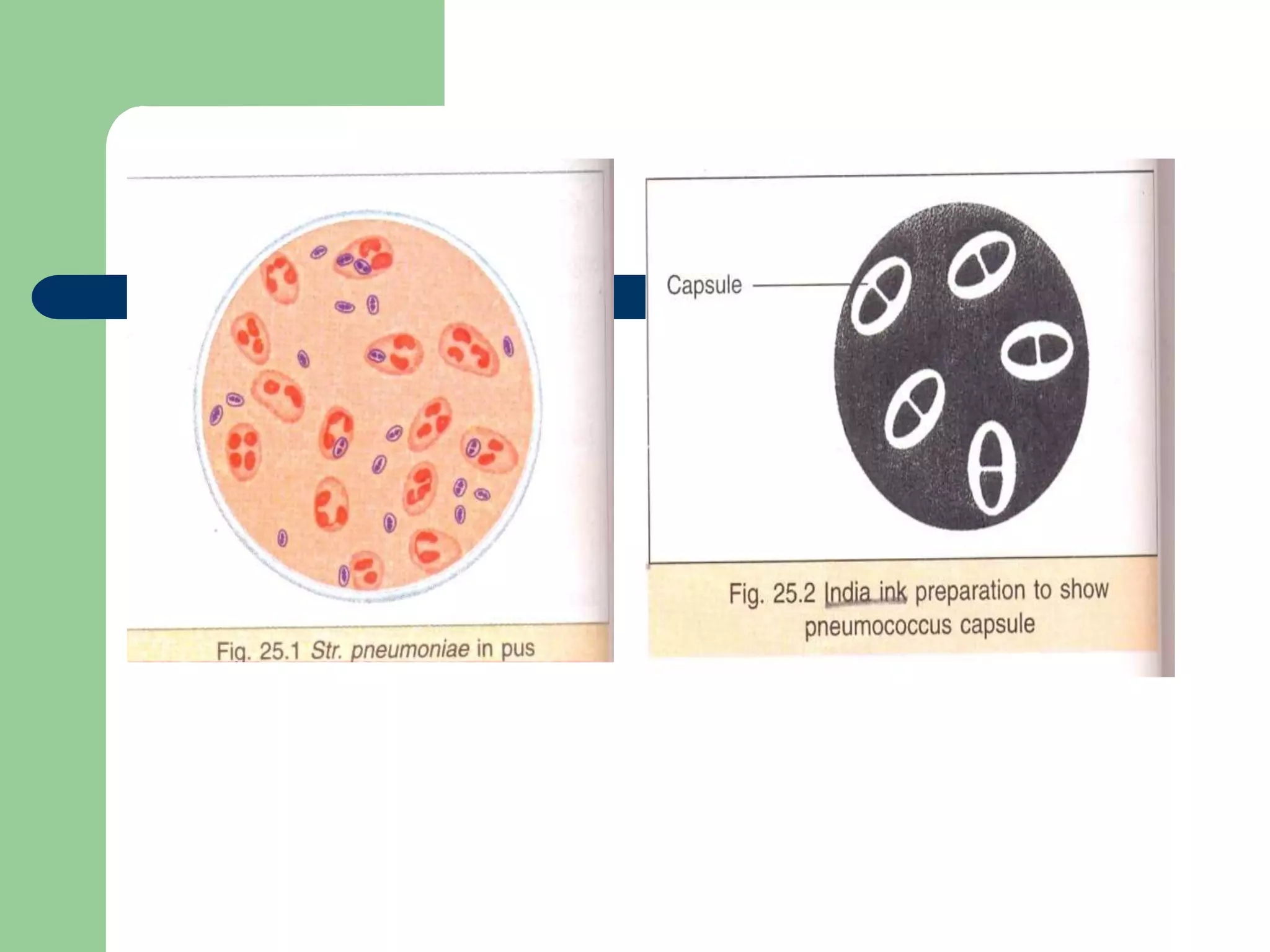
Streptococcus pneumoniae, or pneumococcus, is a gram-positive bacterium commonly found in the upper respiratory tract and is a significant pathogen responsible for pneumonia and otitis media. It is characterized by its lanceolate appearance, being capsulated and nonmotile, with fastidious growth requirements on enriched media, and can be identified using various biochemical tests, including optochin susceptibility. The virulence of pneumococcus is largely due to its capsular polysaccharides, with more than 90 serotypes recognized, leading to diverse clinical manifestations such as pneumonia, bacteremia, and meningitis.