Presentation: the domain name system
- 1. The domain name system (DNS) Skills : none IT concepts : domain, domain name, host, IP address, domain registrar This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 License.
- 2. The domain name system (DNS) in context Internet concepts Applications Technology (TCP/IP) Implications for Individuals Organizations Society Internet skills Application development Content creation Text Images Audio Video
- 3. Domain names We refer to computers on the Internet (Internet hosts ), by names like: bpastudio.csudh.edu These are called domain names or, if you want to be really geeky, “fully qualified domain names.” The key point is that the name identifies a particular computer – no two hosts have the same domain name.
- 4. The parts of a domain name The particular host is called bpastudio The organization that controls it is called csudh This host is at an educational organization bpastudio. csudh . edu A domain is a group of related hosts.
- 5. How are these hosts related? bpastudio.csudh. edu www.ucla. edu sws.csudh. edu chemistry.stanford. edu They all belong to educational institutions. They are members of the edu top-level domain (TLD) .
- 6. How are these hosts related? bpastudio. csudh.edu www. csudh.edu sws. csudh.edu chemistry. csudh.edu They all belong to the same organization, CSUDH . They are members of the csudh.edu second-level domain .
- 7. A unique host bpastudio.csudh.edu This is the domain name of a unique host. It is a member of the csudh.edu domain, but it is the only one with the name bpastudio . It is like a family – all the brothers and sisters have the same last name, but it would be confusing if two of them also had the same first name.
- 8. There are a limited number of top-level domains (TLDs), including: .edu, educational .com, commercial .gov, government .org, non profit .net, networking organizations These are called “ generic ” TLDs.
- 9. There are also country code top-level domain names for every nation, like: .us, United States .mx, Mexico .cl, Chile .uk, United Kingdom .tv, Tuvalu These are called “ country code ” top-level domains ( ccTLD s). The organization or host do not necessarily have to be in the country to register the name. For example, .tv is popular everywhere.
- 10. Some TLDs use a four-level hierarchy http://www.google.co.uk/ http://www.unam.edu.mx/ http://www.ox.ac.uk/ http://www.google.com.mx/
- 11. Registrars sell domain names For most generic TLDs there are many registrars and a competitive registration market place: http://www.icann.org/en/registrars/accredited-list.html The registrar for .edu is a professional society called Educause: http://net.educause.edu/edudomain/ List of organizations responsible for registrars in the country code domains: http:// www.iana.org /domains/root/db/#
- 12. Regstering a domain – check for availability
- 13. Larrypress.com was taken, but these are available and for sale
- 14. Getting a name and IP address at CSUDH A computer center staff person assigns them. No two IP addresses or domain names can be the same. The staff person updates the table of domain names and IP addresses stored on the CSUDH domain name server.
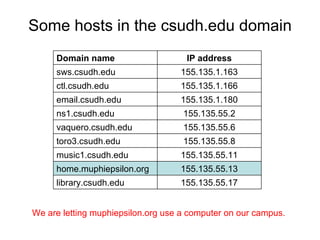
- 15. Some hosts in the csudh.edu domain We are letting muphiepsilon.org use a computer on our campus. IP address Domain name 155.135.55.17 library.csudh.edu 155.135.55.13 home.muphiepsilon.org 155.135.55.11 music1.csudh.edu 155.135.55.8 toro3.csudh.edu 155.135.55.6 vaquero.csudh.edu 155.135.55.2 ns1.csudh.edu 155.135.1.180 email.csudh.edu 155.135.1.166 ctl.csudh.edu 155.135.1.163 sws.csudh.edu
- 16. Some hosts in the csudh.edu domain Every domain has a domain name server (DNS). Our DNS is ns1.csudh.edu. It does the IP address lookups for TCP. . IP address Domain name 155.135.55.17 library.csudh.edu 155.135.55.13 home.muphiepsilon.org 155.135.55.11 music1.csudh.edu 155.135.55.8 toro3.csudh.edu 155.135.55.6 vaquero.csudh.edu 155.135.55.2 ns1.csudh.edu 155.135.1.180 email.csudh.edu 155.135.1.166 ctl.csudh.edu 155.135.1.163 sws.csudh.edu
- 17. DNS search If your DNS knows the IP address it returns it. Otherwise it will contact another DNS to get the result. Etc. until it is found or determined that it does not exist, in which case an error message is returned.
- 18. Food for thought Is the <your name>.com domain name available? When you try to go to http://www.google.xom, you get an error message, but http://www.gooogle.com takes you to Google. Why? http://wwww.google.com also returns an error message. Why?