Presentation of DBMS (database management system) part 2
- 2. GROUP 9 Junaid Nadeem Osama Mirza Arshad khan m. Ikram meo M. Faheem Ahmad ch. Flat Database & Relation Database Purpose of DBMS Types of DBMS Models Advantages of DBMS TOPIC
- 3. FLAT DATABASE A FLAT FILE DATABASE IS A DATABASE DESIGNED AROUND A SINGLE TABLE. THE FLAT FILE DESIGN PUTS ALL DATABASE INFORMATION IN ONE TABLE, OR LIST, WITH FIELDS TO REPRESENT ALL PARAMETERS. BECAUSE OF THE LIMITATIONS OF FLAT DATABASES, THEY ARE NOT UNSUITABLE FOR MOST SOFTWARE APPLICATIONS IN WHICH THERE IS A NEED TO REPRESENT AND STORE COMPLEX BUSINESS RELATIONSHIPS.
- 4. FLAT DATABASE IN THE VERY, VERY OLD DAYS…. EVEN LARGE AMOUNTS OF DATA WAS STORED IN TEXT FILES, KNOWN AS FLAT-FILE DATABASES ALL RELATED INFO WAS STORED IN A SINGLE LONG, TAB- OR COMMA-DELIMITED TEXT FILE EACH GROUP OF INFORMATION CALLED A RECORD. EACH RECORD CONSISTED OF A GROUP OF FIELDS, EACH FIELD CONTAINING SOME DISTINCT DATA ITEM MOST PEOPLE USE FLAT DATABASE TO STORE DATA IN COMPUTER
- 5. FLAT DATABASE EASY TO UNDERSTAND ALL RECORDS ARE STORED IN ONE PLACE LESS HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE REQUIREMENTS SIMPLE SORTING OF RECORDS CAN BE CARRIED OUT LESS SKILLS SET ARE REQUIRED TO HAND FLAT DATABASE SYSTEMS. EASY TO SET UP USING A NUMBER OF STANDARD OFFICE APPLICATIONS RECORD CAN BE VIEWED OR EXTRACTED ON THE BASIS OF SIMPLE CRITERIA ADVANTAGES/PURPOSE AND WHY PEOPLE USE THIS NOW A DAY
- 6. FLAT DATABASE SLOW FOR HUGE DATABASE DON'T CALCULATE COMPLEX CALCULATIONS SEARCHING PROCESS IS TIME CONSUMING LESS SECURITY EASY TO EXTRACT INFORMATION DATA REDUNDANCY: THE APPEARANCE OF THE SAME DATA FACTOR IN MORE THAN ONE FIELD OR TABLE OF DATA DATA INCONSISTENCY: DATA INCONSISTENCY IS A CONDITION THAT OCCURS BETWEEN FILES WHEN SIMILAR DATA IS KEPT IN DIFFERENT FORMATS IN TWO DIFFERENT FILES, OR WHEN MATCHING OF DATA MUST BE DONE BETWEEN FILES INTEGRITY PROBLEMS: INTEGRITY MEANS RELIABILITY AND ACCURACY OF DATA. FLAT DATABASE GENERATE INTEGRITY PROBLEMS BECAUSE OF DATA REDUNDANCY AND DATA INCONSISTENCY DISADVANTAGES
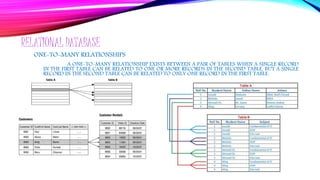
- 8. RELATIONAL DATABASE RELATIONAL DATABASES ARE CONSISTING OF TWO OR MORE RELATED TABLES. ON THE OTHER HAND, INCORPORATES MULTIPLE TABLES WITH METHODS FOR THE TABLES TO WORK TOGETHER. THE RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN TABLE DATA CAN BE COLLATED, MERGED AND DISPLAYED IN DATABASE FORMS. CONTAINS FACILITIES FOR CREATING, MODIFYING AND VERIFIED RELATIONAL DATABASES.
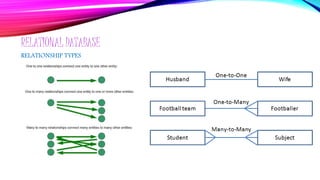
- 10. RELATIONAL DATABASE ONE-TO-ONE RELATIONSHIPS A PAIR OF TABLES BEARS A ONE-TO-ONE RELATIONSHIP WHEN A SINGLE RECORD IN THE FIRST TABLE IS RELATED TO ONLY ONE RECORD IN THE SECOND TABLE, AND A SINGLE RECORD IN THE SECOND TABLE IS RELATED TO ONLY ONE RECORD IN THE FIRST TABLE.
- 11. RELATIONAL DATABASE ONE-TO-MANY RELATIONSHIPS A ONE-TO-MANY RELATIONSHIP EXISTS BETWEEN A PAIR OF TABLES WHEN A SINGLE RECORD IN THE FIRST TABLE CAN BE RELATED TO ONE OR MORE RECORDS IN THE SECOND TABLE, BUT A SINGLE RECORD IN THE SECOND TABLE CAN BE RELATED TO ONLY ONE RECORD IN THE FIRST TABLE.
- 12. RELATIONAL DATABASE MANY-TO-MANY RELATIONSHIPS A PAIR OF TABLES BEARS A MANY-TO-MANY RELATIONSHIP WHEN A SINGLE RECORD IN THE FIRST TABLE CAN BE RELATED TO ONE OR MORE RECORDS IN THE SECOND TABLE AND A SINGLE RECORD IN THE SECOND TABLE CAN BE RELATED TO ONE OR MORE RECORDS IN THE FIRST TABLE.
- 13. RELATIONAL DATABASE MOST RELATIONAL DATABASES OFFER FUNCTIONALITY TO SHARE DATA: ACROSS NETWORKS OVER THE INTERNET WITH LAPTOPS AND OTHER ELECTRONIC DEVICES, SUCH AS PALM PILOTS WITH OTHER SOFTWARE SYSTEMS
- 14. RELATIONAL DATABASE BETTER SECURITY SEARCHING PROCESS IS VERY FAST CALCULATE COMPLEX CALCULATIONS EASIER TO CHANGE DATA AND ITS FORMAT DATA REDUNDANCY CONTROL: CONTROL THE APPEARANCE OF THE SAME DATA FACTOR IN MORE THAN ONE FIELD OR TABLE OF DATA DATA INCONSISTENCY CONTROL: DATA INCONSISTENCY IS A CONDITION THAT OCCURS BETWEEN FILES WHEN SIMILAR DATA IS KEPT IN DIFFERENT FORMATS IN TWO DIFFERENT FILES, OR WHEN MATCHING OF DATA MUST BE DONE BETWEEN FILES. RELATIONAL DATABASE CONTROL THE INCONSISTENCY INTEGRITY : INTEGRITY MEANS RELIABILITY AND ACCURACY OF DATA. RELATION DATABASE GENERATE INTEGRITY BECAUSE IT CONTROL THE DATA REDUNDANCY AND DATA INCONSISTENCY ADVANTAGES
- 15. RELATIONAL DATABASE INCREASED COSTS: DATABASE SYSTEMS REQUIRE SOPHISTICATED HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE AND HIGHLY SKILLED PERSONNEL. THE COST OF MAINTAINING THE HARDWARE, SOFTWARE, AND PERSONNEL REQUIRED TO OPERATE AND MANAGE A DATABASE SYSTEM CAN BE SUBSTANTIAL. TRAINING, LICENSING, AND REGULATION COMPLIANCE COSTS ARE OFTEN OVERLOOKED WHEN DATABASE SYSTEMS ARE IMPLEMENTED. HIGHER HARDWARE COST HIGHER PROGRAMING COST MANAGEMENT COMPLEXITY: DATABASE SYSTEMS INTERFACE WITH MANY DIFFERENT TECHNOLOGIES AND HAVE A SIGNIFICANT IMPACT ON A COMPANY’S RESOURCES AND CULTURE. THE CHANGES INTRODUCED BY THE ADOPTION OF A DATABASE SYSTEM MUST BE PROPERLY MANAGED TO ENSURE THAT THEY HELP ADVANCE THE COMPANY’S OBJECTIVES. GIVEN THE FACT THAT DATABASE SYSTEMS HOLD CRUCIAL COMPANY DATA THAT ARE ACCESSED FROM MULTIPLE SOURCES, SECURITY ISSUES MUST BE ASSESSED CONSTANTLY. DATABASE FAILURES: IN MOST OF THE ORGANIZATIONS, ALL DATA IS INTEGRATED INTO A SINGLE DATABASE. IF DATABASE IS CORRUPTED DUE TO POWER FAILURE OR IT IS CORRUPTED ON THE STORAGE MEDIA, THEN OUR VALUABLE DATA MAY BE LOST OR WHOLE SYSTEM STOPS. DISADVANTAGES
- 16. RELATIONAL DATABASE EXAMPLES ( DIFFERENT SOFTWARE'S ) ACCESS FILEMAKER PRO SQL SERVER ORACLE DB2 OBJECTIVITY/DB MYSQL POSTGRES
- 17. DATABASE MODEL A DATABASE MODEL DEFINES THE LOGICAL DESIGN OF DATA. THE MODEL DESCRIBES THE RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN DIFFERENT PARTS OF THE DATA. IN HISTORY OF DATABASE DESIGN, THREE MODELS HAVE BEEN IN USE. HIERARCHICAL MODEL NETWORK MODEL RELATIONAL MODEL
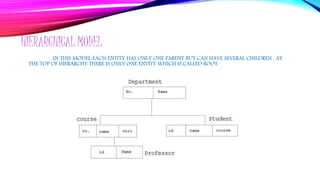
- 18. HIERARCHICAL MODEL IN THIS MODEL EACH ENTITY HAS ONLY ONE PARENT BUT CAN HAVE SEVERAL CHILDREN . AT THE TOP OF HIERARCHY THERE IS ONLY ONE ENTITY WHICH IS CALLED ROOT.
- 19. NETWORK MODEL IN THE NETWORK MODEL, ENTITIES ARE ORGANIZED IN A GRAPHING WHICH SOME ENTITIES CAN BE ACCESSED THROUGH SEVERAL PATH
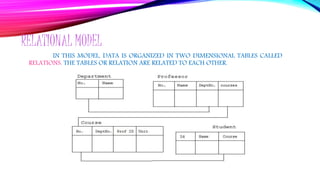
- 20. RELATIONAL MODEL IN THIS MODEL, DATA IS ORGANIZED IN TWO DIMENSIONAL TABLES CALLED RELATIONS. THE TABLES OR RELATION ARE RELATED TO EACH OTHER.
- 21. PURPOSE OF DATABASE SYSTEMS To see why database management systems are necessary, let's look at a typical “file-processing system” supported by a conventional operating system. The application is a savings bank: • Savings account and customer records are kept in permanent system files. • Application programs are written to manipulate files to perform the following tasks: Debit or credit an account. Add a new account. Find an account balance. Generate monthly statements. Development of the system proceeds as follows: New application programs must be written as the need arises. New permanent files are created as required. but over a long period of time files may be in different formats, and Application programs may be in different languages.
- 22. PURPOSE OF DATABASE SYSTEMS So we can see there are problems with the straight file-processing approach: Data redundancy and inconsistency • Same information may be duplicated in several places. • All copies may not be updated properly. Difficulty in accessing data • May have to write a new application program to satisfy an unusual request. • E.g. find all customers with the same postal code. • Could generate this data manually, but a long job... Data isolation • Data in different files. • Data in different formats. • Difficult to write new application programs. Multiple users • Want concurrency for faster response time. • Need protection for concurrent updates. Security problems • Every user of the system should be able to access only the data they are permitted to see. • E.g. payroll people only handle employee records, and cannot see customer accounts; tellers only access account data and cannot see payroll data. • Difficult to enforce this with application programs. Integrity problems • Data may be required to satisfy constraints. • E.g. no account balance below $25.00. • Again, difficult to enforce or to change constraints with the file-processing approach.
- 23. ADVANTAGES OF THE DBMS Improved data sharing: The DBMS helps create an environment in which end users have better access to more and better-managed data. Such access makes it possible for end users to respond quickly to changes in their environment. Improved data security: The more users access the data, the greater the risks of data security breaches. Corporations invest considerable amounts of time, effort, and money to ensure that corporate data are used properly. A DBMS provides a framework for better enforcement of data privacy and security policies. Better data integration: Wider access to well-managed data promotes an integrated view of the organization’s operations and a clearer view of the big picture. It becomes much easier to see how actions in one segment of the company affect other segments. Data inconsistency: Data inconsistency exists when different versions of the same data appear in different places.
- 24. ADVANTAGES OF THE DBMS Improved decision making: Better-managed data and improved data access make it possible to generate better-quality information, on which better decisions are based. The quality of the information generated depends on the quality of the underlying data. Data quality is a comprehensive approach to promoting the accuracy, validity, and timeliness of the data. While the DBMS does not guarantee data quality, it provides a framework to facilitate data quality initiatives. Data Atomicity: A transaction in commercial databases is referred to as atomic unit of work. Backup and Recovery Procedures: In a computer file-based system, the user creates the backup of data regularly to protect the valuable data from damaging due to failures to the computer system or application program. It is a time consuming method, if volume of data is large. Most of the DBMSs provide the 'backup and recovery' sub-systems that automatically create the backup of data and restore data if required. Increased end-user productivity: The availability of data, combined with the tools that transform data into usable information, empowers end users to make quick, informed decisions that can make the difference between success and failure in the global economy. Data Consistency: By controlling the data redundancy, the data consistency is obtained. If a data item appears only once, any update to its value has to be performed only once and the updated value (new value of item) is immediately available to all users.
- 25. DISADVANTAGES OF DATABASE Increased costs: Database systems require sophisticated hardware and software and highly skilled personnel. The cost of maintaining the hardware, software, and personnel required to operate and manage a database system can be substantial. Training, licensing, and regulation compliance costs are often overlooked when database systems are implemented. Management complexity: Database systems interface with many different technologies and have a significant impact on a company’s resources and culture. The changes introduced by the adoption of a database system must be properly managed to ensure that they help advance the company’s objectives. Given the fact that database systems hold crucial company data that are accessed from multiple sources, security issues must be assessed constantly. Maintaining currency: To maximize the efficiency of the database system, you must keep your system current. Therefore, you must perform frequent updates and apply the latest patches and security measures to all components. Because database technology advances rapidly, personnel training costs tend to be significant. Vendor dependence. Given the heavy investment in technology and personnel training, companies might be reluctant to change database vendors.
- 26. DISADVANTAGES OF DATABASE Frequent upgrade/replacement cycles: DBMS vendors frequently upgrade their products by adding new functionality. Such new features often come bundled in new upgrade versions of the software. Some of these versions require hardware upgrades. Not only do the upgrades themselves cost money, but it also costs money to train database users and administrators to properly use and manage the new features. Database Failures: In most of the organizations, all data is integrated into a single database. If database is corrupted due to power failure or it is corrupted on the storage media, then our valuable data may be lost or whole system stops.
- 27. THANK YOU FOR WATCHING AND LISTENING OUR PRESENTATION