Presentation on network_protocols
- 1. IUBAT-International University of Business Agriculture & Technology Name ID Md. Shibly Noman 14303131 Tahmid Uddin Mahmud Nishat 14303132 “The Optimist” Presenting By Group Members Course Instructor: Dr. Abhijit Saha Course: CSC 465 Section: B
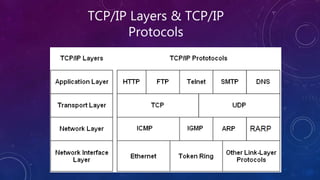
- 2. TCP/IP Protocol • TCP/IP protocols map to a four-layer conceptual model known as the DARPA model , named after the U.S. government agency that initially developed TCP/IP. • The four layers of the DARPA model are: Application, Transport, Internet, and Network Interface. Each layer in the DARPA model corresponds to one or more layers of the seven-layer Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model.
- 4. TCP/IP Layers & TCP/IP Protocols
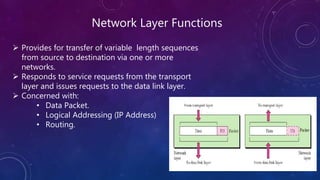
- 5. Network Layer This layer deals with Packets (Data Bundles). Responsible for logical addressing and routing. Devices: • Routers, layer 3 switches, firewalls etc. Network Layer Protocols: • ICMP, IGMP, ARP, RARP etc.
- 6. Network Layer Functions Provides for transfer of variable length sequences from source to destination via one or more networks. Responds to service requests from the transport layer and issues requests to the data link layer. Concerned with: • Data Packet. • Logical Addressing (IP Address) • Routing.
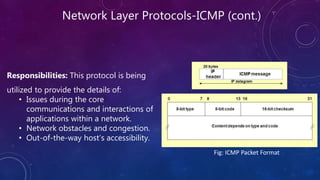
- 7. Network Layer Protocols-ICMP • ICMP protocol is a bunch or error, queries and response messages that are helping us every day to troubleshoot and manage our networks. • Network protocol “ICMP” is known as a control protocol because it is used for the purpose of administration and management within an IP network. • ICMP is a vital part of Internet protocol implementations, but it is not holding the application data. It carries the network status information.
- 8. Network Layer Protocols-ICMP (cont.)
- 9. Network Layer Protocols-ICMP (cont.) Responsibilities: This protocol is being utilized to provide the details of: • Issues during the core communications and interactions of applications within a network. • Network obstacles and congestion. • Out-of-the-way host’s accessibility. Fig: ICMP Packet Format
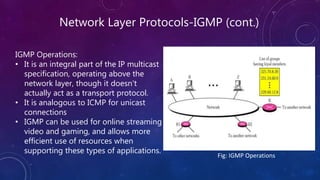
- 10. Network Layer Protocols-IGMP The Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) is a communications protocol used to manage the membership of Internet Protocol multicast groups. IGMP is used by IP hosts and adjacent multicast routers to establish multicast group memberships.
- 11. Network Layer Protocols-IGMP (cont.) IGMP Operations: • It is an integral part of the IP multicast specification, operating above the network layer, though it doesn't actually act as a transport protocol. • It is analogous to ICMP for unicast connections • IGMP can be used for online streaming video and gaming, and allows more efficient use of resources when supporting these types of applications. Fig: IGMP Operations
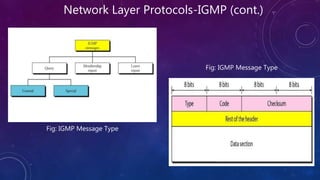
- 12. Network Layer Protocols-IGMP (cont.) Fig: IGMP Message Type Fig: IGMP Message Type
- 13. Network Layer Protocols-ARP • Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) resolve an IPv4 address (32 bit Logical Address) to the physical address (48 bit MAC Address). • Network Applications at the Application Layer use IPv4 Address to communicate with another device. • But at the Datalink layer, the addressing is MAC address (48 bit Physical Address), and this address is burned into the network card permanently.
- 14. Network Layer Protocols-ARP (cont.) ARP Protocol Data Unit:
- 15. Network Layer Protocols-ARP (cont.) Purpose of ARP: The purpose of Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is to find out the MAC address of a device in your Local Area Network (LAN), for the corresponding IPv4 address, which network application is trying to communicate. • Assume broadcast nature of LAN • Broadcast IP address of the destination • Destination replies it with its MAC address. • Source maintains a cache of IP and MAC address binding
- 16. Network Layer Protocols-RARP The Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP) is an obsolete computer networking protocol used by a client computer to request its Internet Protocol (IPv4) address from a computer network, when all it has available is its link layer or hardware address, such as a MAC address. The client broadcasts the request, and does not need prior knowledge of the network topology or the identities of servers capable of fulfilling its request.
- 17. Network Layer Protocols-RARP (cont.) Mechanism: Both the machine that issues the request and the server that responds use physical network addresses during their brief communication. Usually, the requester does not know the physical address. So, the request is broadcasted to all the machines on the network. Now, the requester must identify itself uniquely to the server. For this either CPU serial number or the machine's physical network address can be used. But using the physical address as a unique id has two advantages. • These addresses are always available and do not have to be bound into bootstrap code. • Because the identifying information depends on the network and not on the CPU vendor, all machines on a given network will supply unique identifiers
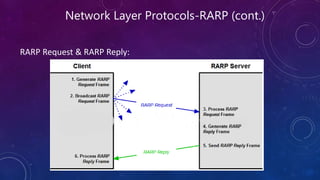
- 18. Network Layer Protocols-RARP (cont.) RARP Request & RARP Reply:
- 19. Network Layer Protocols-RARP (cont.) RARP Example:
- 20. Thanks for your attention