Projectile Motion at an Angle || Grade 9 Physics || Physics Notes
- 1. PROJECTILES LAUNCHED AT AN ANGLE (Nonhorizontally launched Projectile) PRESENTED BY SUJHS PHYSICS TEACHERS GRADE 9 PHYSICS
- 2. Learning Targets I can describe the horizontal and vertical motions of a projectile. I can investigate the relationship between the angle of release and the height and range of the projectile.
- 3. PROJECTILE MOTION o Motion of an object that has an initial horizontal velocity and acted upon by gravity (Neglecting air resistance) Horizontal velocity is always constant Vertical velocity decreases as the projectile moves up and increases while it moves down along its trajectory Velocity Horizontal acceleration is always zero Vertical acceleration is always equal to the acceleration due to gravity, -9.8 m/s2 (on Earth) Acceleration Horizontal distance – range Vertical distance – maximum height Distance
- 4. PROJECTILES LAUNCHED AT AN ANGLE (Nonhorizontally launched Projectiles)
- 5. The horizontal velocity always remains the same. Projectile Motion PhET Simulation PROJECTILES LAUNCHED AT AN ANGLE The vertical velocity changes at constant acceleration due to gravity (g = - 9.8 m/s2). The initial velocity of a projectile is broken into its horizontal & vertical components. Due to its horizontal & vertical components, a projectile launched at an angle follows a parabolic trajectory.
- 6. THE HORIZONTAL & VERTICAL COMPONENTS OF PROJECTILE MOTION 29.4 m/s 2 m/s 9.8 m/s 0 m/s 2 m/s 2 m/s 2 m/s 2 m/s 2 m/s 19.6 m/s 2 m/s - 29.4 m/s - 19.6 m/s - 9.8 m/s From the point of release, its vertical velocity decreases until it becomes zero when it reaches its maximum height From the maximum height, its vertical velocity increases until it hits the ground. Note: The negative sign indicates its downward direction.
- 7. Projectile Motion PhET Simulation As the angles increase towards 45 degrees, what happens to the range of the projectile? As the angles increase from 45 degrees to 90 degrees, what happens to the maximum height of the projectile? What angle of release results to the longest range? P R O J E C T I L E S L A U N C H E D W I T H T H E S A M E I N I T I A L V E L O C I T Y AT D I F F E R E N T A N G L E S
- 8. P R O J E C T I L E S L A U N C H E D W I T H T H E S A M E I N I T I A L V E L O C I T Y AT D I F F E R E N T A N G L E S Angles of release closer to 45° result in longer ranges. The angle of release equal to 45° results in the longest range. 25° 30° 40° 45° 50° Projectile Motion PhET Simulation
- 9. Angles of release closer to 90° result in higher maximum heights. P R O J E C T I L E S L A U N C H E D W I T H T H E S A M E I N I T I A L V E L O C I T Y AT D I F F E R E N T A N G L E S Projectile Motion PhET Simulation 45° 60° 70° 80° 90°
- 10. 60° 30°
- 11. 50° 40°
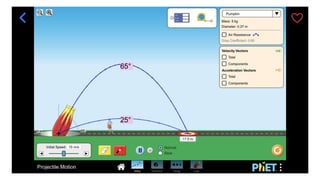
- 12. 65° 25°
- 13. PROJECTILES LAUNCHED AT AN ANGLE (Given the same initial velocity) Angles of release closer to 45° result in longer ranges. The angle of release equal to 45° results in the longest range. Complementary angles of release have the same range. Angles of release closer to 90° result in higher maximum heights.
- 14. PROJECTILES LAUNCHED AT AN ANGLE (Nonhorizontally launched Projectile) PRESENTED BY SUJHS PHYSICS TEACHERS GRADE 9 PHYSICS
- 15. REFERENCES Department of Education (2016). K to 12 Curriculum Guide for Science: Kindergarten to Grade 10. Retrieved from http://deped.gov.ph/sites/default/files/page/2016/Science%20CG.pdf Moros, E.M., Avilla, R.A., Greogorio, J.B., & Pineda, M.G.F. (2018). Practical science 9. Makati City: University Press First Asia Papa, E. C. R., Moros, E.M., Pineda, M. G. P., & Gregorio, J.B. (2018). Practical Science 7. Makati City: University Press of First Asia Projectiles Launched at an Angle. (n.d.). Www.youtube.com. Retrieved April 5, 2021, from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CgBpwVSS9tY&t=201s
Editor's Notes
- #4: Horizontal velocity is always constant Vertical velocity decreases as the projectile moves up and increases while it moves down along its trajectory Horizontal acceleration is always zero Vertical acceleration is always equal to the acceleration due to gravity, -9.8 m/s2 (on Earth) Horizontal distance – range Vertical distance – maximum height
- #6: In this Projectile Motion PhET Simulation, we can see the projectile’s parabolic trajectory and its vertical and horizontal velocities represented by the vertical and horizontal arrows. The initial velocity of a projectile is broken into its horizontal & vertical components. Due to its horizontal & vertical components, a projectile launched at an angle follows a parabolic trajectory. From our previous discussion, we have learned that: The horizontal velocity remains the same at all times while the vertical velocity changes at constant acceleration due to gravity (g = - 9.8 m/s2).
- #7: The vertical velocity of a projectile changes at constant acceleration due to gravity. Its vertical velocity decreases by 9.8 m/s every second from the point of release until it reaches zero at its maximum height. For example, it starts with an initial vertical velocity of 29.4 m/s going up. It will become 19.6 m/s in the next second, then 9.8 m/s in the next second until it becomes zero vertical velocity. At this point, it will momentarily stop going up but continues to move forward due to its horizontal velocity of 2 m/s that does not change throughout its motion. However, note that it does not have a zero total velocity at its maximum height since it still has its horizontal velocity. After that, its vertical velocity increases as it falls in a curve manner. From zero vertical velocity at its maximum height, it becomes - 9.8 m/s in the next second, then -19.6 m/s in the next second, and becomes -29.4 m/s at its endpoint. The values of its horizontal and vertical velocities on its way up and down along its trajectory are symmetrical. In other words, the values are the same; only the signs and the directions differ. Correspondingly, the horizontal and vertical accelerations and the time taken to go up to the maximum height and go down to the same level where it was launched are equal. Its vertical velocity decreases from the point of release until it becomes zero when it reaches its maximum height.
- #8: Let’s now investigate the relationship between the angle of release and the height and the range of the projectile. Let’s observe this simulation of a projectile launched at different angles given the same initial velocity. For comparison, the projectile was launched with the same initial velocity of 15 m/s, forward at the following angles: 25 degrees, 30 degrees, 40 degrees, 45 degrees, 55 degrees, 65 degrees, and 70 degrees. As the angles increase towards 45 degrees, what happens to the range of the projectile? As the angles increase from 45 degrees to 90 degrees, what happens to the maximum height of the projectile? What angle of release results to the longest range?
- #9: Let us now investigate the relationship between the angle of release and the height, and the range of the projectile. Let us compare the ranges and heights reached by the projectile launched with the same initial velocity of 15 m/s, forward at the following angles: 25 degrees, 30 degrees, 40 degrees, 45 degrees, and 50 degrees. As the angle of release increases from 25 to 45 degrees, the range, and height of the projectile increase. Angles of release closer to 45° result in longer ranges. The angle of release equal to 45° results in the longest range.
- #10: Let us now investigate the relationship between the angle of release and the height, and the range of the projectile. Let us compare the ranges and heights reached by the projectile launched with the same initial velocity of 15 m/s, forward at the following angles: 45 degrees, 60 degrees, 70 degrees, 80 degrees, and 90 degrees. As the angle of release increases from 0 to 90 degrees, the height of the projectile also increases. Angles of release closer to 90° result in higher maximum heights. Note that at 90 degrees, the object is in free fall, not in projectile motion since there is no horizontal motion.
- #14: Angles of release closer to 45° result in longer ranges. The angle of release equal to 45° results in the longest range. Angles of release closer to 90° result in higher maximum heights.