Practical application of scrum final
- 1. Agile Implementation Lessons Learned from Practical Application Presented to NM Women In Technology June 28, 2012 Ana Lopez, Certified Scrum Master Lisa Milmine, Certified Scrum Master Software Application Engineering Sandia National Laboratories
- 2. Presentation Overview • Agile Development • The Scrum Framework • Lessons Learned and Recommendations (So what)
- 3. What is Agile? Frequently delivering business value while adapting to change Agile is a philosophy Agile is applied through a method (like XP or Scrum) See: Shore, James and Shane Warden. The Art of Agile Development, Sabastopol, CA: O’Reilly Media, Inc. , 2008. Print.
- 4. How Agile Evolved 1990s – common methodologies emerged Face to face communication Frequent delivery of business value Self managing teams Adaptable coding practices In 2001 - Agile Summit See: What is Agile Software Development: http://www.agilealliance.org/the-alliance/what-is-agile/ Agile Software Development: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Agile_software_development
- 5. Agile Manifesto “We are uncovering better ways of developing software by doing it and helping others do it. Through this work we have come to value: • Individuals and interactions over processes and tools • Working software over comprehensive documentation • Customer collaboration over contract negotiation • Responding to change over following a plan That is, while there is value in the items on the right, we value the items on the left more.” See: Manifesto for Agile Software Development: http://agilemanifesto.org/
- 6. 12 Principles Satisfy the customer through early and continuous delivery of valuable software. Deliver working software frequently, from a couple of weeks to a couple of months, with a preference to the shorter timescale. Welcome changing requirements, even late in development. Regular adaptation to changing circumstances See: Manifesto for Agile Software Development: http://agilemanifesto.org/principles.html
- 7. 12 Principles (Cont.) Build projects around motivated individuals. Self-organizing teams Continuous attention to technical excellence and good design Working software is the primary measure of progress. See: Manifesto for Agile Software Development: http://agilemanifesto.org/principles.html
- 8. 12 Principles (Cont.) Business people and developers must work together daily throughout the project. The most efficient and effective method of conveying information to and within a development team is face-to-face conversation. Simplicity- The art of maximizing the amount of work not done - is essential Agile processes promote sustainable development. See: Manifesto for Agile Software Development: http://agilemanifesto.org/principles.html
- 9. Why everyone likes agile • Executives and Senior Management − Return on investment − Software longevity • Users and Stakeholders − Influence the direction of software development − Teams focus on delivering useful and valuable software − Increased delivery frequency • Project Managers − Change direction as business needs change, − Make and meet commitments − Improved stakeholder satisfaction • Developers − Increased technical quality − Greater influence over estimates and schedules and team autonomy • Testers − Part of the team − Influence quality at all stages of the project See: Shore, James and Shane Warden. The Art of Agile Development, Sabastopol, CA: O’Reilly Media, Inc. , 2008. Print.
- 10. What is Scrum? An agile framework focused on delivering business value in short incremental periods (sprints) Created in the early 1993 at Easel Corporation Specifically suited for complex problems Defined in The Scrum Guide: The Definitive Guide to Scrum: The Rules of the Game - Developed and Sustained by Ken Schwaber and Jeff Sutherland Term “scrum” inspired by a Rugby formation for players used to restart the play of a game usually after an infraction. A team approach. Origins: http://scrum.jeffsutherland.com
- 11. Scrum Philosophy • Software development is - Complex - Always Broken • A proven method for meeting customer needs is to use the ideas of Agile, including empirical process control. • Empirical Process Control: • Inspection • Adaptation • Transparency Empirical Process: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Empirical_process_(process_control_model)
- 12. The Process Three Questions Two Questions Sprint Backlog Tasks User Story Process: http://www.scrumalliance.org/learn_about_scrum
- 13. The Product Backlog Three Questions Two Questions Sprint Backlog Tasks User Story
- 14. The Sprint Planning Three Questions Two Questions Sprint Backlog Tasks User Story
- 15. The Sprint Planning Tasks Three Questions Two Questions Sprint Backlog Tasks User Story
- 16. The Sprint Three Questions Two Questions Sprint Backlog Tasks User Story
- 17. The Daily Standup Three Questions Two Questions Sprint Backlog Tasks User Story
- 18. The Sprint Objective – Working Software Three Questions Two Questions Sprint Backlog Tasks User Story
- 19. The Review Three Questions Two Questions Sprint Backlog Tasks User Story
- 20. The Retrospective Three Questions Two Questions Sprint Backlog Tasks User Story
- 21. The Iterative Process Three Questions Two Questions Sprint Backlog Tasks User Story
- 22. Scrum Roles • Product Owner (PO) Responsible for the success/business value of project Empathetically represents customers Uses insight to prioritize essential/incidental requirements • Scrum Master (SM) A process facilitator, NOT a project/people manager Resolves impediments, helps team focus on value • Team Self managed, self organizing to get the work done Owns/takes responsibility for process Scrum recommends 7 +/- 2 team members at most
- 23. Scrum Artifacts • Product backlog Prioritized list of desired project requirements Founded from product Vision • Sprint backlog/Task backlog Set of work from the product backlog that the team agrees to complete in a sprint, broken into tasks Follow a clearly defined Definition of Done • Burn-down or Burn-up chart At-a-glance look at the work remaining • Release set Minimally marketable release
- 24. Ceremonies (aka meetings) • Sprint planning The team and product owner estimate and negotiate a set of work to deliver during a sprint • Daily scrum The team meets each day to report progress, next steps, and impediments Facilitated by SM – team reports to each other • Sprint reviews The team demonstrates to the product owner and stakeholders what it has completed during the sprint (working software) • Sprint retrospectives The team looks for ways to improve the process. Facilitated by SM
- 25. User Stories • Describes functionality that is valuable to a user/stakeholder The “what” not the “how” • Written from the customers perspective • Represents customer priorities • Reminders to have a conversation • A user story is NOT a contract or agreement Everything can go in the backlog
- 26. Backlog Grooming • A regular meeting to manage the backlog of stories Grooming activities include: • Creating /Removing stories in response to newly discovered needs • Re-assessing the relative priority of stories • Assigning estimates to stories which have yet to receive one • Correcting estimates in light of newly discovered information • Splitting large user stories into multiple sprint sized stories • Development of acceptance criteria
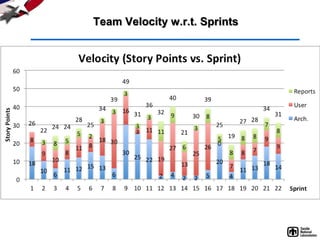
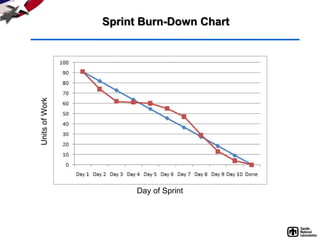
- 27. Project Status/Information Radiators • Level of Effort Story Points, T-shirt sizes, etc. • Rate of Production Velocity (velocity = story pts completed per sprint) Basis for planning/projecting • Sprint Burn-Down Chart Daily display of work remaining in a sprint Pitfall: fails to show effect of changing • Release Burn-Up Chart Tracks how much work is done wrt product backlog Projections give insight for release planning goals
- 28. Team Velocity w.r.t. Sprints
- 29. Team Velocity w.r.t. Sprints
- 31. Sprint Burn-Down Chart Units of Work Day of Sprint
- 33. So… What have we learned in practice? What wont the textbooks tell you?
- 34. People • Development Team Members − Elicit team-oriented characteristics − Comfortable with not knowing all details up front − Appropriately sized − Trained on agile method • ScrumMaster − Posses or acquire good facilitation skills − Focus on facilitating and not managing the process − Try to develop good coaching skills − Should be independent of development and customer responsibilities
- 35. People (Cont.) • Project Manager − Responsible for managing process areas not called out by Scrum (risk management, communications, etc.) − Empower self management of your team − Report frequently to build management confidence • Product Owner − Fully committed to project − Product owner trained/certified − Empowered by management to have decision authority − Understands that they have ultimate authority
- 36. People (Cont.) • Management − Knowledgeable of process at a high level − Supportive of team’s empowerment to manage • Customers and Stakeholders − Flexible on scope − Committed and engaged through the duration of the project
- 37. Practices • Definition of Done − Do it for task, story, and sprint − Revisit Often − Adapt as necessary • Backlog Grooming − Conduct regularly throughout project − Project owner representation is required • Reporting (progress/status) − Use the Scrum terminology/measurements − Familiarize Management ahead of time
- 38. Structure • Sprint Tasks − Allow the team to develop a method that adds value to them − Preserve differentiation of stories and tasks − Maintain goal of transparency of work at hand • Execution of Development within Process − Remember: Failed acceptance tests or unfinished work equal additional backlog or defect work − Plan for adequate testing/acceptance within sprint − Prevent scope creep! Only work on planned work
- 39. Structure • Planning − Come prepared! − Conduct sufficient discussion of stories with dev team − Obtain verbal commitment to sprint backlog • Review − Maintain consistent forum for demonstrating work/obtaining feedback − Keep reviews efficient − Plan for review “demo” preparation time • Retrospective − Revisit previous retro notes − Ensure all team members have opportunity to contribute
- 40. Tips for Getting Started • Select an agile method that • Establish your sprint schedule & suits your team logistics • Get management’s • Establish communication lines commitment/trust for distance separated teams • Ensure PO is empowered and • Set up your team can respond rapidly room/workspace • Get your team and customers • Create a vision for your product trained and motivated • Spend just enough time on • Clearly define roles and architecture & design to avoid responsibility disjointed components • Obtain acceptance from all • Have a kickoff team members Have Fun and Explore – Be Agile!
- 41. Questions and Discussion Contact Information: Lisa Milmine, (505) 284-4103, [email protected] Ana Lopez, (505) 284-1873, [email protected]
- 42. Backup Slides
- 43. Velocity Statistics |Velocity Min| 19.00 |Velocity Max| 49.00 |Velocity Avg| 30.18 |Velocity Std Dev| 7.29 |Cum. SP Slope| 31.55 |SP/Story| 3.88 |Vel Avg Last 3| 31.00
- 44. Sprint Backlog Task Board
- 45. General Story Format As a <who: insert role or persona> I want <what: insert functionality> So that <why: for what business value> Acceptance Criteria: ◦ verifies the story works as the customer expected ◦ Specifies tests
- 46. Agile References Shore, James and Shane Warden. The Art of Agile Development, Sabastopol, CA: O’Reilly Media, Inc. , 2008. Print. What is Agile Software Development?. 2012. Agile Alliance. 27 June 2012. < http://www.agilealliance.org/the-alliance/what-is-agile/> Agile Software Development. 2012. Wikipedia. 27 June 2012. <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Agile_software_development > Manifesto for Agile Software Development. 2001. Ward Cunningham. 27 June 2012. <http://agilemanifesto.org/>
- 47. Additional Scrum References Schwaber and Sutherland, The Scrum Guide (“The official Scrum Body Of Knowledge” – scrum.org, “Canonical Scrum” - Dan Mezick) http://www.scrum.org/scrumguides/ Schwaber, Agile Project Management with Scrum, 2004, ISBN-13: 978-0735619937 (The “Scrum Bible”) Amazon link Scrum In 5 Minutes http://www.infoq.com/news/2006/11/scrum-in-five-minutes WikiPedia Scrum Page http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scrum_(development) Shalloway and Trott, Lean-Agile Pocket Guide for Scrum Teams Amazon Link Scrum For Team System’s web page FAQ http://www.scrumforteamsystem.com/ProcessGuidanceOld/v2/FAQ/FAQ.aspx Scrum Alliance web page http://www.scrumalliance.org/