Parts and functions of a microscope
- 1. Microscope -Sir Leomered P. Medina
- 2. MICROSCOPE A microscope is an instrument used to see objects that are too small for the naked eye. The science of investigating small objects using such an instrument is called microscopy. Microscopic means invisible to the eye unless aided by a microscope.
- 3. Parts and Functions of a Compound Microscope
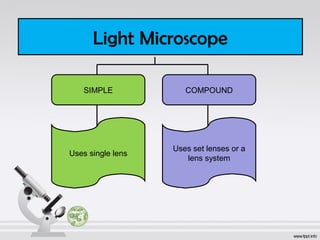
- 4. Light Microscope SIMPLE COMPOUND Uses single lens Uses set lenses or a lens system
- 7. Compound Microscope Mechanical Parts Magnifying Parts Illuminating Parts Adjustments and Support Enlarge the specimen Provide the light
- 8. Mechanical Parts o Base – Bottommost portion that supports the entire/lower microscope o Pillar – Part above the base that supports the other parts o Inclination Joint – Allows for tilting of the microscope for convenience of the user
- 9. Inclination Joint Pillar Base
- 10. Mechanical Parts o Arm/Neck – Curved/slanted part which is held while carrying the microscope o Stage – Platform where object to be examined is placed o Stage Clips – Secures the specimen to the stage
- 11. Mechanical Parts o Stage Opening o Body Tube – Attached to the arm and bears the lenses o Draw Tube – Cylindrical structure on top of the body tube that holds the ocular lenses
- 12. Draw Tube Stage Body Tube Arm / Neck
- 13. Mechanical Parts o Revolving/Rotating Nosepiece – Rotating disc where the objectives are attached o Dust Shield – Lies atop the nosepiece and keeps dust from settling on the objectives
- 14. Dust Shield Revolving Nosepiece
- 15. o Coarse Adjustment Knob – Geared to the body tube which elevates or lowers when rotated bringing the object into approximate focus o Fine Adjustment Knob – A smaller knob for delicate focusing bringing the object into perfect focus
- 16. Coarse Adjustment Knob Fine Adjustment Knob
- 17. Mechanical Parts • Condenser Adjustment Knob – Elevates and lowers the condenser to regulate the intensity of light • Iris Diaphragm Lever – Lever in front of the condenser and which is moved horizontally to open/close the diaphragm
- 18. Iris Diaphragm Lever Condenser Adjustment Knob
- 19. Illuminating Parts o Mirror – Located beneath the stage and has concave and plane surfaces to gather and direct light in order to illuminate the object o Electric Lamp – A built-in illuminator beneath the stage that may eb used if sunlight is not preferred or is not available
- 20. Mirror / Electric Lamp
- 21. MAGNIFYING PARTS • Ocular / Eyepiece – Another set of lens found on top of the body tube which functions to further magnify the image produced by the objective lenses. It usually ranges from 5x to 15x.
- 23. MAGNIFYING PARTS • Objectives – Metal cylinders attached below the nosepiece and contains especially ground and polished lenses • LPO / Low Power Objective – Gives the lowest magnification, usually 10x • HPO / High Power Objective – Gives higher magnification usually 40x or 43x • OIO / Oil Immersion Objective – Gives the highest magnification, usually 97x or 100x, and is used wet either with cedar wood oil or synthetic oil
- 24. Total Magnification MMaaggnniiffiiccaattiioonn == OObbjjeeccttiivvee lleennss XX EEyyeeppiieeccee lleennss e.g. What is the total magnification if the objective lens is twenty times (X20) and the eyepiece lens five times (X5)? Magnification = 20 X 5 = X100
- 25. As magnification increases, detail increases but Onion cell 40x Onion cell 100x Onion cell 400x less of the cell is seen
- 26. Caring for the Microscope 1. Do not let any liquids to come in contact with the microscope. 2. Always store the microscope inside a box after use. 3. Return the objective lens onto low power after use. 4. Carry the microscope by the arm. 5. Use a soft clean tissue to wipe the lenses
- 28. Preparing a slide as a wet mount.
- 29. Use of stains some parts of a plant cell can be clearly seen when the cell is mounted in water E.g. an Elodea leaf cell: cell wall several chloroplasts
- 30. other cell structures which are not so obvious can often be shown up more clearly by the addition of dyes called STAINS Iodine Solution Used to stain plant cells Methylene Blue Used to stain animal cells
- 31. A thin inner layer of epidermis is peeled off. 1 2 An onion is cut into quarters. One of the fleshy scale leaves is removed. Snapping leaf backwards exposes the epidermis. Epidermis is placed on slide & covered with 2-3 drops of distilled water . Coverslip is lowered. A drop of stain is put at one end of slide. 3 5 4 6 7 Stain is drawn over specimen using a small piece of filter paper.
- 32. End -Sir Leomered P. Medina