE DUPLICATED TABLE Products ( StockNo NUMBER PRIMARY KEY , Description VARCHAR2(20) , Price NUMBER(6,2)) );
- 31. Sharded Table Families •We can shard multiple tables to the same database shard using table families •All tables in a table family must have the same equi- partition sharding key: • Using Reference partitions • Using the PARENT clause http://brillix.co.il31
- 32. Example – Sharded Table Family Creation (REF) http://brillix.co.il32 CREATE SHARDED TABLE Customers ( CustNo NUMBER NOT NULL , Name VARCHAR2(50) , Address VARCHAR2(250) , CONSTRAINT RootPK PRIMARY KEY(CustNo) ) PARTITION BY CONSISTENT HASH (CustNo) PARTITIONS AUTO TABLESPACE SET ts1; CREATE SHARDED TABLE Orders ( OrderNo NUMBER NOT NULL , CustNo NUMBER NOT NULL , OrderDate DATE , CONSTRAINT OrderPK PRIMARY KEY (CustNo, OrderNo) , CONSTRAINT CustFK FOREIGN KEY (CustNo) REFERENCES Customers(CustNo) ) PARTITION BY REFERENCE (CustFK);
- 33. Example – Sharded Table Family Creation (PARENT) http://brillix.co.il33 CREATE SHARDED TABLE Customers ( CustNo NUMBER NOT NULL , Name VARCHAR2(50) , Address VARCHAR2(250) , region VARCHAR2(20) , class VARCHAR2(3) , signup DATE ) PARTITION BY CONSISTENT HASH (CustNo) TABLESPACE SET ts1 PARTITIONS AUTO; CREATE SHARDED TABLE Orders ( OrderNo NUMBER , CustNo NUMBER , OrderDate DATE ) PARENT Customers PARTITION BY CONSISTENT HASH (CustNo) TABLESPACE SET ts1 PARTITIONS AUTO;
- 34. Non-Table Objects •We can create non-table objects in the logical databases • Schema objects: users, roles, views, indexes, synonyms, functions, procedures, and packages • Non-schema objects: tablespaces, tablespace sets, directories, and contexts •Objects will be created on all shards http://brillix.co.il34
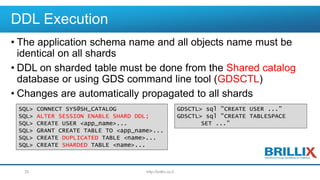
- 35. DDL Execution • The application schema name and all objects name must be identical on all shards • DDL on sharded table must be done from the Shared catalog database or using GDS command line tool (GDSCTL) • Changes are automatically propagated to all shards http://brillix.co.il35 SQL> CONNECT SYS@SH_CATALOG SQL> ALTER SESSION ENABLE SHARD DDL; SQL> CREATE USER <app_name>... SQL> GRANT CREATE TABLE TO <app_name>... SQL> CREATE DUPLICATED TABLE <name>... SQL> CREATE SHARDED TABLE <name>... GDSCTL> sql "CREATE USER ..." GDSCTL> sql "CREATE TABLESPACE SET ..."
- 36. Sharding Physical Structure •Physical data distribution based on chunks – each chunk is one table partition •Each chunk is located on a different tablespace •Tablespaces are defined using tablespace sets (tablespace templates) http://brillix.co.il36
- 37. Resharding and Hotspots Handling • Adding/Removing shards or hotspot elimination requires chunk movement (automatically or manually) • This will generate an RMAN backup, restore and recovery of the chunk (tablespace) in the new node. Old chunk will be automatically removed once done. • We can also split hotsposts using GDSCTL split command http://brillix.co.il37 GDSCTL> MOVE CHUNK -CHUNK 12 -SOURCE sh01 -TARGET sh12 GDSCTL> SPLIT CHUNK -CHUNK 12
- 38. Sharding High Availability •Data replication with Data Guard is a crucial component in SDB environment • High availability, disaster recovery, read offloading • Replication deployment performed fully automatically • The logical unit of data replication is a shardgroup http://brillix.co.il38
- 39. High Availability Setup Example http://brillix.co.il39 GDSCTL> create shardcatalog -database shdard01:1521:repo -chunks 12 -user mygdsadmin/<pwd> -sdb sharddb -region london,Amsterdam –repl DG –sharding system -protectmode maxavailability ... GDSCTL> add shardgroup -shardgroup shardgrp1 -deploy_as primary -region london GDSCTL> add shardgroup -shardgroup shardgrp2 -deploy_as active_standby -region london GDSCTL> add shardgroup -shardgroup shardgrp3 -deploy_as active_standby -region amsterdam
- 40. Session Routing (single shard) • Application must be compatible with sharding architecture • When connecting to the database, the application must provide the sharding key (and super key) to the connection • All SQL operations in this session are related to the specified sharding key (shard) • To work on another sharding key value, the application needs to create a new session http://brillix.co.il40
- 41. Statement Routing/Cross-Shard Query •Client connection to the Coordinator (Catalog) Database is required • No sharding key necessary in the connect descriptor •Cross-shard SQL are executed via DB Link to Shards • Partition and Shard pruning http://brillix.co.il41
- 42. Optimizer Changes and Adaptive Query Optimization 12.1.0.2 + 12.2.0.1 http://brillix.co.il42
- 43. Adaptive Query Optimization http://brillix.co.il43 Adaptive Query Optimization Adaptive Plans Adaptive Statistics At compile time At run timeJoin Methods Parallel distribution Methods
- 44. Adaptive Execution Plans (12.1) • Allows the Optimizer to make runtime adjustments to execution plans and to discover additional information that can lead to better statistics • Good SQL execution without intervention • Final plan decision is based on rows seen during execution • Bad effects of skew eliminated http://brillix.co.il44
- 45. Adaptive Execution Plans: Join Methods • Join method decision deferred until runtime • Default plan is computed using available statistics • Alternate sub-plans are pre-computed and stored in the cursor • Statistic collectors are inserted at key points in the plan • Final decision is based on statistics collected during execution • Possible sub-plans are nested loop joins or hash joins and vice versa http://brillix.co.il45
- 46. Displaying the Default Plan •Explain plan command always shows default plan •Example shows a nested loops join as default plan •No statistics collector shown in plan http://brillix.co.il46
- 47. Displaying the Final Plan • After the statement has completed use DBMS_XPLAN.DISPLAY_CURSOR to see the final plan selected • Example shows that hash join picked at execution time • Again the statistics collector is not visible in the plan http://brillix.co.il47
- 48. Displaying Plan With +adaptive & +report Formats • Additional information displayed on why operations are inactive can be seen with format parameter ‘+report’ http://brillix.co.il48
- 49. Adaptive Execution Plans In V$SQL http://brillix.co.il49
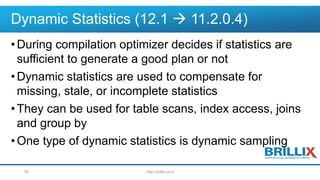
- 50. Dynamic Statistics (12.1 11.2.0.4) •During compilation optimizer decides if statistics are sufficient to generate a good plan or not •Dynamic statistics are used to compensate for missing, stale, or incomplete statistics •They can be used for table scans, index access, joins and group by •One type of dynamic statistics is dynamic sampling http://brillix.co.il50
- 51. Dynamic Statistics • Dynamic sampling has a new level 11(AUTO) • Decision to use dynamic sampling depends on the complexity of predicate, existing statistics and total execution time • Dynamic statistics shared among queries http://brillix.co.il51
- 52. Adaptive Statistics/Statistics Feedback Re-optimization Pre 12c: • During execution optimizer estimates are compared to execution statistics • If statistics vary significantly then a new plan will be chosen for subsequent executions based on execution statistics • Re-optimization uses statistics gathered from previous executions Re-optimization in 12c • Join statistics are also monitored • Works with adaptive cursor sharing for statement with binds • New Column in V$SQL IS_REOPTIMIZABLE • Information found at execution time is persisted as SQL Plan Directives http://brillix.co.il52
- 54. Re-optimization – indicator in V$SQL •New column in V$SQL: IS_REOPTIMIZABLE •Indicates that the statement will be re-parsed on the next execution http://brillix.co.il54
- 55. More Optimizer Changes… •Adaptive Statistics/Statistics Feedback (12.1) •Concurrent Execution of UNION and UNION ALL Branches (12.1) •Cost-Based OR Expansion Transformation (12.2) •Enhanced Join Elimination (12.2) •Approximate Query Processing (12.1 + 12.2) http://brillix.co.il55
- 57. Histograms • Histograms tell the Optimizer about the data distribution in a Column for better cardinality estimations • Default create histogram on any column that has been used in the WHERE clause or GROUP BY of a statement AND has a data skew • Oracle 12c changes histograms methods: • Top-Frequency (new) • Height balanced (obsolete) • Hybrid (new) http://brillix.co.il57
- 58. Histograms: Top Frequency • Traditionally a frequency histogram is only created if NDV < 254 • But if a small number of values occupies most of the rows (>99% rows), creating a frequency histograms on that small set of values is very useful even though NDV is greater than 254 • Ignores the unpopular values to create a better quality histogram for popular values • Built using the same technique used for frequency histograms • Only created with AUTO_SAMPLE_SIZE http://brillix.co.il58
- 59. Top Frequency Histogram Example • Table PRODUCT_SALES contains information on Christmas ornament sales • It has 1.78 million rows • There are 620 distinct TIME_IDs • But 99.9% of the rows have less than 254 distinct TIME_IDs TIME_ID column perfect candidate for top-frequency histogram http://brillix.co.il59
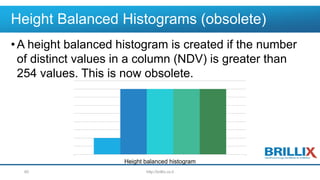
- 60. Height Balanced Histograms (obsolete) •A height balanced histogram is created if the number of distinct values in a column (NDV) is greater than 254 values. This is now obsolete. Height balanced histogram http://brillix.co.il60
- 61. Hybrid Histograms •Hybrid histogram is created if the number of distinct values in a column (NDV) is greater than 254 values but uses actual frequencies of bucket endpoints Hybrid histogram http://brillix.co.il61
- 62. Hybrid Histograms • Similar to height balanced histogram as created if the NDV >254 • Store the actual frequencies of bucket endpoints in histograms • No values are allowed to spill over multiple buckets • More endpoint values can be squeezed in a histogram • Achieves the same effect as increasing the # of buckets • Only created with AUTO_SAMPLE_SIZE http://brillix.co.il62
- 63. Height-balanced versus Hybrid Histogram Oracle Database 11g Oracle Database 12c http://brillix.co.il63
- 64. Session Private Statistics for GTT’s • GTT’s had only one set of statistics that were shared among all sessions even though the table could contain different data in different sessions • Starting Oracle 12c, GTT’s now have session private statistics, which is a different set of statistics for each session • Queries against GTT use statistics from their own session • Improves the performance and manageability of GTT’s • Reduces the possibility of errors in the cardinality estimates for GTT’s and ensures that the optimizer has the data to generate optimal execution plans http://brillix.co.il64
- 65. Online Statistics Gathering for Bulk Loads • Table statistics are gathered automatically during bulk loads: • CREATE TABLE AS SELECT • INSERT INTO … SELECT • Improved performance: avoids an additional table scan to gather table statistics • Improved manageability: no user intervention is required to gather statistics after a bulk load • To disable use hint: NO_GATHER_OPTIMIZER_STATISTICS http://brillix.co.il65
- 66. Optimizer Statistics Advisor (12.2) • Optimizer Statistics Advisor is built-in diagnostic software that analyzes the quality of statistics and statistics-related tasks http://brillix.co.il66
- 67. Optimizer Statistics Advisor (12.2) •The advisor automatically diagnoses problems in the existing practices for gathering statistics •The advisor does not gather a new or alternative set of optimizer statistics •The output of the advisor is a report of findings and recommendations http://brillix.co.il67
- 68. What Can Go Wrong With Statistic Gathering? •Legacy scripts may not keep pace with new best practices, which can change from release to release •Resources are wasted on unnecessary statistics gathering •Statistics can sometimes be missing, stale, or incorrect •Automatic statistics gathering jobs do not guarantee accurate and up-to-date statistics http://brillix.co.il68
- 69. Optimizer Statistics Advisor: Output Example http://brillix.co.il69 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- GENERAL INFORMATION ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Task Name : MY_TASK Execution Name : EXEC_52 Created : 12-07-16 11:31:40 Last Modified : 12-07-16 11:32:37 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- SUMMARY ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- For execution EXEC_52 of task MY_TASK, the Statistics Advisor has 6 finding(s). The findings are related to the following rules: USECONCURRENT, AVOIDSETPROCEDURES, USEDEFAULTPARAMS, USEGATHERSCHEMASTATS, AVOIDSTALESTATS, UNLOCKNONVOLATILETABLE. Please refer to the finding section for detailed information. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- FINDINGS ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ...
- 70. Optimizer Statistics Advisor: Output Example (2) http://brillix.co.il70 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- FINDINGS ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Rule Name: UseConcurrent Rule Description: Use Concurrent preference for Statistics Collection Finding: The CONCURRENT preference is not used. Recommendation: Set the CONCURRENT preference. Example: dbms_stats.set_global_prefs('CONCURRENT', 'ALL'); Rationale: The system's condition satisfies the use of concurrent statistics gathering. Using CONCURRENT increases the efficiency of statistics gathering. ---------------------------------------------------- ...
- 71. More Statistics Features •Concurrent statistics gathering (12.1) •Automatic Column Group Detection for extended statistics (12.2) •Enhancements to Incremental Statistics •Enhancements to System Statistics •More… http://brillix.co.il71
- 73. Summary •We talked about DBIM and the column store solution •We overviewed the new Sharding solution •We looked into new Optimizer and Statistics changes •12c has a lot to offer us, try it – use it! •12cR2 release date for on-prem usage: March 15, 2017 (March 1st for Exadata) http://brillix.co.il73
- 74. What Did We NOT Talk About •SQL Plan Management framework • Automatic Plan Evolution • Enhanced Auto Capture • Capture from AWR Repository •Indexing, Partitioning, and many other performance related new features… http://brillix.co.il74
- 75. Thank You Zohar Elkayam twitter: @realmgic [email protected] www.realdbamagic.com http://brillix.co.il75