php&mysql with Ethical Hacking
- 1. SUMMER TRAINNING REPORT TOPIC :- 1. Developing Dynamic Web Application with MYSQL and PHP. 2. Introduction to Security and Ethical Hacking. STUDENT’S DETAIL’S :- NAME : Saikat Das ROLL NO : 74037309 DEPT : Information Technology. TRAINNING INSTITUTE : NIIT Limited ( Camac Street,Kolkata-17)
- 2. [PART–A] .Developing Dynamic Web Application with. .MYSQL and PHP. Objective:-[ course status – under progress] This instructor-led training is for planning on developing application that makes use of MYSQL and PHP . Implementation of PHP and MYSQL as a cohesive platform for the development of complex dynamic web application. [PART-B] .Introduction to Security and Ethical Hacking. Objective:- [course status – complete] Importance of implementing security in order to protect and safeguard the IT resources of an enterprise. basic aspect is associated with implementing security ,common threats and various attacks .the concept of ethical hacking and various type of hacking techniques.
- 3. [Part–A] Course Agenda – 1. Verify the correct installation of the WAMP component. 2. Utilize the basic components of PHP to build a foundation for more complex Web application. 3. Understand the basic components of MySQL to build a foundation for the development of fully dynamic and data driven sites. 4. Manage Database and tables within MySQL. 5. Utilize SQL query commands and SQL expression to retrieve data (using join operation) from the MySQL Database. 6. Manipulate table data using the SQL DML commands. 7. Utilize session , error and exception handling within PHP during program execution. 8. Integrate PHP’s object orient programming functionality into design of web application.
- 4. 9. Securing PHP and MySQL to improve the integrity of application and subsequent data. WAMP ::: WAMP refers to a solution stack of software , usually free and open source software, used to run dynamic Web sites or servers. The original expansion is as follows: W => Windows => Operating System A => Apache => Web server M => MySQL => Database Management System P => PHP => Scripting language PHP What is PHP ? PHP is a widely-used general-purpose scripting language that is especially suited for Web development and can be embedded into HTML. Example <body>
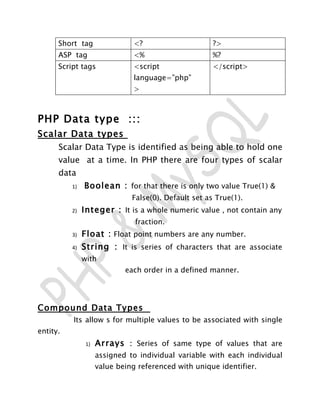
- 5. <?php phpinfo(); ?> </body> Feature of PHP PHP can be used on all major operating systems. PHP has also support for most of the web servers today. you also have the choice of using procedural programming or object oriented programming, or a mixture of them. It supports a wide range of Databases. PHP tags ::: Tag style Start tag End tag Standard tag <?php ?>
- 6. Short tag <? ?> ASP tag <% %? Script tags <script </script> language=”php” > PHP Data type ::: Scalar Data types Scalar Data Type is identified as being able to hold one value at a time. In PHP there are four types of scalar data 1) Boolean : for that there is only two value True(1) & False(0). Default set as True(1). 2) Integer : It is a whole numeric value , not contain any fraction. 3) Float : Float point numbers are any number. 4) String : It is series of characters that are associate with each order in a defined manner. Compound Data Types Its allow s for multiple values to be associated with single entity. 1) Arrays : Series of same type of values that are assigned to individual variable with each individual value being referenced with unique identifier.
- 7. 2) Object : It is the key to the object oriented programming . it can thought as Black Box. Special Data Types 1) Resources : PHP can interact with some external data sources; 2)Null : Null does not mean a blank space or zero, it truly mean no value . Flow Control loop ::: ‘If…else’…’else if’ >> if statement to be valid is if(condition) true . Syntax …… if(test_condition){ … statement… }else if (test_condition2){ …statement2… }else { …statement3…}; Switch >> It works on the principle of comparing a give value with specified constant and acting upon the first constant that is matched. Syntax …… switch(variable){ Case option1 :
- 8. …statement…. Break; Case option2: …statement… Break; Default: …statement… }; While >> It is the simplest of all the iterative control statement. Statement is repeated as long as condition remains true. Syntax …… while(expression){ …statement… }; Do while >> It is same as while loop . But here first statement is executed then condition is checked. Syntax …… do{ …statement… }while (expression); For >> It is more complex sibling of while function. It provide three expressions. It help to repeat the loop. Syntax …… for(condition1 ; condition2 ; condition3) { … statement … } Foreach >> It is the iterative control statement that is designed specifically for handling array.
- 9. Syntax …… Foreach (array_expression as $value) { … statement… } Break and continue >> It used to manually interrupting the flow of the loops. Define a variable :::: In PHP , all variables are identified by $ symbol. Example …… <?php $a=”Hello” ; $b=”World”; ?> To Display statement & variable :::: In PHP you can use any function to display the all statement and print the value of the variable. To understand more see the example. Example …… <?php print(`<p>Its print function</p>`) ; Print `<p> Display variable` .$var. `in php</p>`; Echo ”<p>Its also print string</p>”; Printf(`<p> %d Euro = $%01.2f US Dollar</p>`,1,1.3);
- 10. Function ::::: In PHP we can also create our own function. Its called user define function. Syntax …… function function name( $argu1, $argu2 ) { // function code here } Define an Array :::: array is a list of variable. It contains multiple elements indexed by numbers or strings. There are two way to make a array , $arrayname = array (“Raja”,”Rohan”,”Rohit”); $arrayname[0]=”Raja”; $arrayname[1]=”Rohan”; $arrayname[2]=”Rohit”; Join an array :::: Join array elements with a glue string. $array = array('Rohit', 'Sharma', 'Kolkata'); $comma_separated = join(",", $array); echo $comma_separated; // output will be “Rohit , Sharma , Kolkata”
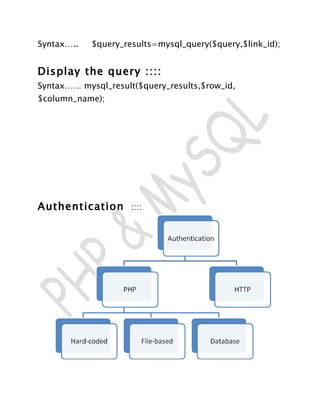
- 11. To replace a string :::: Replace all occurrences of the search string with the replacement string. Syntax …… str_replace ( $search , $replace , $subject) To repeat a string :::: string str_repeat ( string $input , int $multiplier ) connecting to MySQL :::: Mysql_connect() function is used to established an initial connection to the mysql server. Syntax …… mysql_connect ( [hostname [:port] [:/path/to/socket] [,username] [,password] ]) Databases connect :::: Syntax…… mysql_select_db($db_name,$link_id) or die(“could not found”); Querying Mysql ::::
- 12. Syntax….. $query_results=mysql_query($query,$link_id); Display the query :::: Syntax…… mysql_result($query_results,$row_id, $column_name); Authentication ::::
- 13. MySQL How MySQL works ?? Parse Optimize Retrieve store Pluggable Storage Engines When we enter a query to the query browser, then 1st the query is checked by the parse to find the syntax error. After that optimize the query. Then the data retrieve from the database with the help of pluggable storage engines. Basically engines fetch the data. There are different storage engines available . • MyISAM • InnoDB • Memory • NDB
- 14. IMPOTANT COMMANDS … … … … … … … … To see database :::: show databases ; To create databases :::: create database db_name; To use databases :::: use db_name; To delete databases :::: drop database db_name; To display database structure :::: show create database db_nameG; To create table :::: create table <table name>( <column name><column type>[<column option>], <column name><column type>[<column option>],…,] [<index list>])[<table option>]; To display table creation information :::: Show create table <table name>G; To Altering column :::: Alter table <table name> add <column name> <column type> [<column option>]; drop <column name>;
- 15. modify <new column name><column type>[<option>]; change <old column><new column><column type> [<new column option>]; To rename a table :::: rename table <old name> to <new name>; To see the contain of the table :::: Select [<clause option>] <column list > [from] <table name> [<clause option >]; Clauses Definition DISTINCT Eliminates duplicate row FROM Specifies from where to retrieve the data WHERE Decides what data to show ODER BY Sorts data by specific order criteria LIMIT Reduces the amount of records recive
- 16. Object Oriented PHP PHP treats objects in the same way as references or handles, meaning that each variable contains an object reference rather than a copy of the entire object. Two terms are often heard when discussing OOP are class and object.A class is essentially a description of an object , while an object is an instance of that class. Working with Objects o The methods in a class represent either things that an object can do itself,or that another object can cause the class to do.
- 17. o Method and properties can be declared one of the three ways:-public,private,or protected. Class: Every class definition begins with the keyword class, followed by a class name, followed by a pair of curly braces which enclose the definitions of the class's properties and methods. A class may contain its own constants,variables and functions. Class declaration :::: <?php class SimpleClass{ // property declaration public $var = 'a default value'; // method declaration public function displayVar() { echo $this->var; }} ?> New ::::: To create an instance of a class, a new object must be created and assigned to a variable. An object will
- 18. always be assigned when creating a new object unless the object has a constructor defined that throws an exception on error. Classes should be defined before instantiation (and in some cases this is a requirement). Creating an instance <?php $instance = new SimpleClass(); ?> PHP Configurations The first step in any process of securing an application is checking the configuration components that the software is running under. Running PHP in Safe Mode When running PHP in a shared server environment,the use of safe mode needs to be considered and when possible implemented. • Safe mode-When this mode is set to 1(on),the following condition apply: Input/output functions
- 19. External scripts UserID with Authentication MySQL User Data Encryption: Data encryption is the process of scrambling stored or transmitted information so that it is unintelligible until it is unscrambled by the intended recipient.The following are a list of common encryption function in PHP. • md5():-The md5() function returns a 128-bit hash that can then be then be stored with the ultimate outcome of comparing it for security purposes. Example of an encryption …….. <?php $string=”I am A big FanofIce Cream”: $string_md5=md5($string);
- 20. If(md5($string)=$string_md5) { Print “$string=md5($string_md5)”; } ?> Will print: I am A big FanofIce Cream = md5(673d924425c45b1f221fdfcbe21 60cf) Securing the MySQL Server(mysqld) • MySQL process must run under a unique UID/GID that is not used by any other system process. • MySQL root’s account must be protected by a hard to guess password. • The administrator’s account should be renamed. MySQL Access Privelege System:
- 21. shell>mysql –user=<username> --password=<password> db-name [Part–B] Course Agenda – 1.Identify the importance of implementing security(building blocks) in an enterprise. 2.Understand cryptographic security. 3.Various threats and attacks against hardware,software and network. 4.Understanding the importance of hardening. 5.Inside out of an enterprise work. 6.Best practices that should be adopted to secure various services and system. 7.Concept of hacking and ethical hacking. 8.Identyfy the types of hackers and their techniques.
- 22. Module1:-Security –The key to Protection. 1 . Ever-increasing need to secure information accessed over the network for data. 2. Information security seeks to protect the following three specific element:- CONFIDENTIALITY,INTEGRITY,and AVAILABILITY. 3. Major authentication method in use today:- User name and password authentication, Token authentication, biometric authentication. 4. Cryptography is the science of hiding or encrypting information. 5. Certificate-based security involves the use of digital certificates.
- 23. 6. A security policy is formalized statement that defines how security will be implemented with a particular organization. Module2:- Identifying Threats and Attacks. 1. To secure IT infrastructure against various threats like --Unauthorized access, Data theft, Hacking. 2. Hackers can use social engineering, a hacking technique that exploits user’s trust and use physical method and psychological tricks, to collect information. 3. Different social engineering techniques- Impersonation, Bribery, Deception, Conformity. 4. A network attack is a type of attack that is targeted towards getting access to and breaking into a network to disrupt the network connectivity and delay access to the network.
- 24. 5.A hardware attack is an attack that targets a computer’s physical components and peripherals such as hard disk, mother board, keyboard, network cable or USB device. Module3:- Hardening Internal System and services. 1. Hardening is a general term for any security procedure wherin the default configuration of a system is configured to prevent attacks. 2. Few common operating system vulnerabilities: Default Install, Default Accounts, Built-in Application, Physical Access. 3. A directory service is a network that stores information about all the objects, such as user’s groups, servers client computers, printers and network services in a particular network. 4. It is extremely important to protect the company’s Web servers from attack.
- 25. 5.Most of the attacks target public service network,commercial networks and website. Module4:-Hacking and the Ethics Involved. 1. Hacking refers to the practice of breaking into information systems. 2. Ethics are principles that distinguish between right and wrong. 3. System administrator use hacking to check security gaps in networks and software products. 4. Eathical hacking is a combination of integrity, transparency and independence. 5. Ethical hacking of networks and systems should be performed on a regular basis, to detect new
- 26. vulnerabilities and possible breach of security or hacking attempts. 6. To hack a system ,hackers have to first find possible security gaps and vulnerabilities with in the system. 7.Common techniques:-Sniffing attacks, Scanning, Reconnaissance, Internet foot printing , Pharming.


![[PART–A]
.Developing Dynamic Web Application with.
.MYSQL and PHP.
Objective:-[ course status – under progress]
This instructor-led training is for planning on developing
application that makes use of MYSQL and PHP .
Implementation of PHP and MYSQL as a cohesive
platform for the development of complex dynamic web
application.
[PART-B]
.Introduction to Security and Ethical Hacking.
Objective:- [course status – complete]
Importance of implementing security in order to protect
and safeguard the IT resources of an enterprise. basic
aspect is associated with implementing security ,common
threats and various attacks .the concept of ethical
hacking and various type of hacking techniques.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reportallformatfialprint-100826133342-phpapp02/85/php-mysql-with-Ethical-Hacking-2-320.jpg)
![[Part–A]
Course Agenda –
1. Verify the correct installation of the WAMP component.
2. Utilize the basic components of PHP to build a foundation
for more complex Web application.
3. Understand the basic components of MySQL to build a
foundation for the development of fully dynamic and data
driven sites.
4. Manage Database and tables within MySQL.
5. Utilize SQL query commands and SQL expression to
retrieve data (using join operation) from the MySQL
Database.
6. Manipulate table data using the SQL DML commands.
7. Utilize session , error and exception handling within PHP
during program execution.
8. Integrate PHP’s object orient programming functionality
into design of web application.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reportallformatfialprint-100826133342-phpapp02/85/php-mysql-with-Ethical-Hacking-3-320.jpg)





![Function ::::: In PHP we can also create our own
function. Its called user define function.
Syntax …… function function name( $argu1, $argu2 )
{
// function code here
}
Define an Array ::::
array is a list of variable. It contains multiple elements
indexed by numbers or strings. There are two way to make
a array ,
$arrayname = array (“Raja”,”Rohan”,”Rohit”);
$arrayname[0]=”Raja”;
$arrayname[1]=”Rohan”;
$arrayname[2]=”Rohit”;
Join an array :::: Join array elements with a
glue string.
$array = array('Rohit', 'Sharma', 'Kolkata');
$comma_separated = join(",", $array);
echo $comma_separated;
// output will be “Rohit , Sharma , Kolkata”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reportallformatfialprint-100826133342-phpapp02/85/php-mysql-with-Ethical-Hacking-10-320.jpg)
![To replace a string ::::
Replace all occurrences of the search string with the
replacement string.
Syntax …… str_replace ( $search , $replace , $subject)
To repeat a string ::::
string str_repeat ( string $input , int
$multiplier )
connecting to MySQL ::::
Mysql_connect() function is used to established an initial
connection to the mysql server.
Syntax ……
mysql_connect ( [hostname [:port] [:/path/to/socket]
[,username] [,password] ])
Databases connect ::::
Syntax……
mysql_select_db($db_name,$link_id) or die(“could not
found”);
Querying Mysql ::::](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reportallformatfialprint-100826133342-phpapp02/85/php-mysql-with-Ethical-Hacking-11-320.jpg)

![IMPOTANT COMMANDS … … … … … … … …
To see database :::: show databases ;
To create databases :::: create database db_name;
To use databases :::: use db_name;
To delete databases :::: drop database db_name;
To display database structure ::::
show create database
db_nameG;
To create table :::: create table <table name>(
<column name><column type>[<column
option>],
<column name><column type>[<column
option>],…,]
[<index list>])[<table option>];
To display table creation information ::::
Show create table <table
name>G;
To Altering column ::::
Alter table <table name>
add <column name> <column type> [<column
option>];
drop <column name>;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reportallformatfialprint-100826133342-phpapp02/85/php-mysql-with-Ethical-Hacking-14-320.jpg)
![modify <new column name><column
type>[<option>];
change <old column><new column><column
type>
[<new column
option>];
To rename a table :::: rename table <old name> to <new
name>;
To see the contain of the table ::::
Select [<clause option>] <column list > [from] <table
name>
[<clause
option >];
Clauses Definition
DISTINCT Eliminates duplicate row
FROM Specifies from where to retrieve the data
WHERE Decides what data to show
ODER BY Sorts data by specific order criteria
LIMIT Reduces the amount of records recive](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reportallformatfialprint-100826133342-phpapp02/85/php-mysql-with-Ethical-Hacking-15-320.jpg)





![shell>mysql –user=<username> --password=<password>
db-name
[Part–B]
Course Agenda –
1.Identify the importance of implementing
security(building blocks) in an enterprise.
2.Understand cryptographic security.
3.Various threats and attacks against
hardware,software and network.
4.Understanding the importance of hardening.
5.Inside out of an enterprise work.
6.Best practices that should be adopted to secure
various services and system.
7.Concept of hacking and ethical hacking.
8.Identyfy the types of hackers and their techniques.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reportallformatfialprint-100826133342-phpapp02/85/php-mysql-with-Ethical-Hacking-21-320.jpg)




