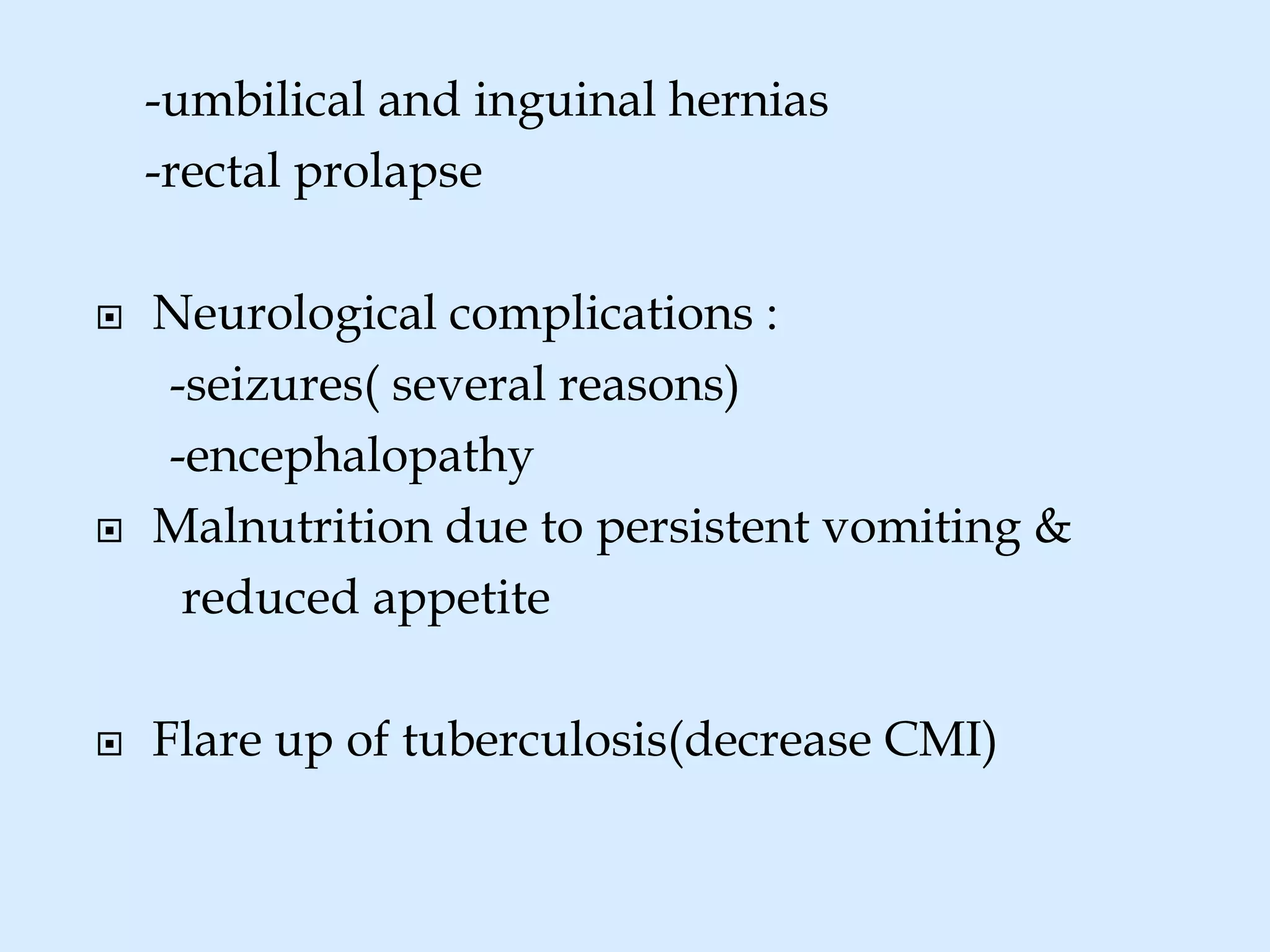
Pertussis, or whooping cough, is an acute respiratory infection caused by the Bordetella pertussis bacteria. It is characterized by intense coughing fits followed by a high-pitched intake of breath, known as the "whoop." While vaccination programs have reduced global prevalence, it remains a public health concern. In India in particular, cases dropped significantly from 1987 to 2011 due to expanded vaccination efforts. The disease is highly contagious, spreading through respiratory droplets. Complications can include pneumonia, seizures, and even death in severe cases, especially for infants under 2 months old. Treatment focuses on supportive care and antibiotics like erythromycin to reduce symptoms and transmission.