Platform for Enterprise Solution - Java EE5
- 1. 1 Platform for Enterprise Solution: Java EE5
- 2. 2 Platform for Enterprise Solutions : JAVA EE5: What is Java EE ? JEE is actually a collection of technologies and APIs for the Java platform designed to support "Enterprise" Applications which can generally be classed as large-scale, distributed, transactional and highly-available applications designed to support mission-critical business requirements. In terms of what an employee is looking for in specific techs, it is quite hard to say, because the playing field has kept changing over the last five years. It really is about the class of problems that are being solved more than anything else. Transactions and distribution are key.
- 3. 3 JAVA EE Platform Overview The Java EE platform is a set of standard specifications that describe application components, APIs, and the runtime containers and services of an application server. Java Platform, Enterprise Edition (Java EE) is the standard in community- driven enterprise software. Java EE is developed using the Java Community Process, with contributions from industry experts, commercial and open source organizations, Java User Groups, and countless individuals. Each release integrates new features that align with industry needs, improves application portability, and increases developer productivity. Today, Java EE offers a rich enterprise software platform, and with over 20 compliant Java EE implementations to choose from, low risk and plenty of options.
- 4. 5 Web core technologies: Servlets and JSP What is the difference between JSF, Servlet and JSP ? Servlet is html in java JSP is java in html
- 5. 6 Java Server Faces (JSF)
- 6. 7 Java Server Faces (JSF) Java Server Faces (JSF) is a Java-based web application framework intended to simplify development integration of web-based user interfaces. Java Server Faces is a standardized display technology which was formalized in a specification through the Java Community Process.
- 7. 8 What is JSF? JSF is a MVC web framework that simplifies the construction of user interfaces (UI) for server-based applications by using reusable UI components in a page. JSF provides facility to connect UI widgets with data sources and to server-side event handlers. The JSF specification defines a set of standard UI components and provides an Application Programming Interface (API) for developing components. JSF enables the reuse and extension of the existing standard UI components.
- 8. 9 JSF Benefits providing reusable UI components making easy data transfer between UI components managing UI state across multiple server requests enabling implementation of custom components wiring client side event to server side application code
- 9. 10 JSF UI component model Core library A set of base UI components - standard HTML input elements Extension of the base UI components to create additional UI component libraries or to extend existing components. Multiple rendering capabilities that enable JSF UI components to render themselves differently depending on the client types
- 10. 11 What is MVC Design Pattern? Module Description Model Carries Data and login View Shows User Interface Controller Handles processing of an application
- 12. 13 JSF - Life Cycle
- 13. 14 Servlets
- 14. 15 Servlets Servlets provide a component-based, platform- independent method for building Web-based applications, without the performance limitations of CGI programs. Servlets have access to the entire family of Java APIs, including the JDBC API to access enterprise databases.
- 15. 16 What are Servlets? Java Servlets are programs that run on a Web or Application server and act as a middle layer between a request coming from a Web browser or other HTTP client and databases or applications on the HTTP server. Using Servlets, we can collect input from users through web page forms, present records from a database or another source, and create web pages dynamically.
- 16. 17 Servlets advantages in comparison with the CGI Performance is significantly better. Servlets execute within the address space of a Web server. It is not necessary to create a separate process to handle each client request. Servlets are platform-independent because they are written in Java. Java security manager on the server enforces a set of restrictions to protect the resources on a server machine. So servlets are trusted. The full functionality of the Java class libraries is available to a servlet. It can communicate with applets, databases, or other software via the sockets and RMI mechanisms that you have seen already.
- 18. 19 Servlets Tasks Read the explicit data sent by the clients (browsers). This includes an HTML form on a Web page or it could also come from an applet or a custom HTTP client program. Read the implicit HTTP request data sent by the clients (browsers). This includes cookies, media types and compression schemes the browser understands, and so forth. Process the data and generate the results. This process may require talking to a database, executing an RMI or CORBA call, invoking a Web service, or computing the response directly. Send the explicit data (i.e., the document) to the clients (browsers). This document can be sent in a variety of formats, including text (HTML or XML), binary (GIF images), Excel, etc. Send the implicit HTTP response to the clients (browsers). This includes telling the browsers or other clients what type of document is being returned (e.g., HTML), setting cookies and caching parameters, and other such tasks.
- 19. 20 Servlets Packages Java Servlets are Java classes run by a web server that has an interpreter that supports the Java Servlet specification. Servlets can be created using the javax.servlet and javax.servlet.http packages, which are a standard part of the Java's enterprise edition, an expanded version of the Java class library that supports large-scale development projects.
- 20. 21 Servlet Development environment setup Setting up Java Development Kit
- 21. 22 Servlet life cycle It is initialized by calling the init () method. It calls service() method to process a client's request. It is terminated by calling the destroy() method. Finally, it is garbage collected by the garbage collector of the JVM.
- 23. 24 Servlets Form Data Client Request Server Response Http Codes Writing Filters Exceptions Cookies Handling Session Tracking Database Access File Uploading Handling Date Page Redirect Hits Counter Auto Refresh Sending Email Packaging Debugging Internationalization
- 24. 25 JSP
- 25. 26 JSP Java Server Pages (JSP) is a server-side programming technology that enables the creation of dynamic, platform-independent method for building Web-based applications. JSP have access to the entire family of Java APIs, including the JDBC API to access enterprise databases.
- 26. 27 What is Java Server Pages? Java Server Pages (JSP) is a technology for developing web pages that support dynamic content which helps developers insert java code in HTML pages by making use of special JSP tags, most of which start with <% and end with %>. A Java Server Pages component is a type of Java servlet that is designed to fulfill the role of a user interface for a Java web application.
- 27. 28 Why Use JSP? Performance is significantly better because JSP allows embedding Dynamic Elements in HTML Pages itself instead of having a separate CGI files. JSP are always compiled before it's processed by the server unlike CGI/Perl which requires the server to load an interpreter and the target script each time the page is requested. Java Server Pages are built on top of the Java Servlets API, so like Servlets, JSP also has access to all the powerful Enterprise Java APIs, including JDBC, JNDI, EJB, JAXP etc. JSP pages can be used in combination with servlets that handle the business logic, the model supported by Java servlet template engines.
- 28. 29 Advantages of JSP vs. Active Server Pages (ASP): The advantages of JSP are twofold. First, the dynamic part is written in Java, not Visual Basic or other MS specific language, so it is more powerful and easier to use. Second, it is portable to other operating systems and non-Microsoft Web servers. vs. Pure Servlets: It is more convenient to write (and to modify!) regular HTML than to have plenty of println statements that generate the HTML.
- 29. 30 Advantages of JSP vs. Server-Side Includes (SSI): SSI is really only intended for simple inclusions, not for "real" programs that use form data, make database connections, and the like. vs. JavaScript: JavaScript can generate HTML dynamically on the client but can hardly interact with the web server to perform complex tasks like database access and image processing etc. vs. Static HTML: Regular HTML, of course, cannot contain dynamic information.
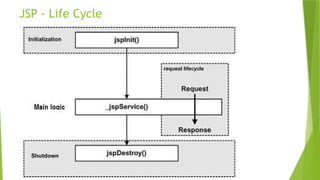
- 32. 33 JSP - Life Cycle Compilation Initialization Execution Cleanup
- 33. 34 JSP - Life Cycle
- 34. 35 JSP Compilation The compilation process involves three steps: Parsing the JSP. Turning the JSP into a servlet. Compiling the servlet.
- 35. 36 JSF, Servlet and JSP JSP is a webpage scripting language that can generate dynamic content while Servlets are Java programs that are already compiled which also creates dynamic web content Servlets run faster compared to JSP JSP can be compiled into Java Servlets It’s easier to code in JSP than in Java Servlets In MVC, JSP act as a view and servlet act as a controller. JSP are generally preferred when there is not much processing of data required. But servlets are best for use when there is more processing and manipulation involved. The advantage of JSP programming over servlets is that we can build custom tags which can directly call Java beans. There is no such facility in servlets. We can achieve functionality of JSP at client side by running JavaScript at client side. There are no such methods for servlets.
Editor's Notes
- #5: JavaServer Faces (JSF) is a Java specification for building component-based user interfaces for web applications. It was formalized as a standard through the Java Community Process and is part of the JavaPlatform, Enterprise Edition.
- #7: Before proceeding with this we should have a basic understanding of Java programming language, text editor and execution of programs etc. Because we are going to develop web based applications using JSF, so it will be good if we have understanding on other web technologies like, HTML, CSS, AJAX etc.
- #9: JSF reduces the effort in creating and maintaining applications which will run on a Java application server and will render application UI on to a target client
- #12: JavaBeans components as models containing application-specific functionality and data A custom tag library for representing event handlers and validators A custom tag library for rendering UI components UI components represented as stateful objects on the server Server-side helper classes Validators, event handlers, and navigation handlers Application configuration resource file for configuring application resources
- #13: Restore view phase Apply request values phase; process events Process validations phase; process events Update model values phase; process events Invoke application phase; process events Render response phase
- #16: I assume you have good understanding of the Java programming language. It will be great if you have a basic understanding of web application and how internet works.
- #17: Common Gateway Interface (CGI) The Java Remote Method Invocation (RMI) system allows an object running in one Java virtual machine to invoke methods on an object running in another Java virtual machine. RMI provides for remote communication between programs written in the Java programming language.
- #19: Object Request Broker (ORB) Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA) technology is the open standard for heterogeneous computing. CORBA complements the Java™ platform by providing a distributed object framework, services to support that framework, and interoperability with other languages. The Java platform complements CORBA by providing a portable, highly productive implementation environment, and a very robust platform. By combining the Java platform with CORBA and other key enterprise technologies, the Java Platform is the ultimate platform for distributed technology solutions.
- #21: You Guise are master in it.
- #23: 1- First the HTTP requests coming to the server are delegated to the servlet container. 2- The servlet container loads the servlet before invoking the service() method. 3- Then the servlet container handles multiple requests by spawning multiple threads, each thread executing the service() method of a single instance of the servlet.
- #24: Internationalization: This means enabling a web site to provide different versions of content translated into the visitor's language or nationality. Localization: This means adding resources to a web site to adapt it to a particular geographical or cultural region for example Hindi translation to a web site. locale: This is a particular cultural or geographical region. It is usually referred to as a language symbol followed by a country symbol which is separated by an underscore. For example "en_US" represents english locale for US.
- #28: Java Server Pages often serve the same purpose as programs implemented using the Common Gateway Interface (CGI). But JSP offer several advantages in comparison with the CGI.
- #31: A JSP container works with the Web server to provide the runtime environment and other services a JSP needs. It knows how to understand the special elements that are part of JSPs.
- #32: The following steps explain how the web server creates the web page using JSP: As with a normal page, our browser sends an HTTP request to the web server. The web server recognizes that the HTTP request is for a JSP page and forwards it to a JSP engine. This is done by using the URL or JSP page which ends with .jsp instead of .html. The JSP engine loads the JSP page from disk and converts it into a servlet content. This conversion is very simple in which all template text is converted to println( ) statements and all JSP elements are converted to Java code that implements the corresponding dynamic behavior of the page. The JSP engine compiles the servlet into an executable class and forwards the original request to a servlet engine. A part of the web server called the servlet engine loads the Servlet class and executes it. During execution, the servlet produces an output in HTML format, which the servlet engine passes to the web server inside an HTTP response. The web server forwards the HTTP response to our browser in terms of static HTML content. Finally web browser handles the dynamically generated HTML page inside the HTTP response exactly as if it were a static page.
- #33: A JSP life cycle can be defined as the entire process from its creation till the destruction which is similar to a servlet life cycle with an additional step which is required to compile a JSP into servlet.
- #34: A JSP life cycle can be defined as the entire process from its creation till the destruction which is similar to a servlet life cycle with an additional step which is required to compile a JSP into servlet.
- #35: When a browser asks for a JSP, the JSP engine first checks to see whether it needs to compile the page. If the page has never been compiled, or if the JSP has been modified since it was last compiled, the JSP engine compiles the page.